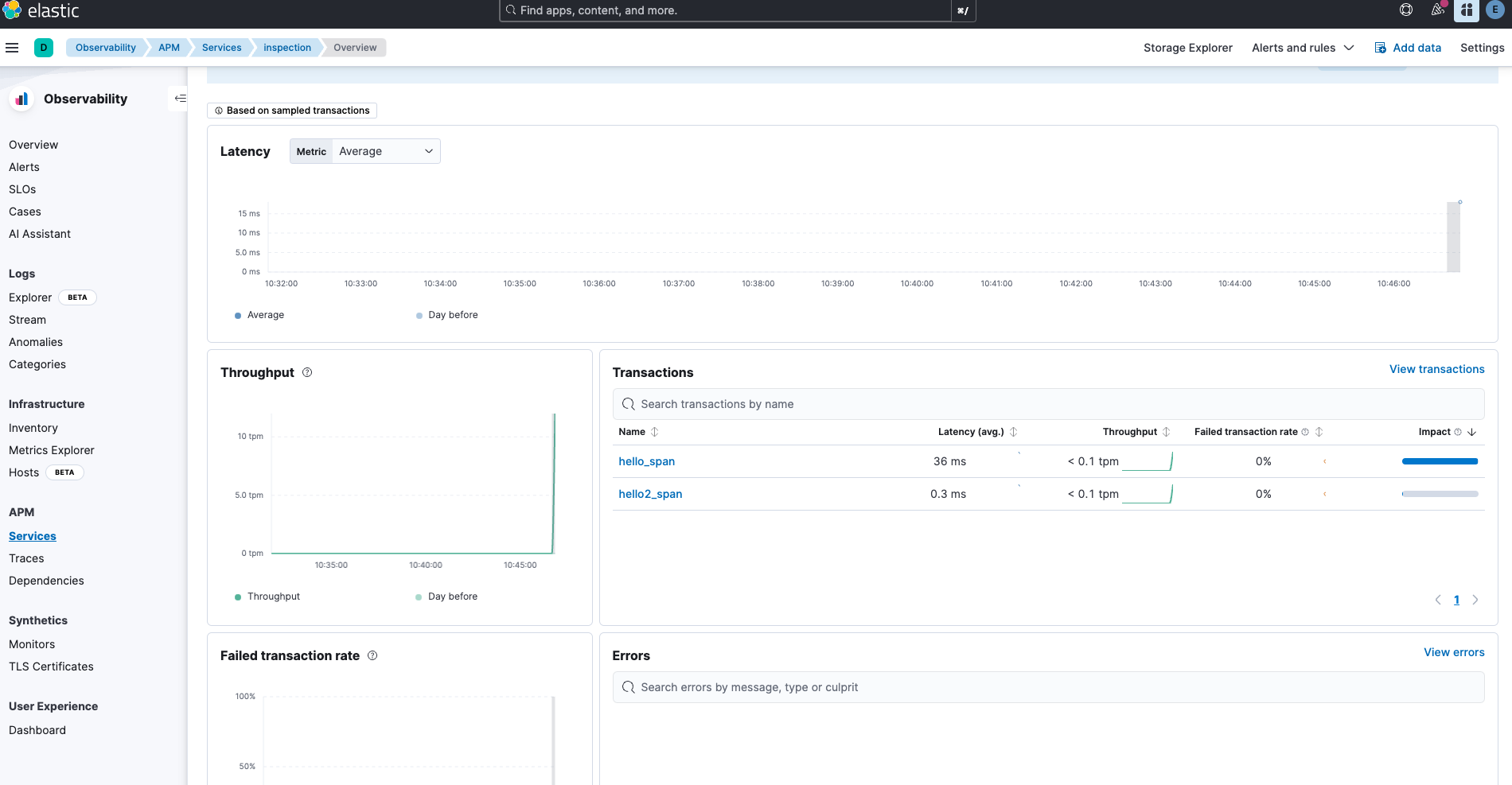
각각의 MSA로 분리된 애플리케이션들이 Opentelemetry SDK를 활용해서
Optentelemetry Collector로 Trace, Metric, Log를 전송 중에 있었다.
나는 이를 시각화해서 한 번에 볼 필요가 있다.ElasticSearch 공식 문서에 따르면
이렇게 애플리케이션의 MLT 파이프라인을 통합할 수있다고 한다.
