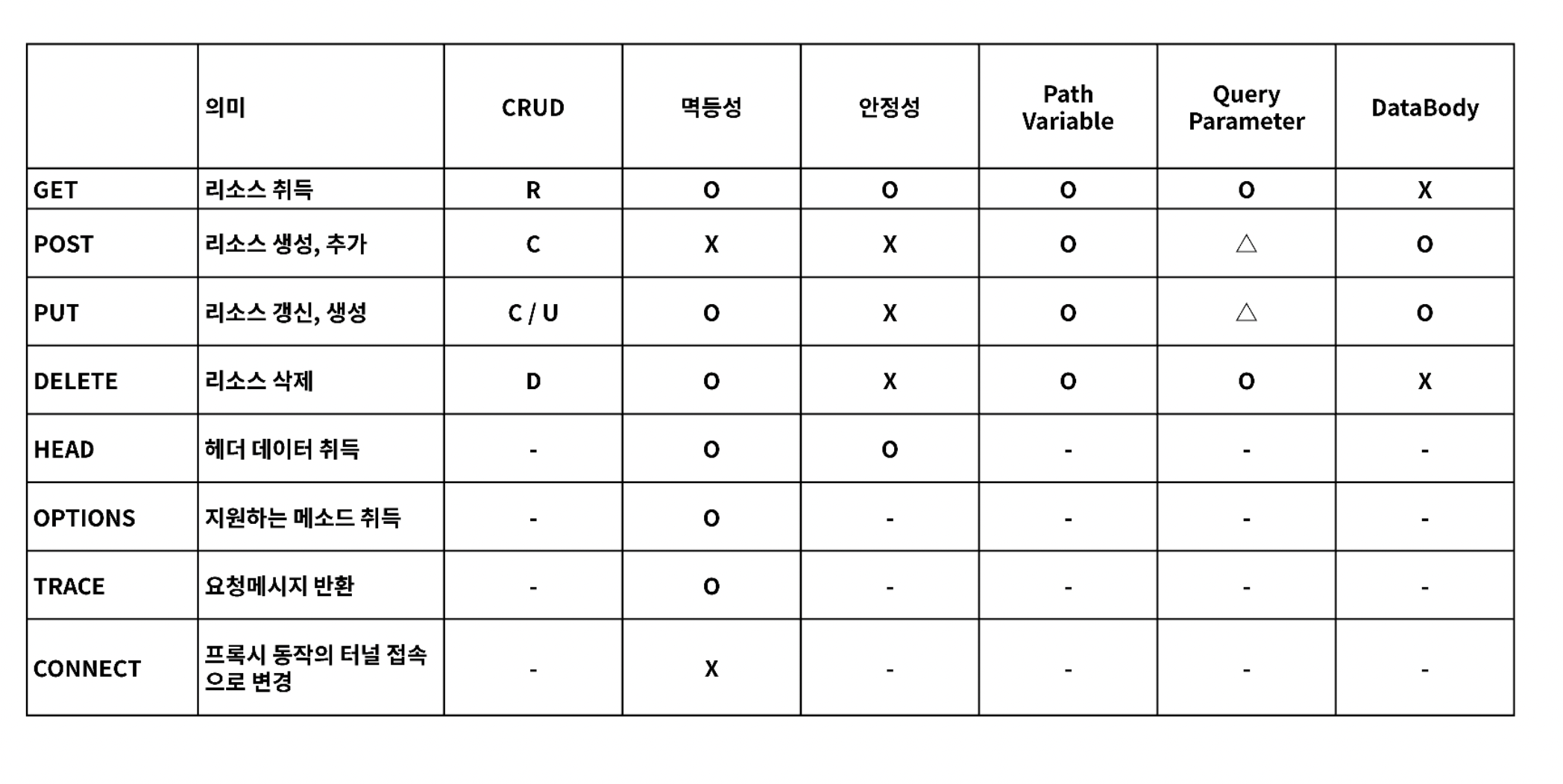
GET
package com.example.hello.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController // 해당 Class는 Rest API를 처리하는 Controller
@RequestMapping("/api") // Request Mapping URI를 지정해주는 Annotation
public class ApiController {
@GetMapping("/hello") // http://localhost:8080/api/hello
public String hello() {
return "hello string boot!";
}
}
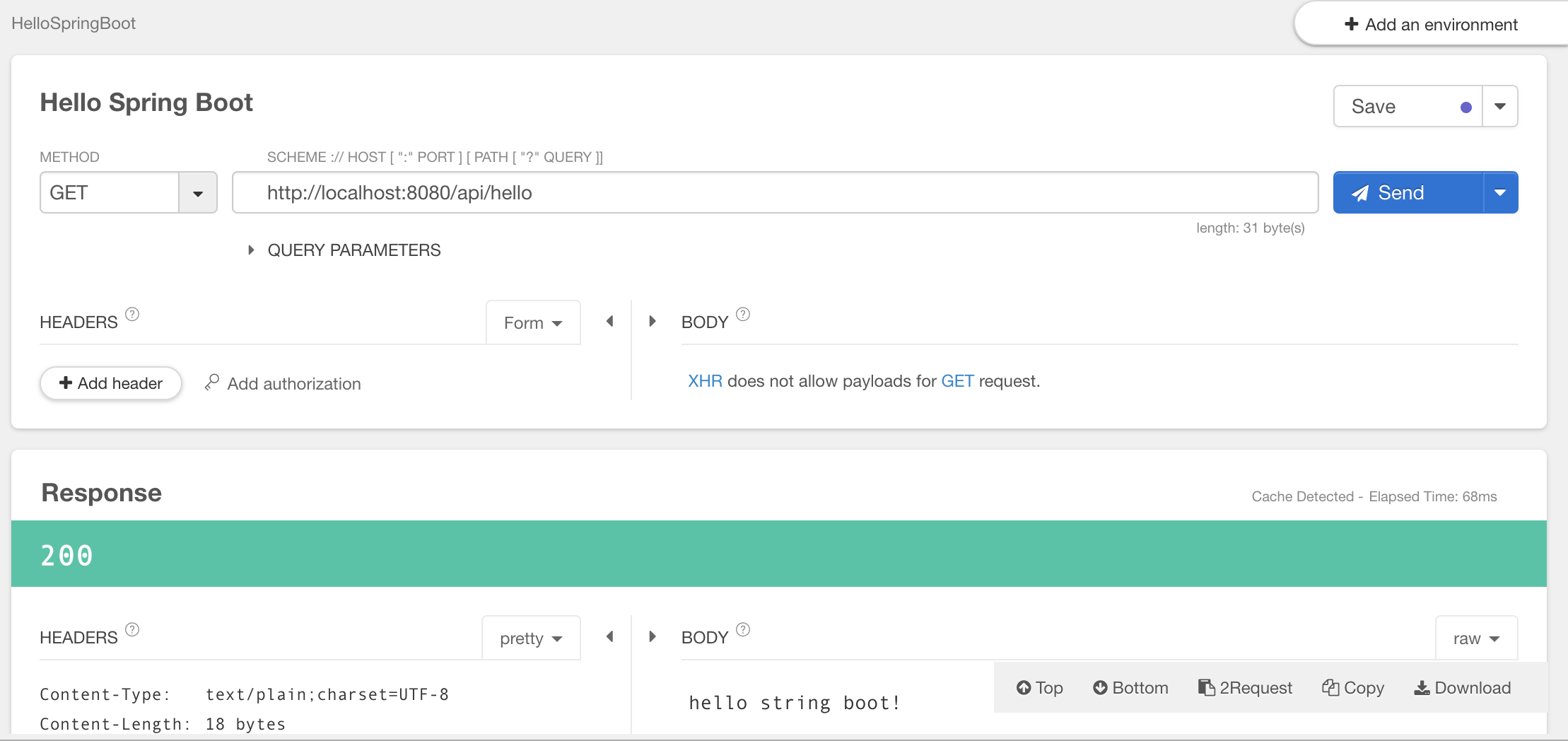
