ref : https://github.com/Mephisto405/Learning-Loss-for-Active-Learning
Abstract
The preformance of deep neural networks improves with more annotated data.
The problem is that the budget for annotation is limited.
보통 네트워크는 더 많은 annotated data를 통해 성능이 향상되는데, 문제는 이러한 annotation이 비용이 많이 든다는 것이다.
One solution to this is
active learning, where a model asks human to annotate data thatit perceived as uncertain.A variety of recent methods have been proposed to apply active learning to deep networks but most of them are either designed specific for their target tasks or computationally inefficient for large networks.
한가지 방법 중에, active learning이라는 방법이 있는데, 이 방법은 모델이 불확실(Uncertainty)하다고 생각하는 데이터에 대해서 사람에게 annotate하도록 요청하게 만드는 것이다.
In this paper, we propose a novel active learning method that is simple but task-agnostic, and works efficiently with the deep networks. We attach a small parametric module, name
"loss prediction module,"to a target network, and learn it to predict target losses of unlabeled inputs. Then this module can suggest data that the target model is likely to produce a wrong prediction. This method is task-agnostic as networks are learned from a single loss regardless of target tasks. We rigorously validate our method through image classification, object detection, and human pose estimation, with the recent network architectures. The results demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms the previous methods over the tasks.
이 논문에서는, task-agnostic하고 매우 효율적인 방법을 제안한다. 모델에 작은 parametric module하나를 붙이는 것인데, 이것의 이름을 loss prediction mudule이라고 정의한다. 이 모듈을 타겟 네트워크에 붙이고, unlabeled inputs에 대한 target loss를 예측하도록 학습한다.