Elasticsearch와 Kibana에서 APM 사용하려면,
보안설정이 되어있어야하고,
TLS를 설정(?)을 해야하는 것 같아보였다.
TLS
도커 컴포즈의 일부분인 tls을 먼저 실행해줘야하기에,
entrypoint.sh와 instance.yml을 작성해주자.
version: "3.8"
services:
tls:
profiles:
- setup
build:
context: tls
args:
ELASTIC_VERSION: ${ELASTIC_VERSION}
user: root
init: true
volumes:
- /tls/entrypoint.sh:/entrypoint.sh:ro,Z
- /tls/instances.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/tls/instances.yml:ro,Z
- /tls/certs:/usr/share/elasticsearch/tls/certs:z- entrypoint.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -eu
set -o pipefail
declare symbol=⠍
echo '[+] CA certificate and key'
if [ ! -f tls/certs/ca/ca.key ]; then
symbol=⠿
bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca \
--silent \
--pem \
--out tls/certs/ca.zip
unzip tls/certs/ca.zip -d tls/certs/ >/dev/null
rm tls/certs/ca.zip
echo ' ⠿ Created'
else
echo ' ⠍ Already present, skipping'
fi
declare ca_fingerprint
ca_fingerprint="$(openssl x509 -fingerprint -sha256 -noout -in tls/certs/ca/ca.crt \
| cut -d '=' -f2 \
| tr -d ':' \
| tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]'
)"
echo " ${symbol} SHA256 fingerprint: ${ca_fingerprint}"
while IFS= read -r file; do
echo " ${symbol} ${file}"
done < <(find tls/certs/ca -type f \( -name '*.crt' -or -name '*.key' \) -mindepth 1 -print)
symbol=⠍
echo '[+] Server certificates and keys'
if [ ! -f tls/certs/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.key ]; then
symbol=⠿
bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert \
--silent \
--pem \
--in tls/instances.yml \
--ca-cert tls/certs/ca/ca.crt \
--ca-key tls/certs/ca/ca.key \
--out tls/certs/certs.zip
unzip tls/certs/certs.zip -d tls/certs/ >/dev/null
rm tls/certs/certs.zip
find tls -name ca -prune -or -type f -name '*.crt' -exec sh -c 'cat tls/certs/ca/ca.crt >>{}' \;
echo ' ⠿ Created'
else
echo ' ⠍ Already present, skipping'
fi
while IFS= read -r file; do
echo " ${symbol} ${file}"
done < <(find tls -name ca -prune -or -type f \( -name '*.crt' -or -name '*.key' \) -mindepth 1 -print)- instance.yml
# This file is used by elasticsearch-certutil to generate X.509 certificates
# for stack components.
#
# Ref. https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/certutil.html#certutil-silent
instances:
- name: elasticsearch
dns:
- elasticsearch # Compose service, resolved by the embedded Docker DNS server name
- localhost # local connections
ip:
- 127.0.0.1 # local connections
- ::1
- name: kibana
dns:
- kibana.127.0.0.1.nip.io # Examples of resolvable domains.
- kibana.127.0.0.1.sslip.io #
- localhost
ip:
- 127.0.0.1
- ::1
- name: fleet-server
dns:
- fleet-server
- localhost
ip:
- 127.0.0.1
- ::1
- name: apm-server
dns:
- apm-server
- localhost
ip:
- 127.0.0.1
- ::1그 다음
docker compose -f <docker-compose 파일> up tls -d를 실행하면 certs 폴더에 각 서비스별 인증서가 발급된 것을 볼 수 있다.
Setup
setup:
profiles:
- setup
build:
context: setup
args:
ELASTIC_VERSION: ${ELASTIC_VERSION}
init: true
volumes:
- /setup/entrypoint.sh:/entrypoint.sh:ro,Z
- /setup/lib.sh:/lib.sh:ro,Z
- /setup/roles:/roles:ro,Z
- /tls/certs/ca/ca.crt:/ca.crt:ro,z
environment:
ELASTIC_PASSWORD: ${ELASTIC_PASSWORD:-}
LOGSTASH_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${LOGSTASH_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
KIBANA_SYSTEM_PASSWORD: ${KIBANA_SYSTEM_PASSWORD:-}
METRICBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${METRICBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
FILEBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${FILEBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
HEARTBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${HEARTBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
MONITORING_INTERNAL_PASSWORD: ${MONITORING_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}
BEATS_SYSTEM_PASSWORD: ${BEATS_SYSTEM_PASSWORD:-}
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
- kibanaTLS를 하고나면 Setup을 해줘야하는데, 셋업에 필요한 파일은 아래와 같다.