package com.example.hello.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/get")
public class GetApiController {
@GetMapping(path = "/hello")
public String hello() {
return "get Hello";
}
}
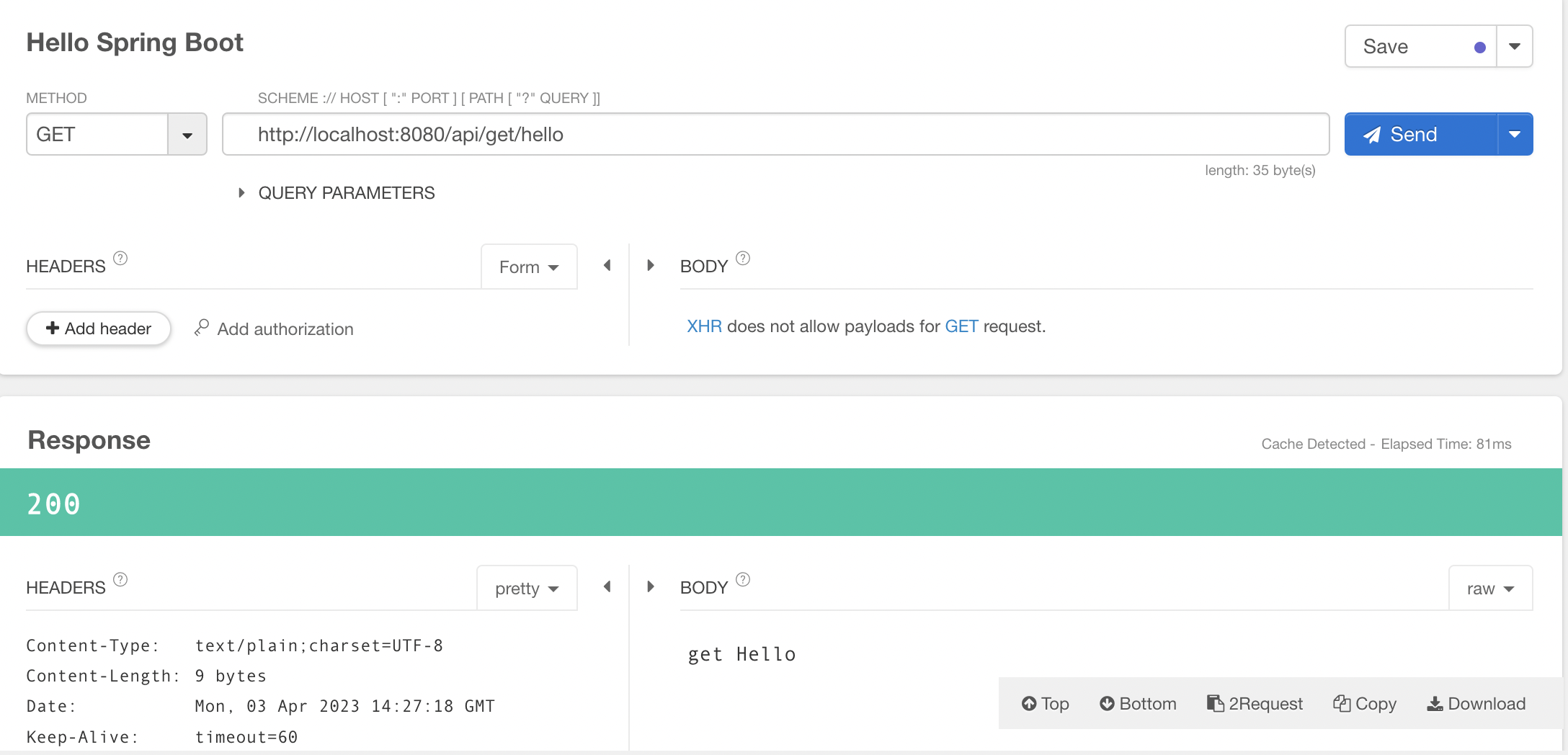
@GetMapping("/path-variable/{name}")
public String pathVariable(@PathVariable String name) {
System.out.println("PathVariable: "+name);
return name;
}위는 아래와 같이 표현할 수도 있다.