그렇게 하면 이 모듈은 어떤 데이터가 틀린 예측을 만들 수 있다는 것을 알려줄 수 있다. 이러한 방법은 테스크에 상관없고 target task에 상관 없이 간단한 loss로 학습이 가능하다.
일반적으로, Active Learning에 사용되는 접근법은 세가지가 존재한다.
An uncertainty-based approachA diversity-based approachexpected model change
Uncertainty Approach
가장 간단한 방법으로 알려져 있는 불확실성(Uncertainty) 기반의 Active learning방법은, 이전 포스트에서 많이 설명했듯이, 불확실성을 정의하기 위하여 class posterior probabilities를 사용한다. 예를 들어 The probability of a predicted class 혹은 an entropy of class posterior probabilities와 같은 것들을 데이터 포인트에 대한 불확실성으로 정의내린다. 이러한 접근은 매우 간단하고, 높은 효율을 보여주지만 일반적으로 분류 문제에서는 효과적일 수 있지만, Object Detection이나 더 복잡한 Semantic Segmentation같은 경우에는 좀 더 복잡한 task-specific uncertainty에 대해 정의 내려하 하는 경우가 많다.
Diversity-based Approach
이 방법은 여러가지 딥 네트워크를 합쳐 그들의 예측들의 차이를 통해 Uncertainty를 정의내린다. (잘모르겠음)
Expected model change
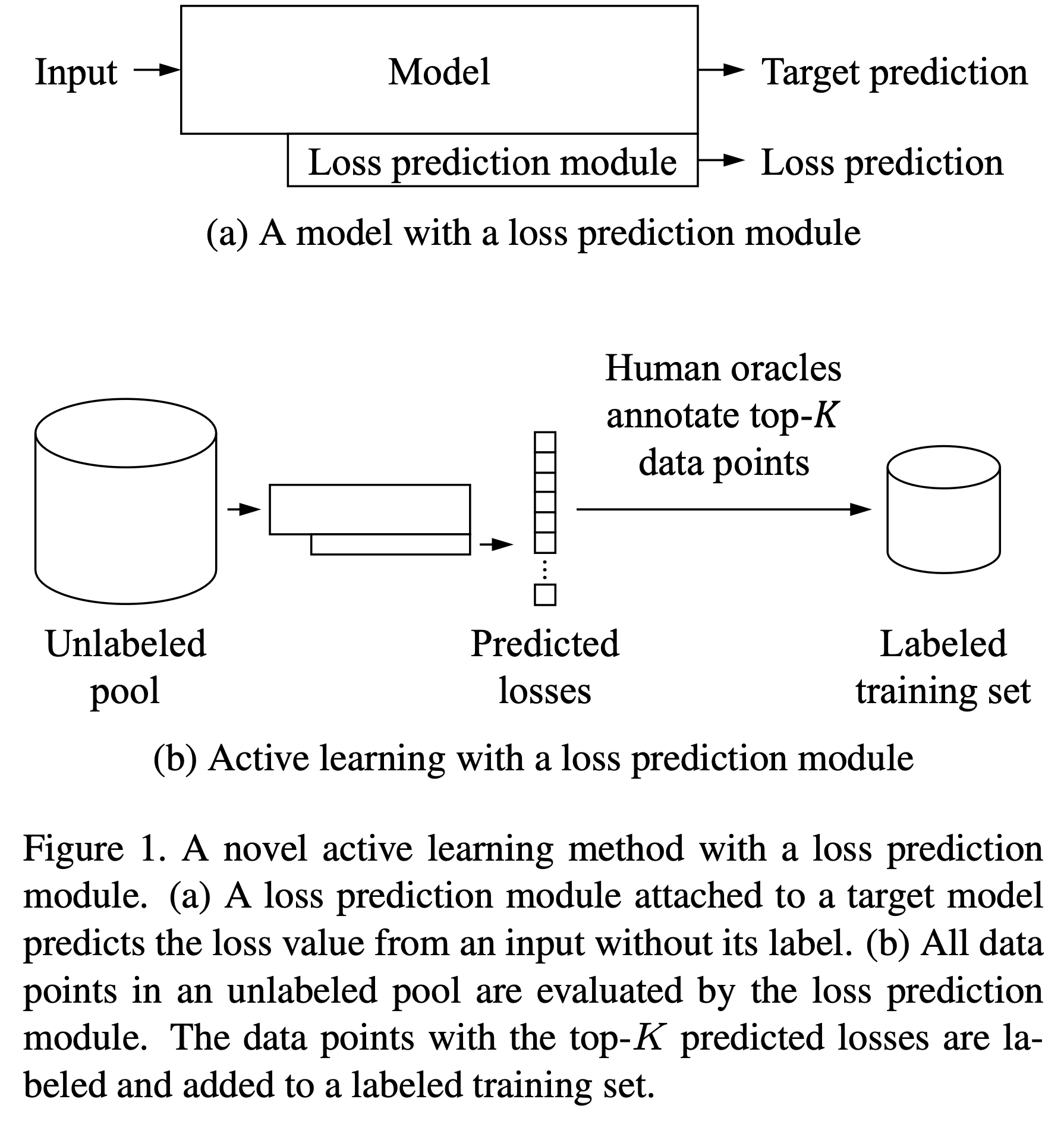
Abstract에서 설명했던 것처럼 본 논문에서 제시하는 Active Learning을 간단하게 도식화 한 것이 위 그림이다. Figure 1-(a)을 살펴보면, 모델에 입력이 들어왓을 때, Loss prediction module도 함께 학습을 진행한다. 아래 그림을 보면 어떤 메커니즘으로 Loss prediction module의 output이 나오는지 확인할 수 있다.
Figure 1-(b)를 보면, 학습을 위해 가장 먼저 해야할 맨 처음 단계에서는 Unlabeled pool에서 K개의 데이터를 uniformly sampling한다. 이 K개의 샘플들을 human oracles를 통해 annotate하여 labeled된 데이터셋 K개를 만들어 낸다(맨 처음 labeled dataset). 이러면 원래의 Unlabeled pool (Unlabeld datset)이 된다. (subscript 0은 initial stage를 의미한다)
이 때 얻은 Labeled datset을 를 통해 initial target model인 과 initial loss prediction module 를 학습시킨다.
가장 첫번 째 학습이 끝난 뒤에, Unlabeled pool안에 존재하는 모든 데이터들에 대해 loss prediction module을 통해 평가를 진행한다. 이러한 평가는 data-loss pairs인 를 얻기 위함이다.
