library
- libary: symbol들을 모아둬 다른 src code에서 접근해서 사용할 수 있게함
- static library :
.a - shared library :
.so- Dependent libarary: 응용 프로그램에서 컴파일시 이거 이거 사용한다 정보 알려두고 컴파일. 그냥 통용적으로 shared library 라고 함
- Dynamic library: 응용 프로그램에서
-ldl,-rdynamic 지정 컴파일,함수 사용법 등이 다름
- static library :
library는 왜 필요한가?
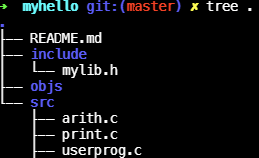
- src, include file 관계
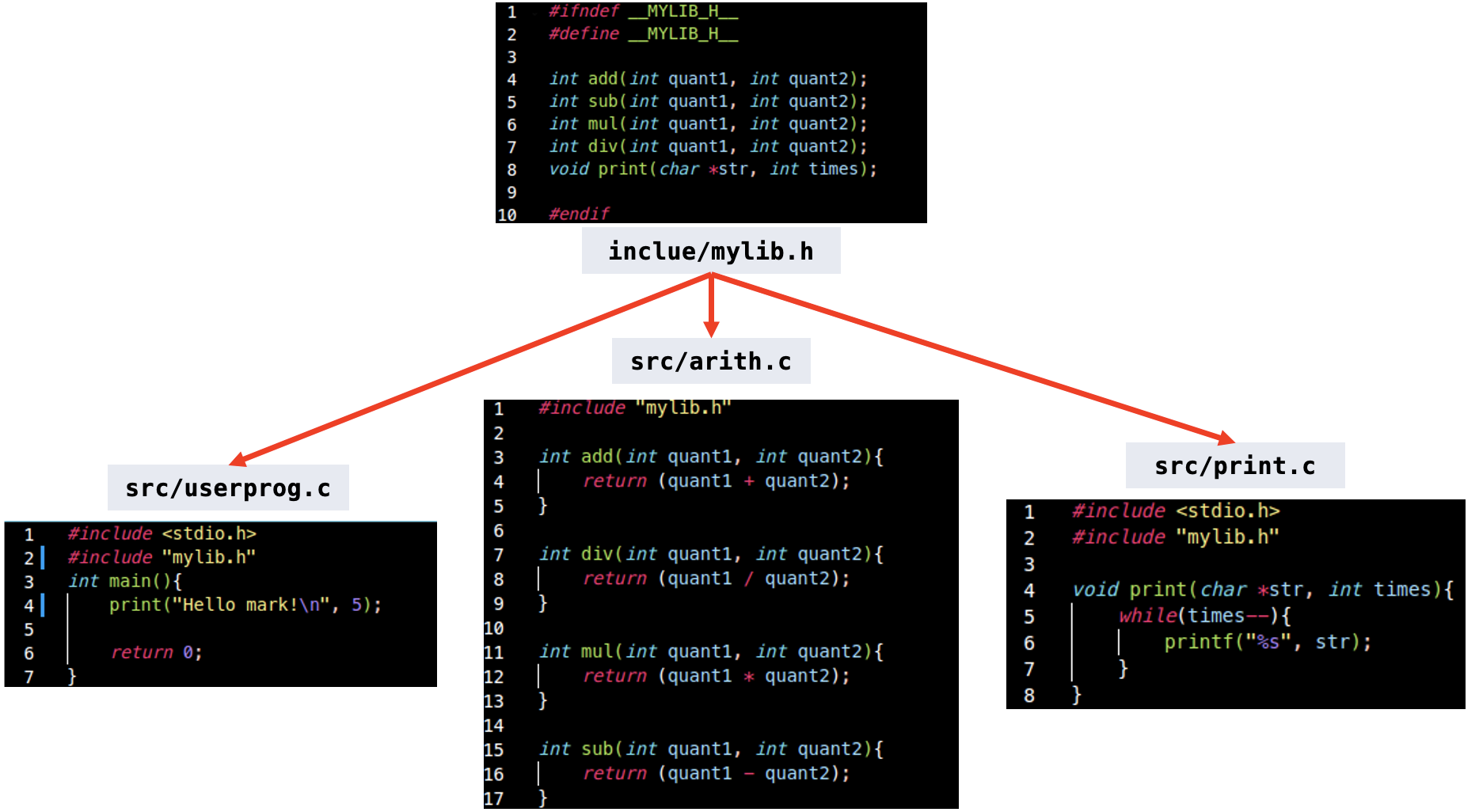
- 위치
$ gcc [options] [src] -o [output_file]gcc -Iinclude src/userprog.c- 쌩뚱맞게 바로
src/userprog.c를 바이너리로 만들면collect2링커가print심볼을 찾지 못해 에러
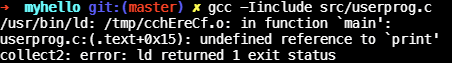
-I옵션은 include할 파일의 위치를 지정한다.-I<header file path>
- object파일 부터 만들어보자.