@GetMapping("/path-variable/{id}")
public String pathVariable(@PathVariable(name = "id") String pathName) {
System.out.println("PathVariable: "+pathName);
return pathName;
}
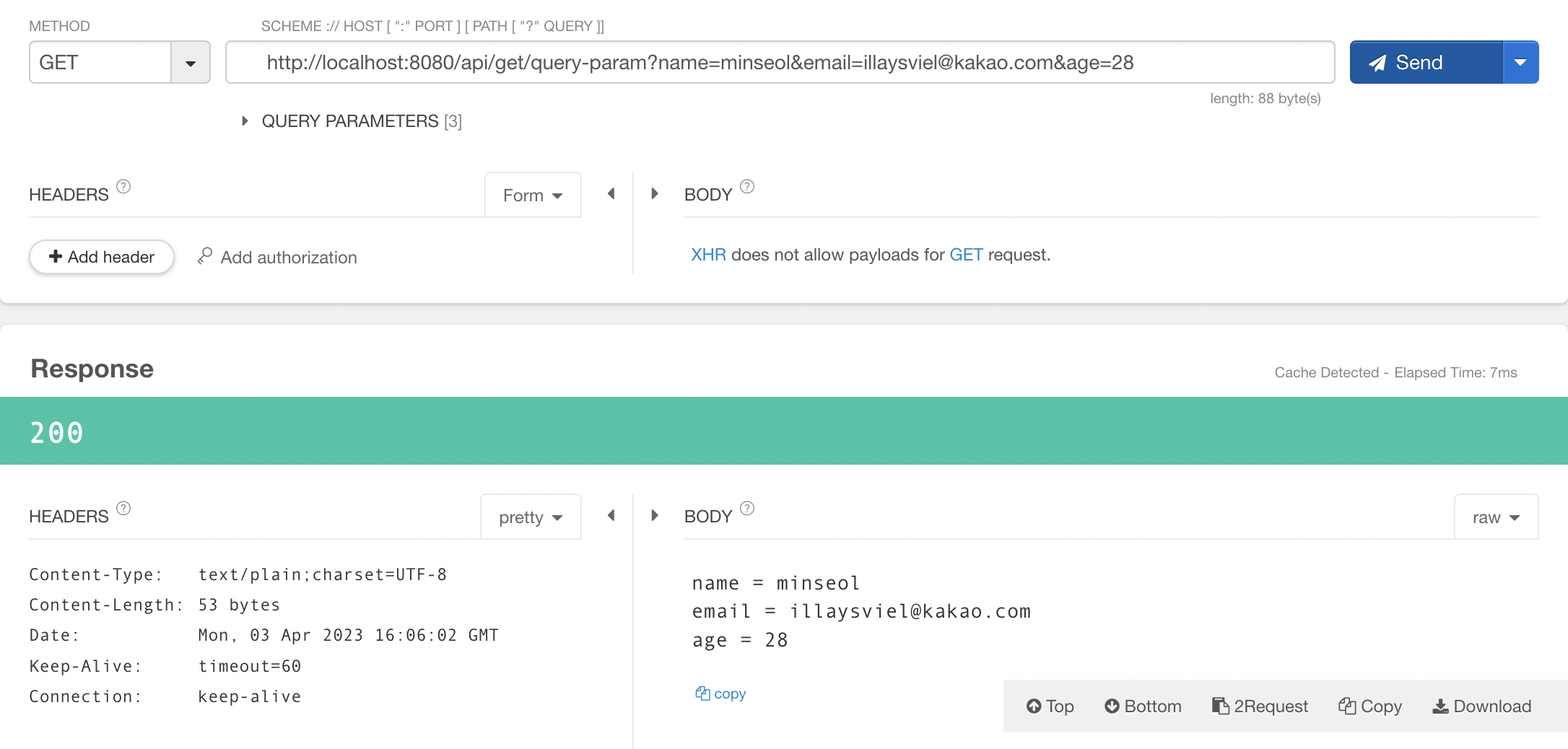
@GetMapping(path = "query-param")
public String queryParam(@RequestParam Map<String, String> queryParam) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
queryParam.entrySet().forEach( entry -> {
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
System.out.println("\n");
sb.append(entry.getKey()+" = "+entry.getValue()+"\n");
});
return sb.toString();
}
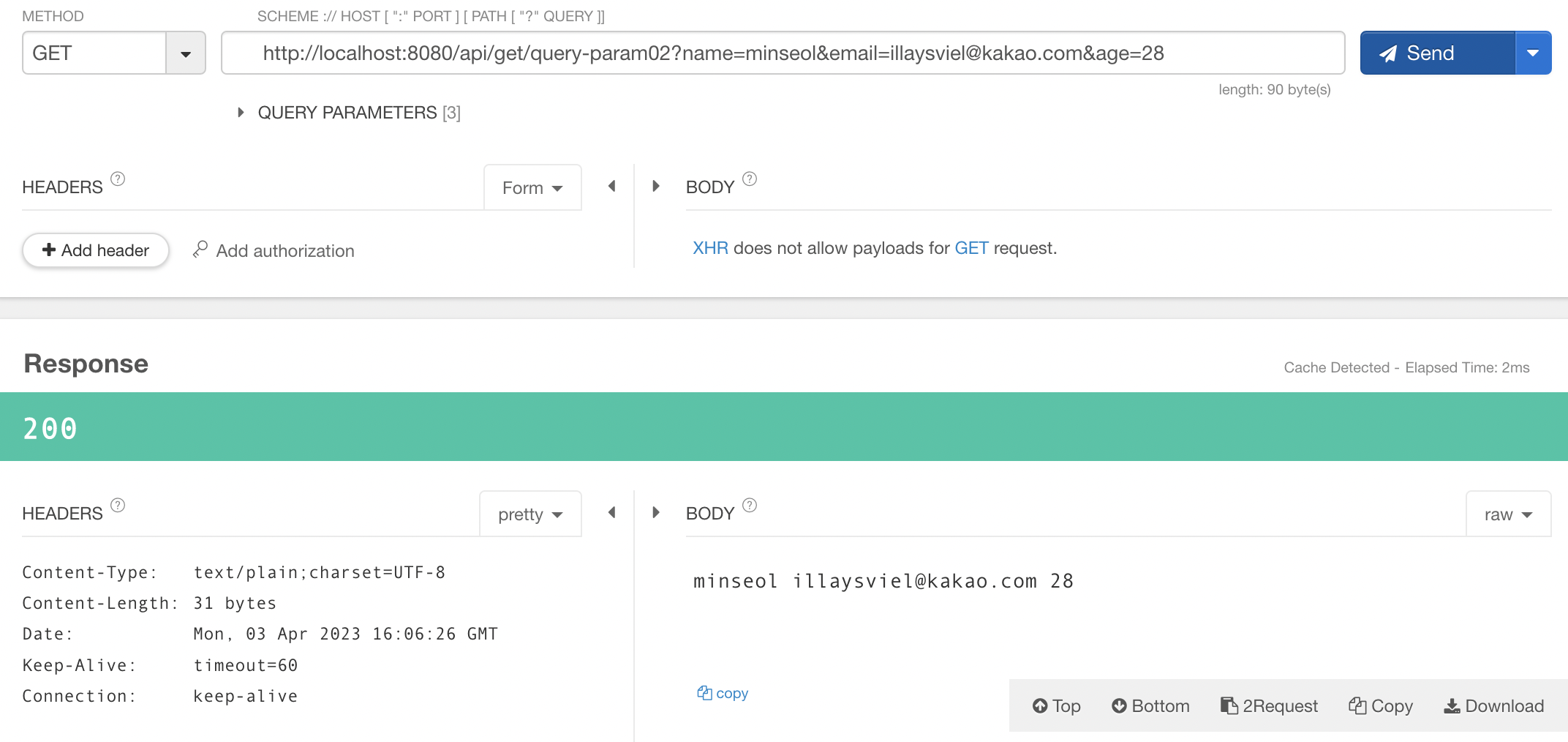
@GetMapping("query-param02")
public String queryParam02(
@RequestParam String name,
@RequestParam String email,
@RequestParam int age
) {
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(email);
System.out.println(age);
return name+" "+email+" "+age;
}위의 두 방법과 달리 가장 많이 쓰이는 방식은 다음과 같은 DTO를 생성하여 @RequestParam 없이 Argument에 넣는 것이다.