- entrypoint.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -eu
set -o pipefail
source "${BASH_SOURCE[0]%/*}"/lib.sh
# --------------------------------------------------------
# Users declarations
declare -A users_passwords
users_passwords=(
[logstash_internal]="${LOGSTASH_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}"
[kibana_system]="${KIBANA_SYSTEM_PASSWORD:-}"
[metricbeat_internal]="${METRICBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}"
[filebeat_internal]="${FILEBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}"
[heartbeat_internal]="${HEARTBEAT_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}"
[monitoring_internal]="${MONITORING_INTERNAL_PASSWORD:-}"
[beats_system]="${BEATS_SYSTEM_PASSWORD=:-}"
)
declare -A users_roles
users_roles=(
[logstash_internal]='logstash_writer'
[metricbeat_internal]='metricbeat_writer'
[filebeat_internal]='filebeat_writer'
[heartbeat_internal]='heartbeat_writer'
[monitoring_internal]='remote_monitoring_collector'
)
# --------------------------------------------------------
# Roles declarations
declare -A roles_files
roles_files=(
[logstash_writer]='logstash_writer.json'
[metricbeat_writer]='metricbeat_writer.json'
[filebeat_writer]='filebeat_writer.json'
[heartbeat_writer]='heartbeat_writer.json'
)
# --------------------------------------------------------
log 'Waiting for availability of Elasticsearch. This can take several minutes.'
declare -i exit_code=0
wait_for_elasticsearch || exit_code=$?
if ((exit_code)); then
case $exit_code in
6)
suberr 'Could not resolve host. Is Elasticsearch running?'
;;
7)
suberr 'Failed to connect to host. Is Elasticsearch healthy?'
;;
28)
suberr 'Timeout connecting to host. Is Elasticsearch healthy?'
;;
*)
suberr "Connection to Elasticsearch failed. Exit code: ${exit_code}"
;;
esac
exit $exit_code
fi
sublog 'Elasticsearch is running'
log 'Waiting for initialization of built-in users'
wait_for_builtin_users || exit_code=$?
if ((exit_code)); then
suberr 'Timed out waiting for condition'
exit $exit_code
fi
sublog 'Built-in users were initialized'
for role in "${!roles_files[@]}"; do
log "Role '$role'"
declare body_file
body_file="${BASH_SOURCE[0]%/*}/roles/${roles_files[$role]:-}"
if [[ ! -f "${body_file:-}" ]]; then
sublog "No role body found at '${body_file}', skipping"
continue
fi
sublog 'Creating/updating'
ensure_role "$role" "$(<"${body_file}")"
done
for user in "${!users_passwords[@]}"; do
log "User '$user'"
if [[ -z "${users_passwords[$user]:-}" ]]; then
sublog 'No password defined, skipping'
continue
fi
declare -i user_exists=0
user_exists="$(check_user_exists "$user")"
if ((user_exists)); then
sublog 'User exists, setting password'
set_user_password "$user" "${users_passwords[$user]}"
else
if [[ -z "${users_roles[$user]:-}" ]]; then
suberr ' No role defined, skipping creation'
continue
fi
sublog 'User does not exist, creating'
create_user "$user" "${users_passwords[$user]}" "${users_roles[$user]}"
fi
done- lib.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
es_ca_cert="${BASH_SOURCE[0]%/*}"/ca.crt
# Log a message.
function log {
echo "[+] $1"
}
# Log a message at a sub-level.
function sublog {
echo " ⠿ $1"