$ gcc -c -Iinclude src/userprog.c -o obj/userprog.o- userprog.o object 파일이 생성된다.
readelf -s userprog.o로 symbol을 보자
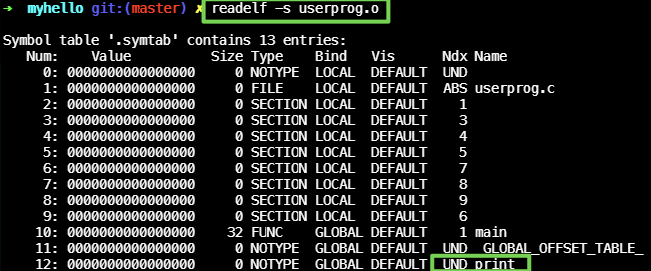
2-1.userprog.o내에print심볼 을 찾는다.
2-2. 링커가 최종적으로 바이너리를 만들 때,print심볼을 찾을 것이다.
2-3.print심볼은src/print.c에print함수이다. 이에 대한 object를 만들어야한다.
- 헤더 파일내 선언되어 있는 함수들 부터 먼저 object 파일로 만들기
$ gcc -c -Iinclude src/print.c -o obj/print.o
$ gcc -c -Iinclude src/arith.c -o obj/arith.o선택의 기로...
1. print.o, arith.o가 심볼로 사용되긴 하는데 다른 프로그램(userprog.c)에 하나의 바이너리로 '합쳐서' 만들 것인가?
2. print.o arith.o를 심볼로 사용하긴 하는데, 라이브러리 로 만들어 다른 프로그램(userprog.c)에서 가져와 사용하게 할 것인가?
-> 여기서 obj를 하나의 라이브러리로 만들어 다른 프로그램에서 가져와서 사용케 할 수 있다.
= 라이브러리
static library: .a
- .a 파일로 static library 생성
- 그냥 위 처럼 object file 모음
- 컴파일에서 링킹 단계에서 링크되어 프로그램 binary에 같이 적재된다.
- 장점: binary에 같이 적재되기에, 속도 빠르다.
- 단점: binary 사이즈가 커지고, 라이브러리만 수정하려면 binary의 src를 다시 빌드해야한다.
파일 형식 및 사용 예
- 라이브러리 이름 형식
lib[라이브러리_이름].a
- 응용 프로그램에서 사용
- 라이브러리 이름:
OpenCL, 라이브러리 파일 명:libOpenCL.a gcc-L'libOpenCL.a 위치'userprog.c-lOpenCL-o userprog
- 라이브러리 이름:
$ gcc -Linclude userprog.c -lOpenCL -o userprogstatic libaray 명령: ar
ar [option] | description | examples |
|---|---|---|
r | 아카이브에 새로운 오브젝트 추가 오래된 오브젝트는 새 오브젝트로 교체 | ar r [lib] [object] |
c | 아카이브가 존재하지 않으면 생성 | ar rcs [lib] [object] |
t | 아카이브에 있는 파일 리스트 출력 | ar t [library] |
x | 아카이브에서 오브젝트 파일 추출 | ar x [library] |
s | 아카이브에 오브젝트파일 idx 넣기이 index는 library에서 lookup-symbol로 컴파일러에서 사용됨 | ar rcs [lib] [object] |
static library 생성
- 재료
- object file
- 생성 커맨드
$ ar rcs <library name> <src1.o> [src2.o ...]
e.g.
$ ar rcs libmyhello.a arith.o print.o
-static 으로 컴파일 시, 모든 라이브러리를 static으로
- 간단한 C 프로그램을 만들어보자.
# ====== sample_native.c ====== #
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
printf("hello world!\n");
return 0;
}$ gcc sample_native.c -o sample_native
- 이 간단한 프로그램은 기본적으로 libc.so(shared library)를 사용한다.

- 또한 정적/동적 링커(
ld-linux-*.so)를 사용한다.