package com.example.hello.dto;
public class UserRequest {
private String name;
private String email;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserRequest{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
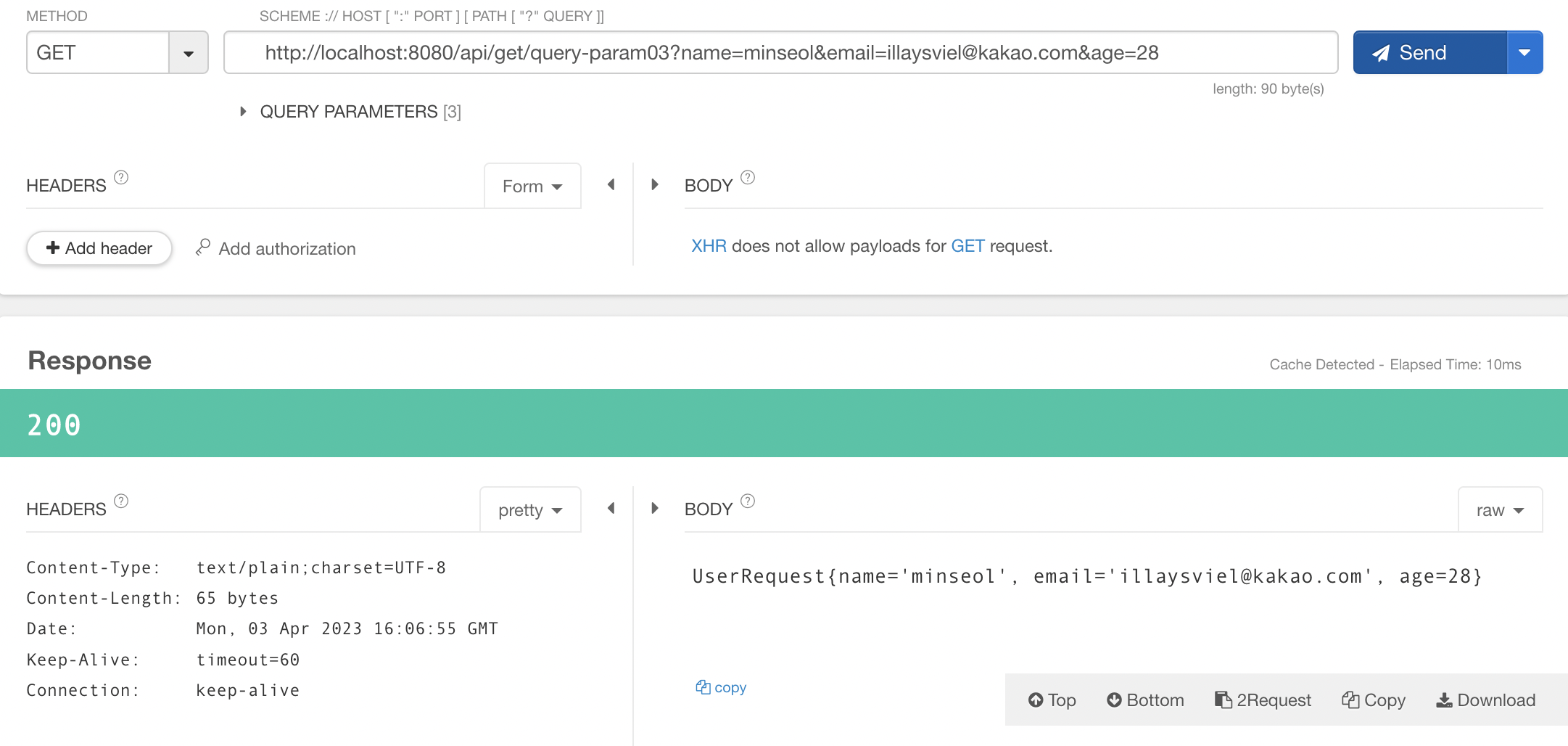
@GetMapping("query-param03")
public String queryParam03(UserRequest userRequest) {
System.out.println(userRequest.getName());
System.out.println(userRequest.getEmail());
System.out.println(userRequest.getAge());
return userRequest.toString();
}
POST
package com.example.hello.controller;
import com.example.hello.dto.PostRequestDto;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PostApiController {
@PostMapping("/post")
public void post(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> requestData) {
requestData.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("Key: " + key);
System.out.println("Value: " + value);
});
}
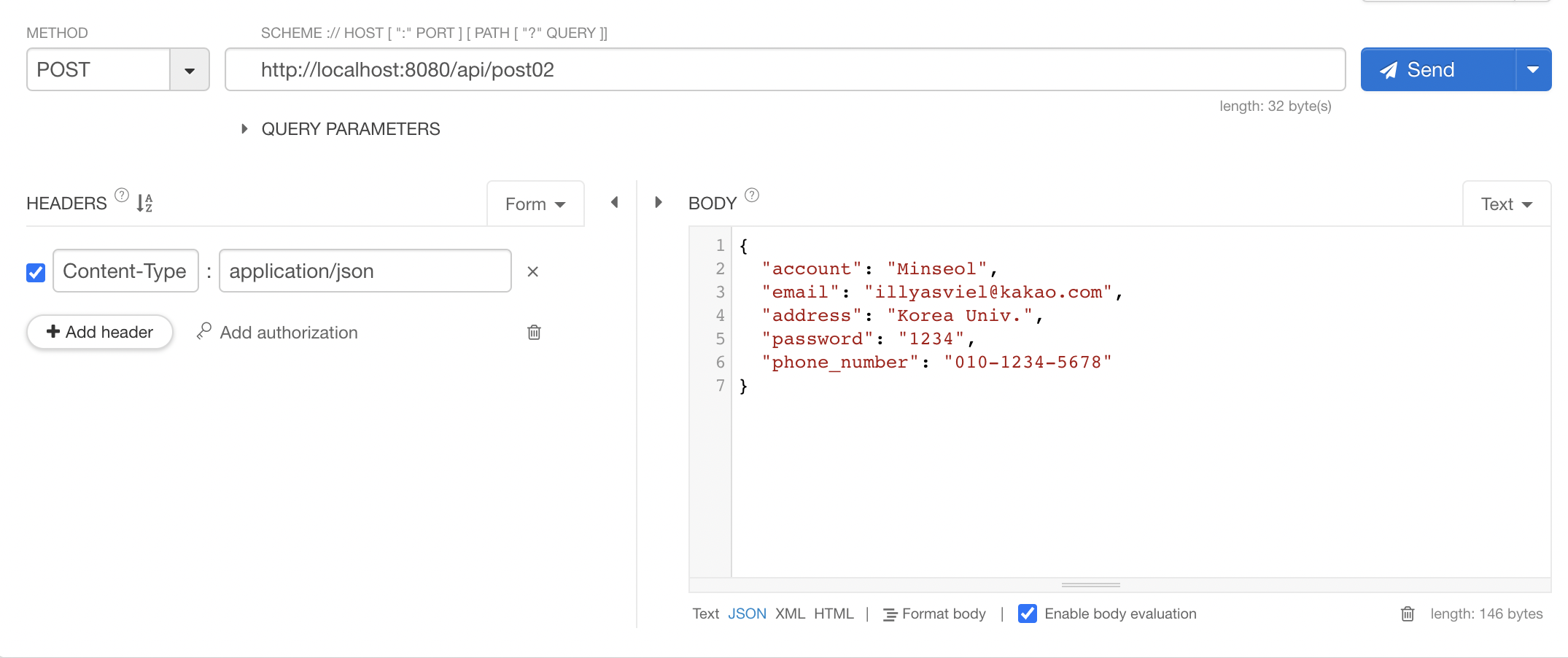
@PostMapping("/post02")
public void post02(@RequestBody PostRequestDto postRequestDto) {
System.out.println(postRequestDto);
}
}package com.example.hello.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
public class PostRequestDto {
private String account;
private String email;
private String address;
private String password;