}
# Log an error.
function err {
echo "[x] $1" >&2
}
# Log an error at a sub-level.
function suberr {
echo " ⠍ $1" >&2
}
# Poll the 'elasticsearch' service until it responds with HTTP code 200.
function wait_for_elasticsearch {
local elasticsearch_host="${ELASTICSEARCH_HOST:-elasticsearch}"
local -a args=( '-s' '-D-' '-m15' '-w' '%{http_code}' 'https://elasticsearch:9200/'
'--resolve' "elasticsearch:9200:${elasticsearch_host}" '--cacert' "$es_ca_cert"
)
if [[ -n "${ELASTIC_PASSWORD:-}" ]]; then
args+=( '-u' "elastic:${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}" )
fi
local -i result=1
local output
# retry for max 300s (60*5s)
for _ in $(seq 1 60); do
local -i exit_code=0
output="$(curl "${args[@]}")" || exit_code=$?
if ((exit_code)); then
result=$exit_code
fi
if [[ "${output: -3}" -eq 200 ]]; then
result=0
break
fi
sleep 5
done
if ((result)) && [[ "${output: -3}" -ne 000 ]]; then
echo -e "\n${output::-3}"
fi
return $result
}
# Poll the Elasticsearch users API until it returns users.
function wait_for_builtin_users {
local elasticsearch_host="${ELASTICSEARCH_HOST:-elasticsearch}"
local -a args=( '-s' '-D-' '-m15' 'https://elasticsearch:9200/_security/user?pretty'
'--resolve' "elasticsearch:9200:${elasticsearch_host}" '--cacert' "$es_ca_cert"
)
if [[ -n "${ELASTIC_PASSWORD:-}" ]]; then
args+=( '-u' "elastic:${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}" )
fi
local -i result=1
local line
local -i exit_code
local -i num_users
# retry for max 30s (30*1s)
for _ in $(seq 1 30); do
num_users=0
# read exits with a non-zero code if the last read input doesn't end
# with a newline character. The printf without newline that follows the
# curl command ensures that the final input not only contains curl's
# exit code, but causes read to fail so we can capture the return value.
# Ref. https://unix.stackexchange.com/a/176703/152409
while IFS= read -r line || ! exit_code="$line"; do
if [[ "$line" =~ _reserved.+true ]]; then
(( num_users++ ))
fi
done < <(curl "${args[@]}"; printf '%s' "$?")
if ((exit_code)); then
result=$exit_code
fi
# we expect more than just the 'elastic' user in the result
if (( num_users > 1 )); then
result=0
break
fi
sleep 1
done
return $result
}
# Verify that the given Elasticsearch user exists.
function check_user_exists {
local username=$1
local elasticsearch_host="${ELASTICSEARCH_HOST:-elasticsearch}"
local -a args=( '-s' '-D-' '-m15' '-w' '%{http_code}'
"https://elasticsearch:9200/_security/user/${username}"
'--resolve' "elasticsearch:9200:${elasticsearch_host}" '--cacert' "$es_ca_cert"
)
if [[ -n "${ELASTIC_PASSWORD:-}" ]]; then
args+=( '-u' "elastic:${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}" )
fi
local -i result=1
local -i exists=0
local output
output="$(curl "${args[@]}")"
if [[ "${output: -3}" -eq 200 || "${output: -3}" -eq 404 ]]; then
result=0
fi
if [[ "${output: -3}" -eq 200 ]]; then
exists=1
fi
if ((result)); then
echo -e "\n${output::-3}"
else
echo "$exists"
fi
return $result
}
# Set password of a given Elasticsearch user.
function set_user_password {
local username=$1
local password=$2
local elasticsearch_host="${ELASTICSEARCH_HOST:-elasticsearch}"
local -a args=( '-s' '-D-' '-m15' '-w' '%{http_code}'
"https://elasticsearch:9200/_security/user/${username}/_password"
'--resolve' "elasticsearch:9200:${elasticsearch_host}" '--cacert' "$es_ca_cert"
'-X' 'POST'
'-H' 'Content-Type: application/json'
'-d' "{\"password\" : \"${password}\"}"
)
if [[ -n "${ELASTIC_PASSWORD:-}" ]]; then
args+=( '-u' "elastic:${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}" )
fi
local -i result=1
local output
output="$(curl "${args[@]}")"
if [[ "${output: -3}" -eq 200 ]]; then
result=0
fi
if ((result)); then
echo -e "\n${output::-3}\n"