이러한 샘플들의 loss를 Figure 1-(a)의 Model과 Loss prediction module을 통해 예측한다. 그리고 나서
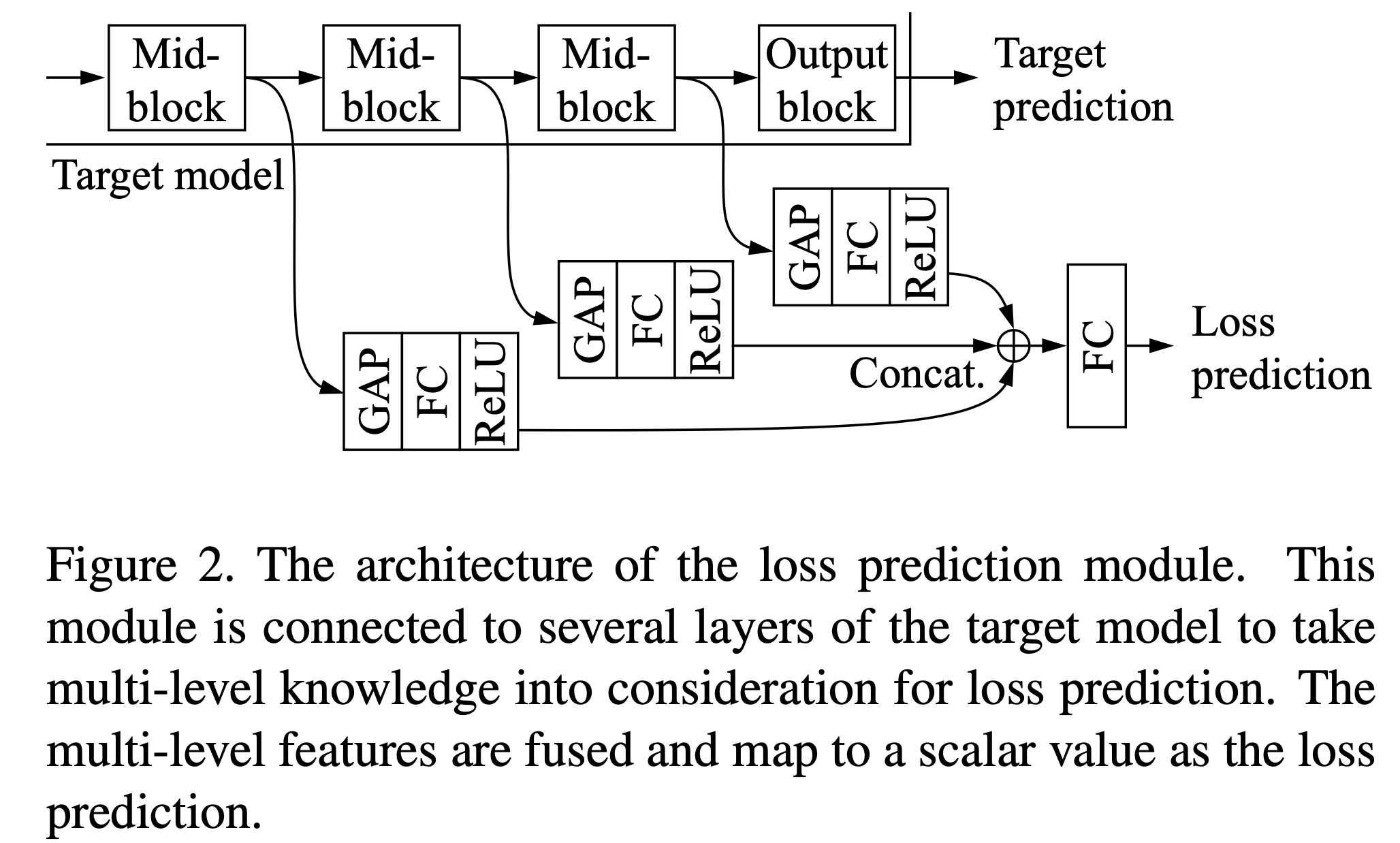
위에서 보는 것처럼, Target Model이라고 불리는 일반적인 deep network에 대해, feature단에서 일부 레이어들이 함께 연결되어 있다. 이러한 레이어들 각각에 대해 Global Average Pooling, FC layer, ReLU를 통과한 multi-level features를 융합하고 맵핑하여 loss prediction이라는 output 값을 나타낸다.