- 현재 바이너리의 크기는
17KB

-static으로 빌드하여, 전부 static으로 링크해보자.
$ gcc -static sample_native.c -o sample_native 크기가
크기가 852KB로 늘었다.- 이는
libc.so에서libc.a로 대체되어 함께 빌드되었기 때문이다.- static library인
libc.a는/usr/lib - shared library인
libc.so는/lib
- static library인
shared library: .so
Dependent library
- .so 파일로 shared library 생성
- 위 처럼 object file 모음
- 컴파일에서 링크 정보만 걸어두고 프로그램 binary 에는 적재하지 않고 바이너리만 컴파일
- 프로그램과 따로 존재해, 프로그램이 시작할 때 dynamic linking 되어 적재
- 프로그램이 시작할 때 매번 찾아 메모리에 올리면 늦기 때문에
/etc/ld.so.conf를 관리
파일 형식 및 사용 예
- 라이브러리 이름 형식
lib[라이브러리_이름].so
- 응용 프로그램에서 사용
- 라이브러리 이름:
OpenCL, 라이브러리 파일 명:libOpenCL.so gcc-L'libOpenCL.a 위치'userprog.c-lOpenCL-o userprog
- 라이브러리 이름:
$ gcc -Linclude userprog.c -lOpenCL -o userprogdependent library 생성
- 재료
- object file
- object file 생성 (with
-fPIC):.c->.o
주의!! object file 부터 옵션을 따로 넣어주면서 생성해야함
$ gcc -fPIC -c print.c # print.o 생성
$ gcc -fPIC -c arith.c # arith.o 생성
-fPIC: Position Independent Code로 compile
- shared library(dependent library) 생성:
.o-> .so
$ gcc -shared -Wl,-soname,<SONAME> -o <Create lib Name> <src1.o> [src2.o ...]
e.g.
$ gcc -shared -Wl,-soname,libmyhello.so.1 -o libmyhello.so.1.0 print.o arith.o
| CFLAGS | description |
|---|---|
-shared | compiler에게 executable한 object에게 link를 걸어 줄 수 있는 shared library를 만든다고 set 하는 flag |
| LDFLAGS | description |
|---|---|
-Wl,[options] | -Wl,은 링커(collect2)에게 gcc 거치지 않고 바로 전해주는 옵션. 뒤에 [options]에 링크 옵션을 넣어준다. |
-Wl,-soname,lib[name].so.1 | 생성하려는 shared library의 soname을 뒤에 지어준다. soname에는 major 버전만 명시 |
shared library 이름 규칙
- libmyhello.so.
major.minor.release no- e.g., : libjpeg.so.8.0.2
- 라이브러리 이름:
jpeg - 메이저 번호: 8
- 마이너 번호: 0
- 배포 번호: 2
- 라이브러리 이름:
- e.g., : libjpeg.so.8.0.2
- libexample.so.1.2 라는 shared library 가 있다고 가정.
| Naming Convention | e.g. | Description | 필요할 때 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (static link) | libexample.a | 정적 링크 | 빌드시 호스트 그래서 호스트에 있음, 그래도 sysroot 내 파일 링크 |
| Linker name | libexample.so | 링커가 '-lexample' 과 같이 링킹할 때 사용되는 이름libexample.so -> libexample.so.1 소프트링크 | 빌드시 호스트 그래서 호스트에 있음, 그래도 아래 Soname file을 symlink함 (결국 Target 용 바이너리 파일 링크) |
| Soname | libexample.so.1 | 모든 shared library 가 가지고 있는 soname 'libexample.so.1' 처럼 major 버전 명시 libexample.so.1 -> libexample.so.1.2 소프트링크 | 실행 시 타겟 그래서 sysroot/ 에 있음 |
| Real Name | libexample.so.1.2 | 실제 shared library 파일. 내부에 soname을 갖고 있음 | 실행 시 타겟 그래서 sysroot/에 있음 |

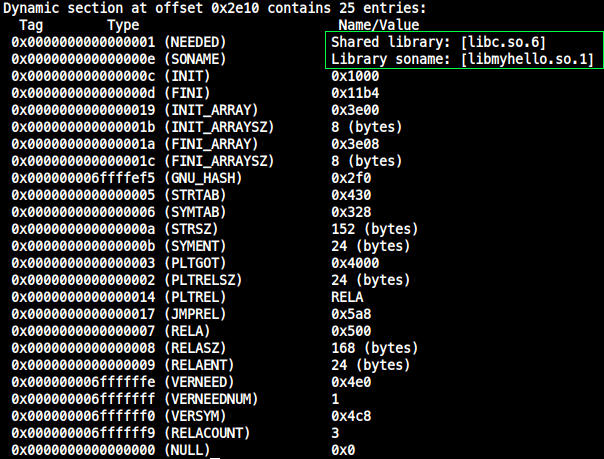
$ readelf -d: soname, rpath 찾기
$ readelf -d <library>- soname 찾기
- rpath 찾기
$ readelf -d userprog | grep RPATH
0x000000000000000f (RPATH) Library rpath: [/library/path]- 이 프로그램이 어떤 라이브러리와 링크됬는지 확인