@JsonProperty("phone_number")
private String phoneNumber;
public String getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getPhoneNumber() {
return phoneNumber;
}
public void setPhoneNumber(String phoneNumber) {
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PostRequestDto{" +
"account='" + account + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", phoneNumber='" + phoneNumber + '\'' +
'}';
}
}만약 DTO에서 정의한 key값과 실제 Request Body의 key값이 다르다면, 위의 코드처럼 @JsonProperty를 통해 매핑시켜준다.
PUT
package com.example.hello.controller;
import com.example.hello.dto.PutRequestDto;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PutApiController {
@PutMapping("/put")
public void put(@RequestBody PutRequestDto putRequestDto) {
System.out.println(putRequestDto);
}
}
package com.example.hello.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.PropertyNamingStrategies;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonNaming;
import java.util.List;
@JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategies.SnakeCaseStrategy.class)
public class PutRequestDto {
private String name;
private int age;
private List<CarDto> carList;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public List<CarDto> getCarList() {
return carList;
}
public void setCarList(List<CarDto> carList) {
this.carList = carList;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PutRequestDto{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", carList=" + carList +
'}';
}
}
위와 같이 @JsonNaming을 이용하여 다른 코딩 스타일 간의 매핑이 가능하다.
package com.example.hello.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
public class CarDto {
private String name;
@JsonProperty("car_number")
private String carNumber;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCarNumber() {
return carNumber;
}
public void setCarNumber(String carNumber) {
this.carNumber = carNumber;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CarDto{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", carNumber='" + carNumber + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
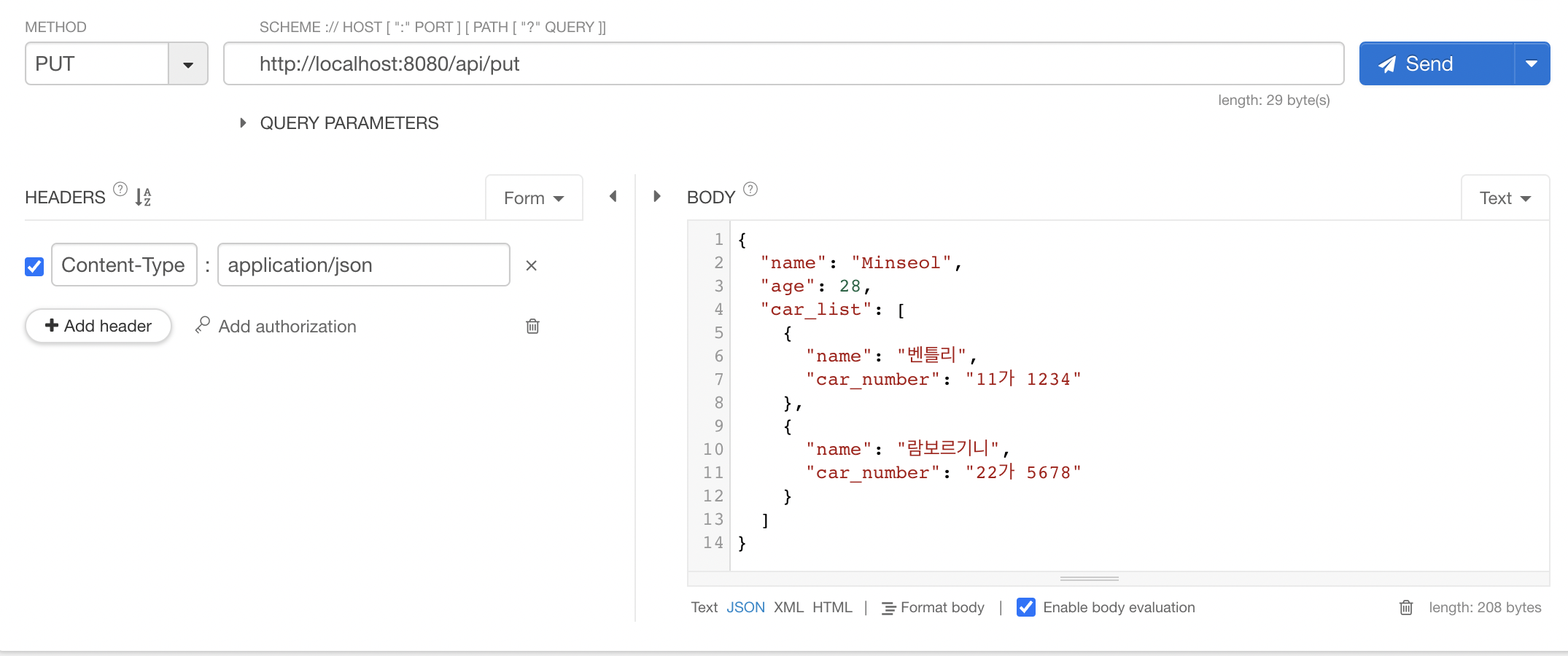
DELETE
package com.example.hello.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class DeleteApiController {
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{userId}")
public void delete(@PathVariable String userId, @RequestParam String account) {
System.out.println(userId);
System.out.println(account);
}
}
Response 생성
package com.example.response.controller;
import com.example.response.dto.User;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ApiController {