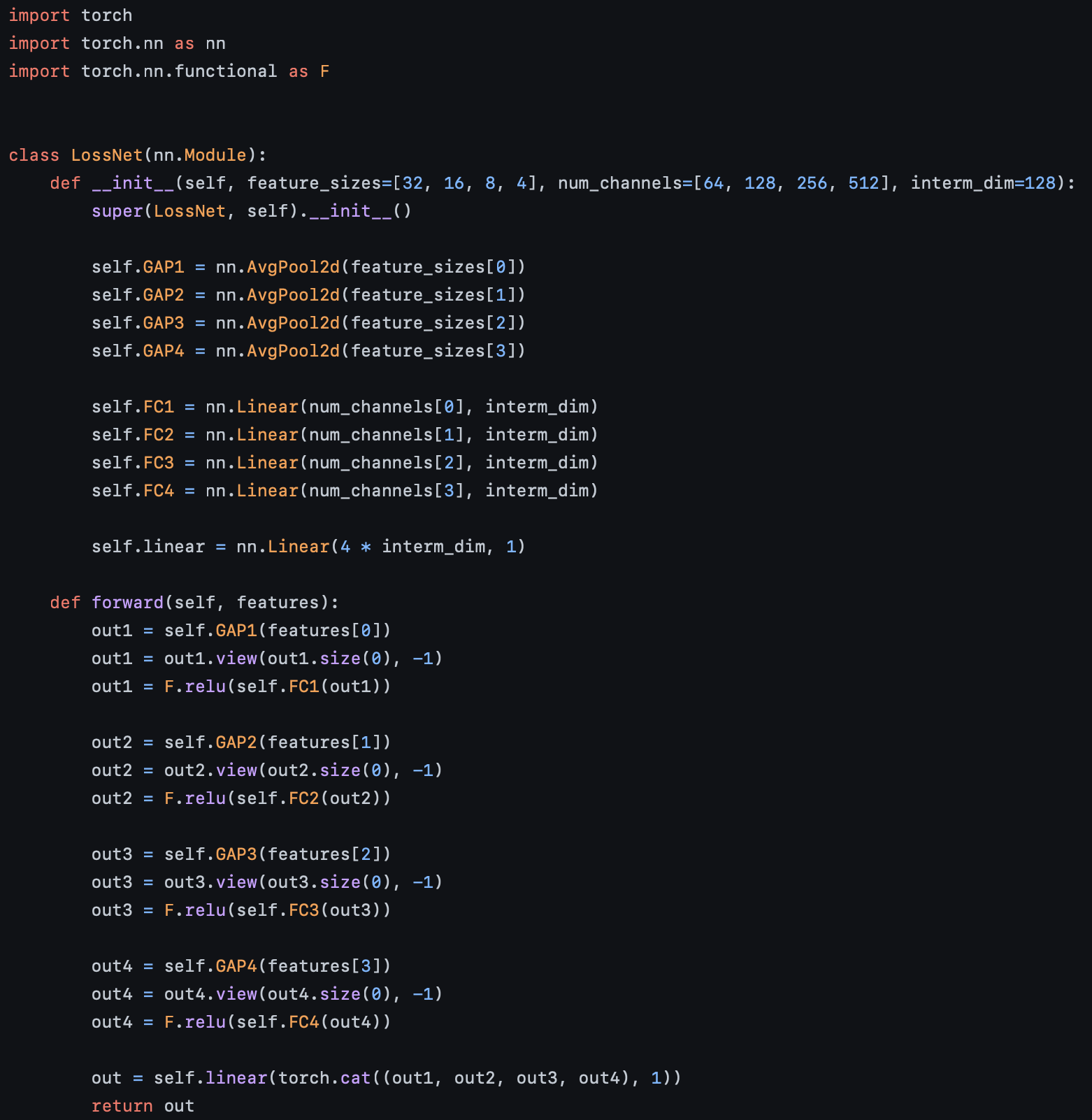