$ arm-gnueabi-readelf -a <shared_library> | grep "Shared library"
- shared libary의 런타임 링커 알기
$ arm-gnueabi-readelf -a <shared_library> | grep "program interpreter"dependent library 활용
main program build 시, 위에서 생성한 shared library 링크해서 빌드
$ gcc -L<library Path> main.c -l<library> -o main-L로 shared library 위치를 알려주어 Compile (LDFLAGS)-l로 shared library link (LDLIBS)
컴파일 되어도, shared library는 프로그램 실행 시 dynamic으로 링크 되기 때문에,
링커가 shared library 위치를 못찾을 수 있음!!
실행 시, 위치
- shared library는 compile 때는
-L<path>를 지정 했기 때문에 알아먹었지만, 실행 시는 동적으로 찾음
그래서 다음과 같이 shared library 관리함
0. 기본적으로 /lib, /usr/lib, /usr/local/lib는 보고 있음
1. 환경 변수 $LD_LIBRARY_PATH에 등록
2. /etc/ld.so.conf, /etc/ld.so.conf.d/libexample.conf, /etc/ld.so.cache
3. 애초에 컴파일 시, -Wl,-rpath,[path] 등록
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH
- export LD_LIBRARY_PATH 환경 변수 지정
$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$HOME/somewhere:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH"/etc/ld.so.conf
- /etc/ld.so.conf 에 shared libary위치 작성
2-1. /etc/ld.so.conf에 직접 위치 작성 (비추천)
최근에는 ld.so.conf 파일에 아래와 같은 문구 만 있음
include /etc/ld.so.conf.d/*.conf즉, /etc/ld.so.conf.d/에 있는 내용을 include함
2-2. /etc/ld.so.conf.d/libexample.conf 파일 작성
# libexample.conf
/some/where/library/path작성 후, /etc/ld.so.cache 를 갱신 하는 명령인 ldconfig 실행
$ ldconfig컴파일 시 링커 옵션 -rpath 사용
$ gcc -L<library/path> -Wl,-rpath,/library/path userprog.c -l<library> -o userprog
$ readelf -d userprog | grep RPATH
0x000000000000000f (RPATH) Library rpath: [/library/path]의존성 체크: ldd
ldd: 응용 프로그램의 의존성을 체크한다.
$ ldd [binary]Dynamic Library: .so
- .so 파일로 shared library 생성으로 dependent library 와 같음
- 그냥 코드와 옵션등이 조금 다름
- 다음의 함수, 헤더를 사용해야함
#include <dlfcn.h>
void *dlopen(const char *filename, int flag);
const char *dlerror(void);
void *dlsym(void *handle, char *symbol);
int dlclose(void *handle);
dlopen()
#include <dlfcn.h>
void *dlopen(const char *filename, int flag);- 기능: dynamic library를 적재하기 위해 사용
| parameter | Description |
|---|---|
*filename | 적재하기 원하는 라이브러리 이름 e.g.: /usr/my/lib/libmyhello.so만약 적재시킬 라이브러리의 이름이 절대경로로 지정되어 있지 않으면, 1. $LD_LIBRARY_PATH에 등록된 디렉터리에 있는지 찾음 2. /etc/ld.so.cache에서 찾음 |
flag | <RTLD_LAZY | RTLD_NOW>1. RTLD_LAZY: 라이브러리의 코드가 실행 시간에 정의되지 않은 심볼을 해결2. RTLD_NOW: dlopen이 실행이 끝나기 전, 라이브러리에 정의되지 않은 심볼 해결 |
| return | Description |
|---|---|
| void | - |
dlerror()
#include <dlfcn.h>
const char *dlerror(void);- 기능:
dleooro(), dlsym(), dlclose(), dlopen()함수 중 마지막 호출된 함수의 에러 메시지를 돌려준다.
dlsym()
#include <dlfcn.h>
void *dlsym(void *handle, char *symbol);- 기능:
dlopen()을 통해 열린 라이브러리를 사용할 수 있도록 심볼 값을 찾아준다.