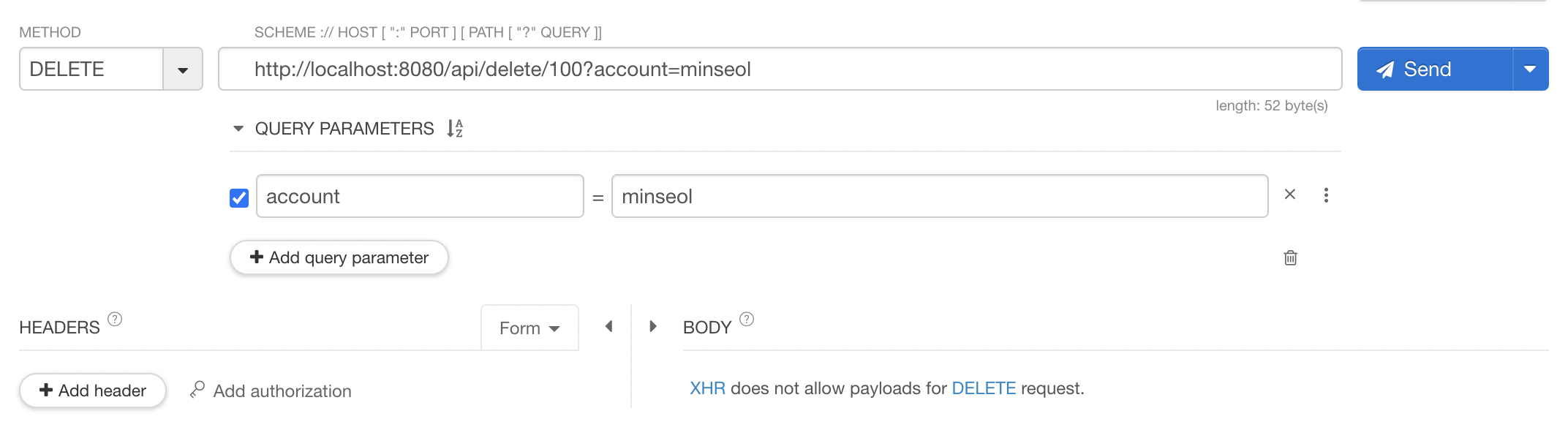
// TEXT
@GetMapping("/text")
public String text(@RequestParam String account) {
return account;
}
// JSON
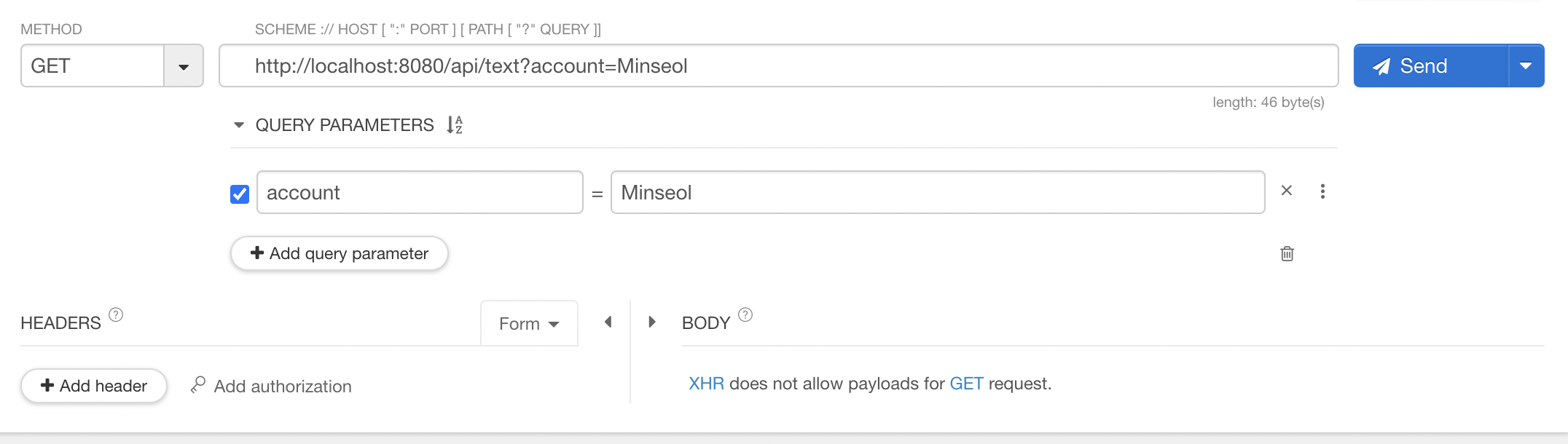
@PostMapping("/json")
public User json(@RequestBody User user) {
return user; // 200 OK
}
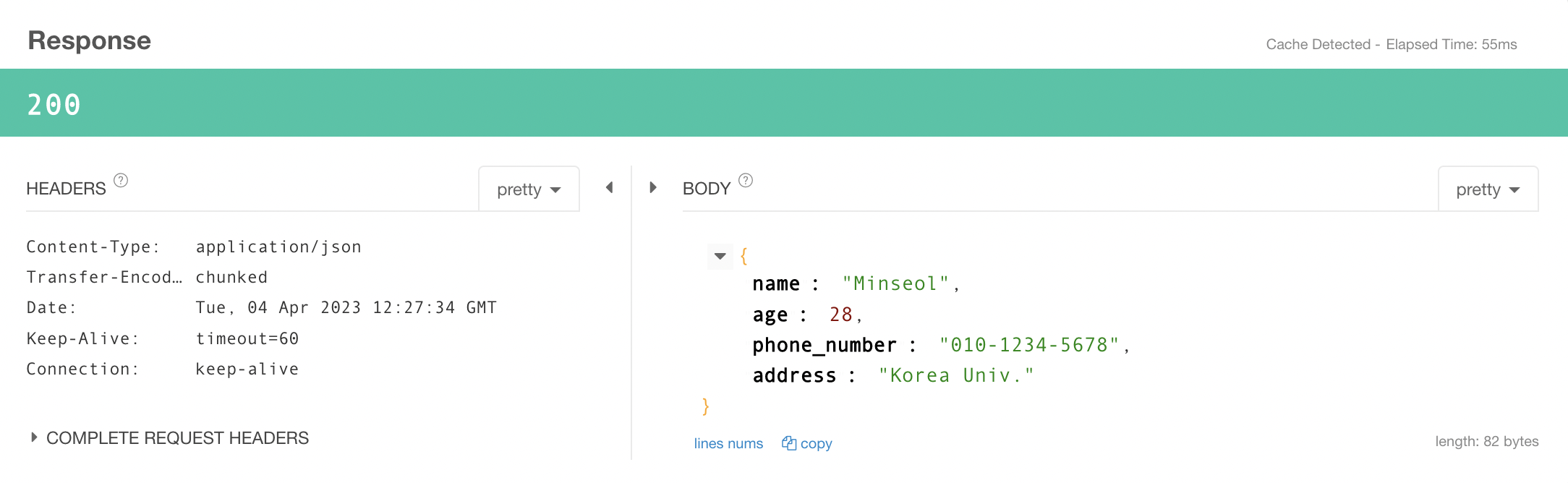
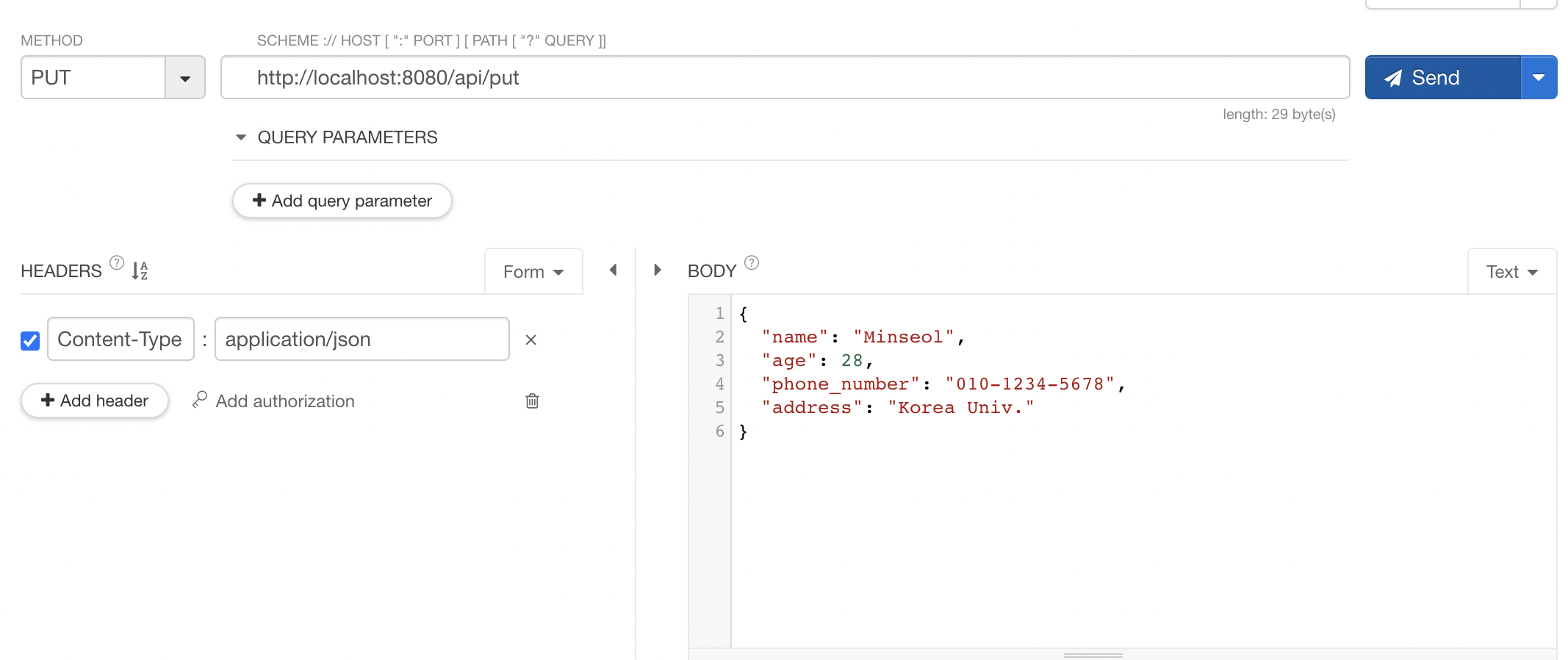
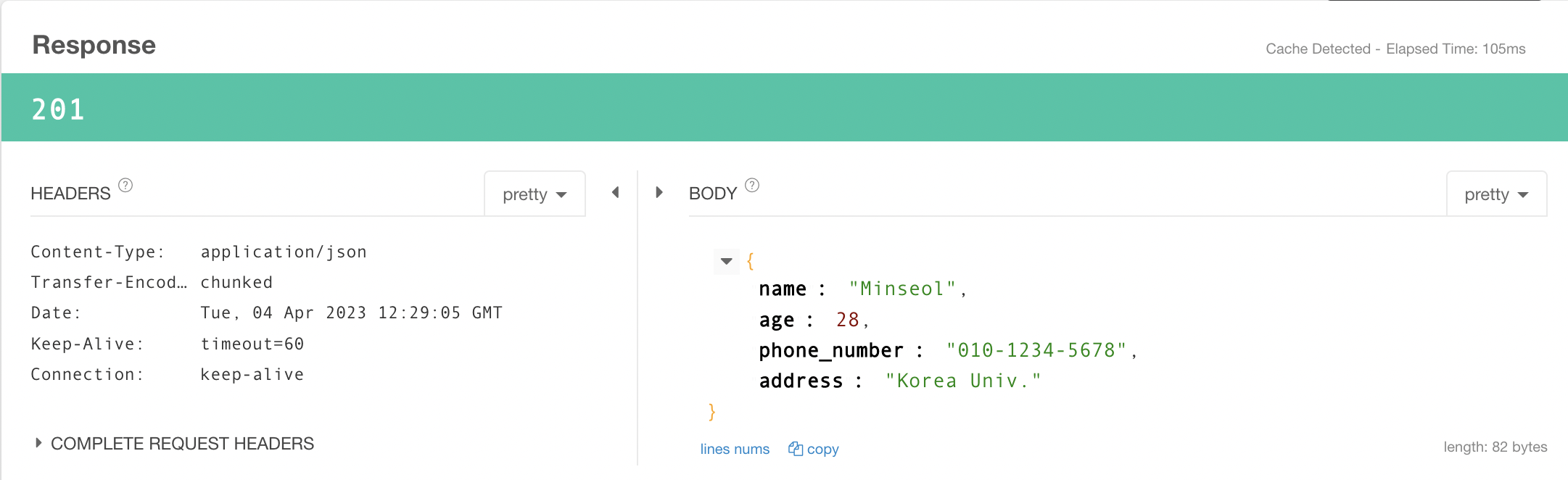
@PutMapping("/put")
public ResponseEntity<User> put(@RequestBody User user) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(user);
}
}package com.example.response.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.PropertyNamingStrategies;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonNaming;
@JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategies.SnakeCaseStrategy.class)
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private String phoneNumber;
private String address;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPhoneNumber() {
return phoneNumber;
}
public void setPhoneNumber(String phoneNumber) {
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
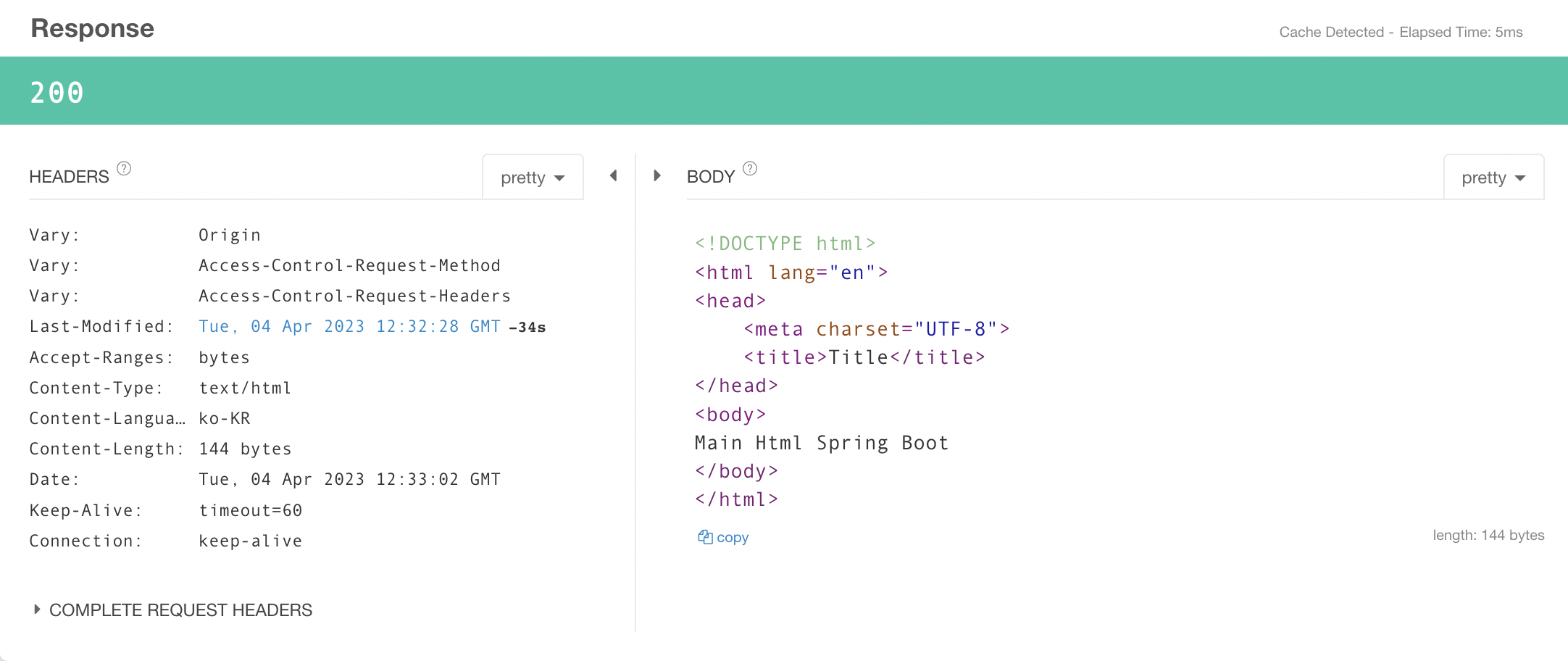
package com.example.response.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class PageController {
@RequestMapping("/main")
public String main() {
return "main.html";
}
}
Object Mapper
package com.example.objectmapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class ResponseApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() throws JsonProcessingException {
System.out.println("--------");
// Text JSON -> Object
// Object -> Text JSON
var objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// object -> text
// object mapper는 get method를 활용한다.
var user = new User("Minseol", 28, "010-1234-5678");
var text = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
System.out.println(text);
// text -> object
// object mapper는 default 생성자를 필요로 한다.
var objectUser = objectMapper.readValue(text, User.class);
System.out.println(objectUser);
}
}package com.example.objectmapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
@JsonProperty("phone_number")
private String phoneNumber;
public User() {
this.name = null;
this.age = 0;
this.phoneNumber = null;
}
public User(String name, int age, String phoneNumber) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getPhoneNumber() {
return phoneNumber;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", phoneNumber='" + phoneNumber + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