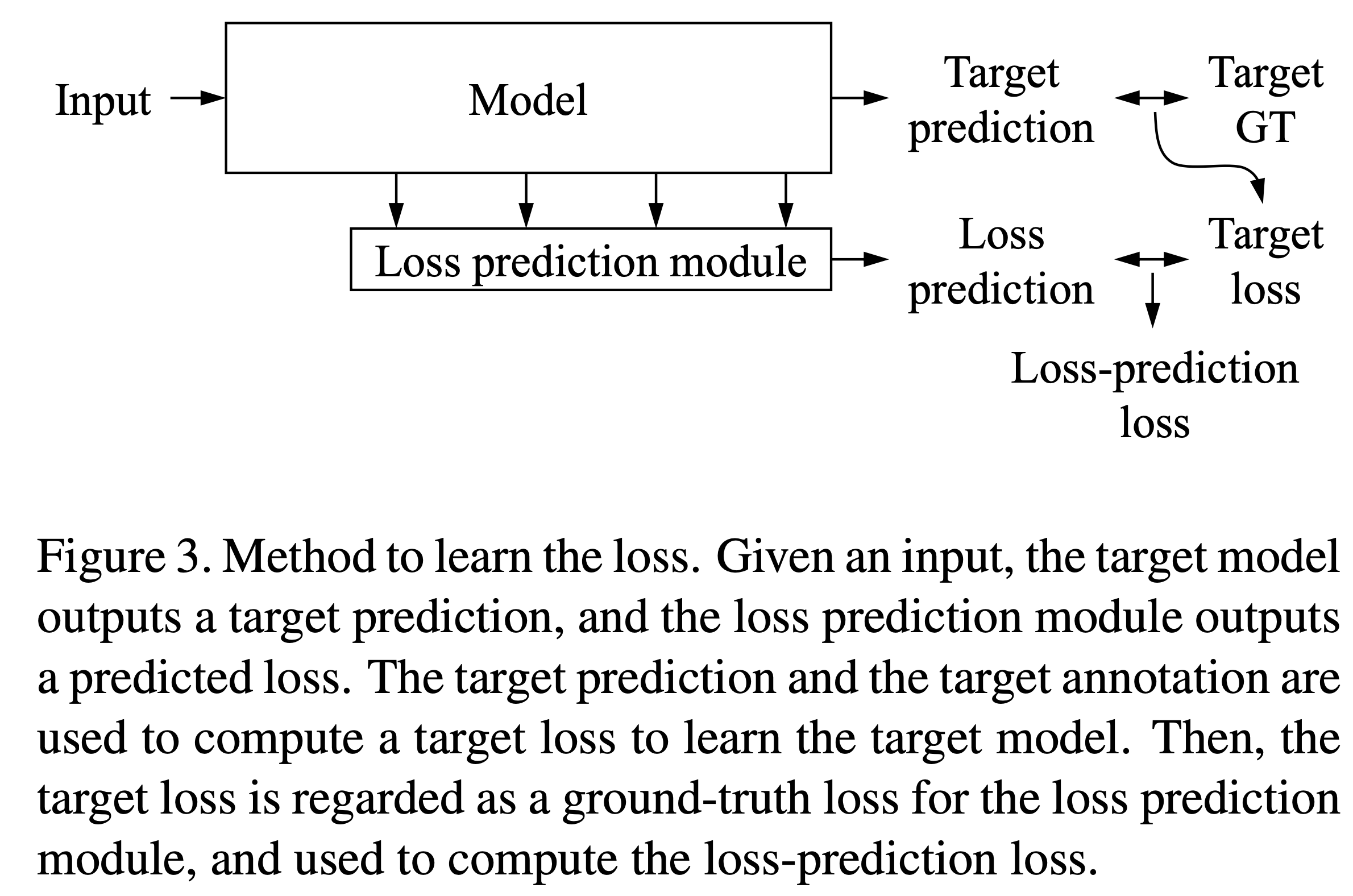
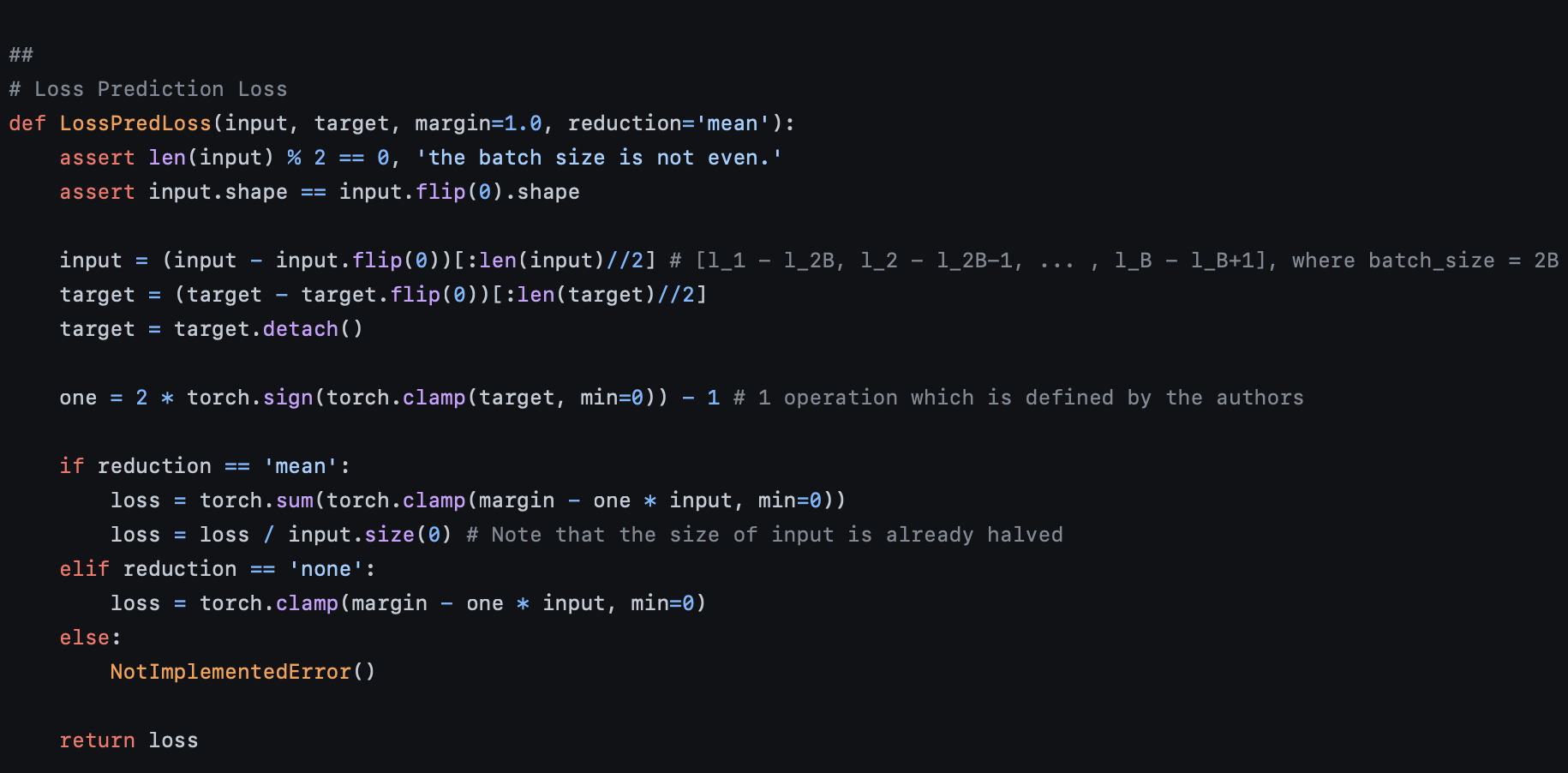
LossPredLoss 는 input과 target을 입력으로 받는다.