심볼은 열린 라이브러리에서 실제 호출할 함수 이름
| parameter | Description |
|---|---|
*handle | dlopen()에 의해 반환된 값 |
*symbol | 열린 라이브러리에서 실제로 호출할 함수 이름 |
| return | Description |
|---|---|
| 성공 | dlopen()으로 열린 라이브러리의 호출함수 가리키는 포인터void* 형 인데, 호출함수가 리턴하는 형을 직접 명시하면, 유지보수가 훨씬 수월하다. |
| 실패 | NULL |
elf 체크해보기
import subprocess
# Return type (bits):
# 0 - not elf
# 1 - ELF
# 2 - stripped
# 4 - executable
# 8 - shared library
# 16 - kernel module
def is_elf(path):
exec_type = 0
result = subprocess.check_output(["file", "-b", path], stderr=subprocess.STDOUT).decode("utf-8")
if "ELF" in result:
exec_type |= 1
if "not stripped" not in result:
exec_type |= 2
if "executable" in result:
exec_type |= 4
if "shared" in result:
exec_type |= 8
if "relocatable" in result:
if path.endswith(".ko") and path.find("/lib/modules/") != -1 and is_kernel_module(path):
exec_type |= 16
return (path, exec_type)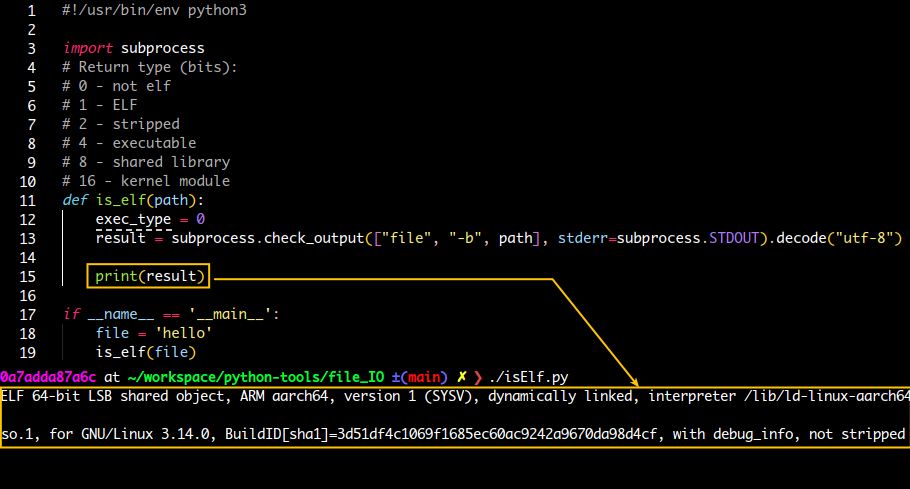
readelf로 어떤 라이브러리 링크?
Shared Library 알아내기
readelf를 사용하여 프로그램이 어떤 라이브러리와 링크되었는지 알 수 있다.
- arm용 툴체인으로 빌드된 바이너리는 arm-readelf를 사용해야한다.
- 이전 글(https://velog.io/@markyang92/toolchain)에서 arm 툴체인을 설치했었다.
$ arm-cortex_a8-linux-gnueabihf-readelf -a <binary> | grep "Shared library"- 예

런타임 링커 알아내기
- 공유 라이브러리는 런타임 링커가 필요한데 다음 명령으로 알아낼 수 있다.
$ arm-cortex_a8-linux-gnueabihf-readelf -a <binary> | grep "program interpreter"Embedded System에서 라이브러리
- 정적링크
1.1. BusyBox와 약간의 스크립트 파일만으로 구성된 작은 시스템을 만든다면, BusyBox를 정적으로 링크해서 런타임 라이브러리 파일과 링커를 복사할 필요가 없는 편이 더 간단하다.
1.2. 전체 C 라이브러리를 제공하기 보다는 응용 프로그램이 사용하는 코드만 링크하기 때문에 크기도 더 작아질 것이다.
1.3. 정적 링크는 또한 런타임 라이브러리를 담을 파일 시스템이 준비되기 전에 프로그램을 실행해야 할 때 유용하다.