fi
return $result
}
# Create the given Elasticsearch user.
function create_user {
local username=$1
local password=$2
local role=$3
local elasticsearch_host="${ELASTICSEARCH_HOST:-elasticsearch}"
local -a args=( '-s' '-D-' '-m15' '-w' '%{http_code}'
"https://elasticsearch:9200/_security/user/${username}"
'--resolve' "elasticsearch:9200:${elasticsearch_host}" '--cacert' "$es_ca_cert"
'-X' 'POST'
'-H' 'Content-Type: application/json'
'-d' "{\"password\":\"${password}\",\"roles\":[\"${role}\"]}"
)
if [[ -n "${ELASTIC_PASSWORD:-}" ]]; then
args+=( '-u' "elastic:${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}" )
fi
local -i result=1
local output
output="$(curl "${args[@]}")"
if [[ "${output: -3}" -eq 200 ]]; then
result=0
fi
if ((result)); then
echo -e "\n${output::-3}\n"
fi
return $result
}
# Ensure that the given Elasticsearch role is up-to-date, create it if required.
function ensure_role {
local name=$1
local body=$2
local elasticsearch_host="${ELASTICSEARCH_HOST:-elasticsearch}"
local -a args=( '-s' '-D-' '-m15' '-w' '%{http_code}'
"https://elasticsearch:9200/_security/role/${name}"
'--resolve' "elasticsearch:9200:${elasticsearch_host}" '--cacert' "$es_ca_cert"
'-X' 'POST'
'-H' 'Content-Type: application/json'
'-d' "$body"
)
if [[ -n "${ELASTIC_PASSWORD:-}" ]]; then
args+=( '-u' "elastic:${ELASTIC_PASSWORD}" )
fi
local -i result=1
local output
output="$(curl "${args[@]}")"
if [[ "${output: -3}" -eq 200 ]]; then
result=0
fi
if ((result)); then
echo -e "\n${output::-3}\n"
fi
return $result
}그 다음, 아래 커맨드로 Setup을 해준다.
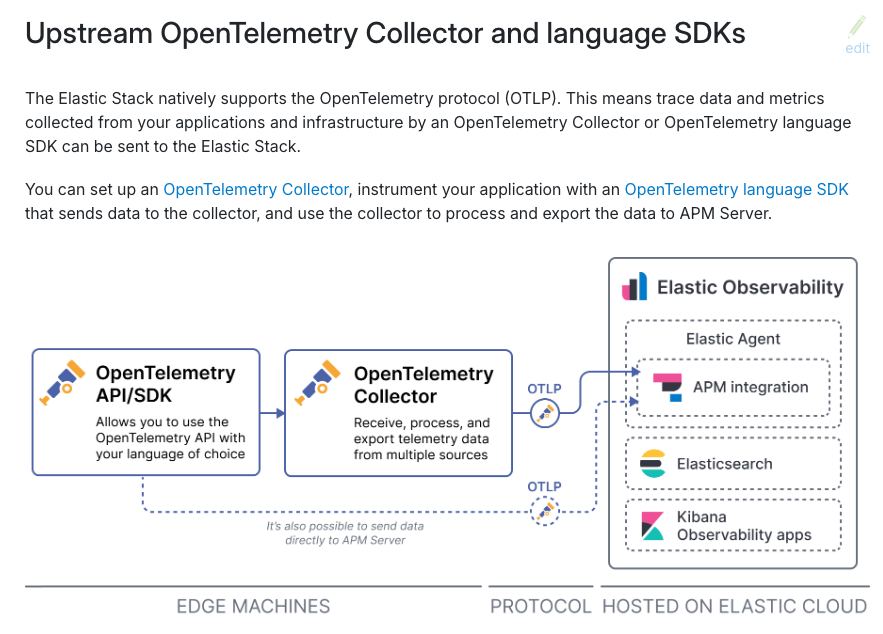
docker compose -f <docker-compose 파일> up setup -dAPM Server + OTEL
이제 우리는 APM 서버와 Opentelemetry Collector를 구성해서
각 애플리케이션들이 SDK를 통해 Opentelemetry Collector로 데이터를 전송하고
Opentelemetry Collector가 APM 서버에게 데이터를 송신하면
Elasticsearch 포맷으로 데이터를 가공한 뒤, 대시보드로 볼 수 있게 되는 것이다.