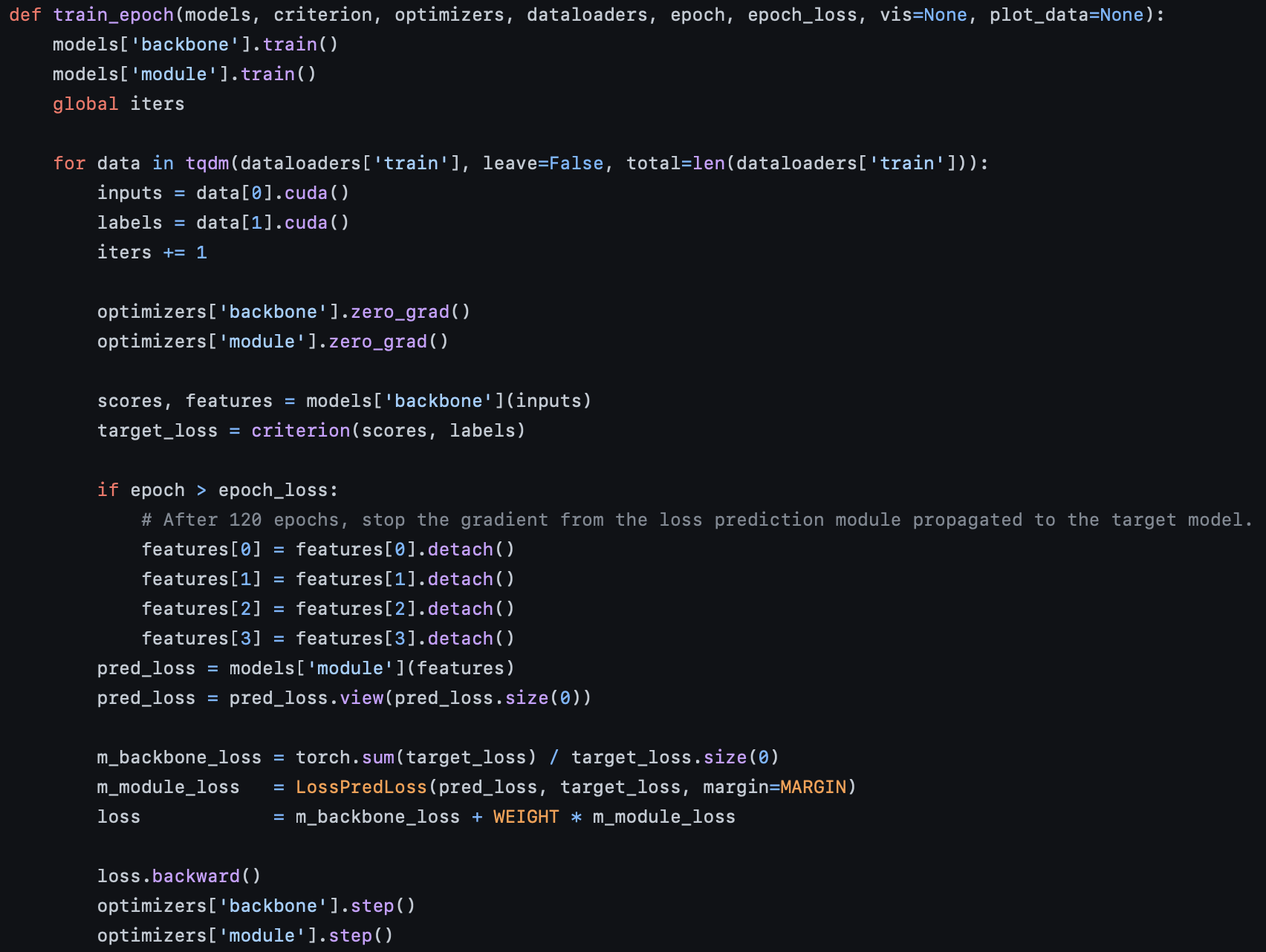
위에서 보는 것처럼, models는 backbone과 module을 가지는데, 위 논문에서 설명한 것과 마찬가지로 backbone은 target model이 되고, module은 Loss prediction module이 된다. 이 때, pred_loss라는 Loss prediction module에서 나온 결과값을 우리는 학습시키기 위해서 target_loss와 비교시켜 학습을 진행한다.