-static을 이용해 빌드 하면 모든 라이브러리를 정적으로 빌드한다.
2.1. 이전글(https://velog.io/@markyang92/toolchain#sysroot)의 sysroot 구조에서 보았드시,
static libary:sysroot/usr/lib
shared library:sysroot/lib
에 존재한다.
- 비글본 블랙용 sample.c 파일을 만들고 크로스 컴파일한다.
# ===== sample.c ===== #
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
printf("hello world!\n");
return 0;
}$ arm-cortex_a8-linux-gnueabihf-gcc sample.c -o sample$ arm-cortex_a8-linux-gnueabihf-readelf -a ./sample | grep "Shared library"$ arm-cortex_a8-linux-gnueabihf-readelf -a ./sample | grep "interpreter"- 정적 링크로 빌드해보자.
4.1. 당연히 현재 빌드 시스템이sysroot의 정적 링크할 라이브러리가 어디있는지 알아야한다.
static libary:sysroot/usr/lib->libc.a
shared library:sysroot/lib->libc.so.6
4.2.arm-gcc -print-sysroot를 사용해 빌드한다.
$ export SYSROOT=$(arm-cortex_a8-linux-gnueabihf-gcc -print-sysroot)
$ arm-cortex_a8-linux-gnueabihf-gcc -static ./sample.c -o sample라이브러리 위치
| Naming Convention | e.g. | Description | 필요할 때 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (static link) | libexample.a | 정적 링크 | 빌드시 호스트 그래서 호스트에 있음, 그래도 sysroot 내 파일 링크 |
| Linker name | libexample.so | 링커가 '-lexample' 과 같이 링킹할 때 사용되는 이름libexample.so -> libexample.so.1 소프트링크 | 빌드시 호스트 그래서 호스트에 있음, 그래도 아래 Soname file을 symlink함 (결국 Target 용 바이너리 파일 링크) |
| Soname | libexample.so.1 | 모든 shared library 가 가지고 있는 soname 'libexample.so.1' 처럼 major 버전 명시 libexample.so.1 -> libexample.so.1.2 소프트링크 | 실행 시 타겟 그래서 sysroot/ 에 있음 |
| Real Name | libexample.so.1.2 | 실제 shared library 파일. 내부에 soname을 갖고 있음 | 실행 시 타겟 그래서 sysroot/에 있음 |
strip을 사용해 디버그 심볼 제거
- 라이브러리와 프로그램은 디버깅과 추적을 돕기 위해, 심볼 테이블에 저장된 약간의 정보를 포함한 채로 컴파일한다.
양산 시스템에서는 거의 필요치 않다.
바이너리에서 심볼 테이블을 Strip해보자.
- 실험대상 hello

- objcopy --only-keep-debug 로 dbg심볼만 가진 hello.dbg 생성
$ objcopy --only-keep-debug ./hello ./hello.dbg (hello에서 keep debug 심볼만 가진 hello.dbg 파일 생성)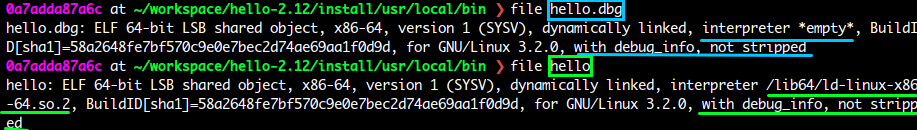
3. objcopy --add-gnu-debuglink 로 debug링크를 원본 hello 〈----〉 hello.dbg 연결
$ objcopy --add-gnu-debuglink ./hello.dbg ./hello- strip --remove-section=.comment --remove-section=-.note 〈file〉
strip --remove-section=.comment --remove-section=.note ./hello
./hello: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, \
version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, \
BuildID[sha1]=58a2648fe7bf570c9e0e7bec2d74ae69aa1f0d9d, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, stripped- objdump -x〈file〉
./hello: file format elf64-x86-64
./hello
architecture: i386:x86-64, flags 0x00000150:
HAS_SYMS, DYNAMIC, D_PAGED
start address 0x00000000000027e0
Program Header:
PHDR off 0x0000000000000040 vaddr 0x0000000000000040 paddr 0x0000000000000040 align 2**3
filesz 0x0000000000000268 memsz 0x0000000000000268 flags r--
INTERP off 0x00000000000002a8 vaddr 0x00000000000002a8 paddr 0x00000000000002a8 align 2**0
filesz 0x000000000000001c memsz 0x000000000000001c flags r--
LOAD off 0x0000000000000000 vaddr 0x0000000000000000 paddr 0x0000000000000000 align 2**12
filesz 0x0000000000001540 memsz 0x0000000000001540 flags r--
LOAD off 0x0000000000002000 vaddr 0x0000000000002000 paddr 0x0000000000002000 align 2**12
filesz 0x0000000000006c71 memsz 0x0000000000006c71 flags r-x
LOAD off 0x0000000000009000 vaddr 0x0000000000009000 paddr 0x0000000000009000 align 2**12