apm-server:
image: docker.elastic.co/apm/apm-server:${ELASTIC_VERSION}
container_name: apm-server
environment:
- output.elasticsearch.hosts=["elasticsearch:9200"]
ports:
- "8200:8200" # APM 서버가 수집할 데이터를 수신하는 포트
volumes:
- /apm/config.yaml:/usr/share/apm-server/apm-server.yml:ro
- ./persistence/apm-server:/var/log/apm-server:rw
- /tls/certs/ca/ca.crt:/usr/share/ca/ca.crt:ro
- /tls/certs/apm-server/apm-server.crt:/usr/share/apm-server/apm-server.crt:ro
- /tls/certs/apm-server/apm-server.key:/usr/share/apm-server/apm-server.key:ro
- /tls/certs/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.crt:/usr/share/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.crt:ro
- /tls/certs/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.key:/usr/share/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.key:ro
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
# OPENTELEMETRY-COLLECTOR
opentelemetry-collector:
image: otel/opentelemetry-collector-contrib:latest
container_name: opentelemetry-collector
user: 0:0
cap_add:
- SYS_ADMIN
privileged: true
volumes:
- /collector/config.yml:/etc/opentelemetry-collector.yml
- /tls/certs/apm-server/apm-server.crt:/etc/apm-server.crt
- /tls/certs/apm-server/apm-server.key:/etc/apm-server.key
- /tls/certs/ca/ca.crt:/etc/ca.crt
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
command:
- "--config=/etc/opentelemetry-collector.yml"
links:
- elasticsearch
- kibana
- apm-server
ports:
- 4317:4317 # OTLP over gRPC receiver
- 4318:4318 # OTLP over HTTP receiver
- 3500:3500 # Loki HTTP receiver
- 3600:3600 # Loki gRPC receiver
- 8888:8888 # metrics endpointAPM 서버 설정은 아래와 같다.
- config.yaml
apm-server:
# Defines the host and port the server is listening on. Use "unix:/path/to.sock" to listen on a unix domain socket.
host: "0.0.0.0:8200"
auth:
secret_token: <직접 만든 Bearer 토큰을 넣으면 된다.>
...
...
..
.
ssl:
enabled: true
certificate: '/usr/share/apm-server/apm-server.crt'
key: '/usr/share/apm-server/apm-server.key'
...
..
..
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["https://elasticsearch:9200"]
username: "elastic"
password: "Qwe123!@#"
ssl.enabled: true
ssl.supported_protocols: [TLSv1.0, TLSv1.1, TLSv1.2]
# List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications.
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/usr/share/ca/ca.crt"]
# Certificate for SSL client authentication.
ssl.certificate: "/usr/share/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.crt"
# Client Certificate Key
ssl.key: "/usr/share/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.key"
...
...
..
# 만약 로깅을 원하면 아래 세팅을 추가하면 된다.
logging.level: debug
logging.to_files: true
logging.files:
# Configure the path where the logs are written. The default is the logs directory
path: /var/log/apm-server
name: apm-server
rotateeverybytes: 10485760 # = 10MB
keepfiles: 7
permissions: 0600
interval: 24h
...
...APM 서버 설정 파일의 기본 템플릿 파일은 검색만 해보면 쉽게 알 수 있다.
그 파일을 가져다가 필요한 부분만 수정하면 된다.
Opentelemetry Collector 설정은 아래와 같다.
- config.yaml
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: "0.0.0.0:4317"
http:
endpoint: "0.0.0.0:4318"
exporters:
logging:
loglevel: debug
otlp/elastic:
endpoint: "https://apm-server:8200"
tls:
insecure: false
ca_file: /etc/ca.crt
cert_file: /etc/apm-server.crt
key_file: /etc/apm-server.key
headers:
Authorization: "Bearer <APM 서버 설정 시 작성한 secret token을 넣으면 된다.>"
processors:
batch:
extensions:
health_check:
pprof:
zpages:
service:
extensions: [health_check]
pipelines:
traces:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: []
exporters: [logging, otlp/elastic]
metrics:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: []
exporters: [logging, otlp/elastic]
logs:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: []
exporters: [logging, otlp/elastic]서버 실행
docker compose -f <docker compose 파일> up -d