filesz 0x00000000000022e8 memsz 0x00000000000022e8 flags r--
LOAD off 0x000000000000bb10 vaddr 0x000000000000cb10 paddr 0x000000000000cb10 align 2**12
filesz 0x0000000000000570 memsz 0x0000000000000728 flags rw-
DYNAMIC off 0x000000000000bc18 vaddr 0x000000000000cc18 paddr 0x000000000000cc18 align 2**3
filesz 0x00000000000001f0 memsz 0x00000000000001f0 flags rw-
NOTE off 0x00000000000002c4 vaddr 0x00000000000002c4 paddr 0x00000000000002c4 align 2**2
filesz 0x0000000000000044 memsz 0x0000000000000044 flags r--
EH_FRAME off 0x0000000000009ed4 vaddr 0x0000000000009ed4 paddr 0x0000000000009ed4 align 2**2
filesz 0x000000000000034c memsz 0x000000000000034c flags r--
STACK off 0x0000000000000000 vaddr 0x0000000000000000 paddr 0x0000000000000000 align 2**4
filesz 0x0000000000000000 memsz 0x0000000000000000 flags rw-
RELRO off 0x000000000000bb10 vaddr 0x000000000000cb10 paddr 0x000000000000cb10 align 2**0
filesz 0x00000000000004f0 memsz 0x00000000000004f0 flags r--
Dynamic Section:
NEEDED libc.so.6
INIT 0x0000000000002000
FINI 0x0000000000008c64
INIT_ARRAY 0x000000000000cb10
INIT_ARRAYSZ 0x0000000000000008
FINI_ARRAY 0x000000000000cb18
FINI_ARRAYSZ 0x0000000000000008
GNU_HASH 0x0000000000000308
STRTAB 0x0000000000000998
SYMTAB 0x0000000000000350
STRSZ 0x00000000000002f7
SYMENT 0x0000000000000018
DEBUG 0x0000000000000000
PLTGOT 0x000000000000ce08
PLTRELSZ 0x00000000000004f8
PLTREL 0x0000000000000007
JMPREL 0x0000000000001048
RELA 0x0000000000000d78
RELASZ 0x00000000000002d0
RELAENT 0x0000000000000018
FLAGS 0x0000000000000008
FLAGS_1 0x0000000008000001
VERNEED 0x0000000000000d18
VERNEEDNUM 0x0000000000000001
VERSYM 0x0000000000000c90
RELACOUNT 0x0000000000000013
Version References:
required from libc.so.6:
0x0d696913 0x00 06 GLIBC_2.3
0x09691974 0x00 05 GLIBC_2.3.4
0x06969194 0x00 04 GLIBC_2.14
0x0d696914 0x00 03 GLIBC_2.4
0x09691a75 0x00 02 GLIBC_2.2.5
Sections:
Idx Name Size VMA LMA File off Algn
0 .interp 0000001c 00000000000002a8 00000000000002a8 000002a8 2**0
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
1 .note.gnu.build-id 00000024 00000000000002c4 00000000000002c4 000002c4 2**2
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
2 .note.ABI-tag 00000020 00000000000002e8 00000000000002e8 000002e8 2**2
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
3 .gnu.hash 00000048 0000000000000308 0000000000000308 00000308 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
4 .dynsym 00000648 0000000000000350 0000000000000350 00000350 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
5 .dynstr 000002f7 0000000000000998 0000000000000998 00000998 2**0
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
6 .gnu.version 00000086 0000000000000c90 0000000000000c90 00000c90 2**1
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
7 .gnu.version_r 00000060 0000000000000d18 0000000000000d18 00000d18 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
8 .rela.dyn 000002d0 0000000000000d78 0000000000000d78 00000d78 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
9 .rela.plt 000004f8 0000000000001048 0000000000001048 00001048 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
10 .init 0000001b 0000000000002000 0000000000002000 00002000 2**2
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, CODE
11 .plt 00000360 0000000000002020 0000000000002020 00002020 2**4
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, CODE
12 .plt.got 00000008 0000000000002380 0000000000002380 00002380 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, CODE
13 .text 000068d2 0000000000002390 0000000000002390 00002390 2**4
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, CODE
14 .fini 0000000d 0000000000008c64 0000000000008c64 00008c64 2**2
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, CODE
15 .rodata 00000ed3 0000000000009000 0000000000009000 00009000 2**5
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
16 .eh_frame_hdr 0000034c 0000000000009ed4 0000000000009ed4 00009ed4 2**2
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
17 .eh_frame 000010c8 000000000000a220 000000000000a220 0000a220 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, DATA
18 .init_array 00000008 000000000000cb10 000000000000cb10 0000bb10 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA
19 .fini_array 00000008 000000000000cb18 000000000000cb18 0000bb18 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA
20 .data.rel.ro 000000f8 000000000000cb20 000000000000cb20 0000bb20 2**5
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA
21 .dynamic 000001f0 000000000000cc18 000000000000cc18 0000bc18 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA
22 .got 000001e8 000000000000ce08 000000000000ce08 0000be08 2**3
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA
23 .data 00000080 000000000000d000 000000000000d000 0000c000 2**5
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, DATA
24 .bss 000001b8 000000000000d080 000000000000d080 0000c080 2**5
ALLOC
SYMBOL TABLE:
no symbols
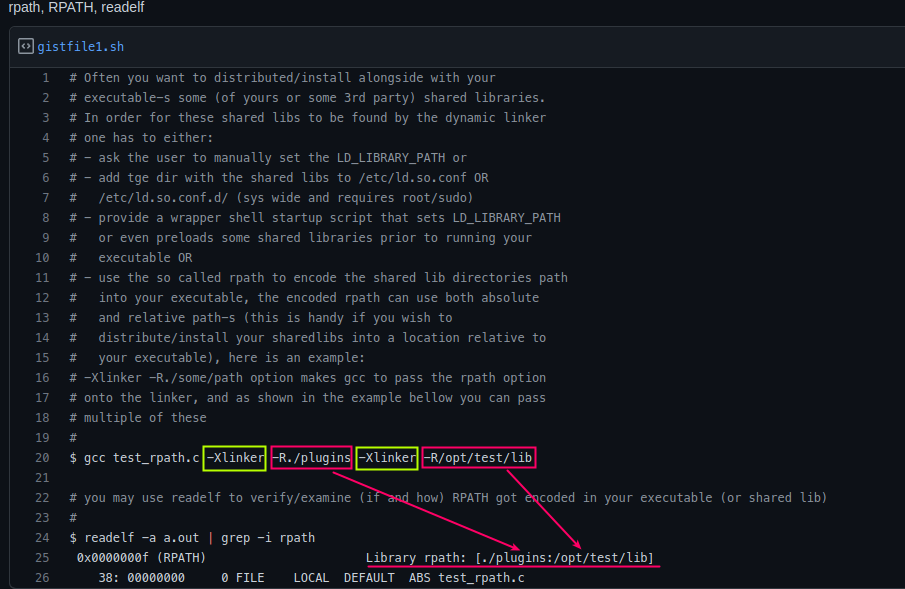
-rpath
- rpath: runtime search path hard-coded in an executable file or library.
- it encodes a path to shared libraries into the header of an executable(or another shlib). This RPATH header value (so named in the ELF header standards) may either override or supplement the system default dynamic linking search paths.
- the rpath of an executable or shlibs is an optional entry inthe
.dynamicSection of the ELF executable or shlibs, with the typeDT_RPATH, called theDT_RPATHattribute. it can be sorted there at link time by the linker. tools suchaschrpathandpatchelf - GNU/ld.so
- The dynamic linker of the GNU C Lib searches for shlibs in the following location in order.
- The (colon-separated)paths in the
DT_RPATHdynamic section attribute of the binary if present and theDT_RUNPATHattibute does not exists. - The (colon-separated) path in the environment variable
LD_LIBRARY_PATH, unless the executable is asetuid/setgidbinary, in which case it ignored.LD_LIBRARY_PATHcan be overridden by calling the dynamic linker with the option--library-path(e.g.,/lib/ld-linux.so.2 --library-path $HOME/mylibs myprogram) - The (colon-separated) paths in the
DT_RUNPATHdynamic section attribute of the binary if present. - Lookup based onthe
ldconfigcache file (often located at/etd/ld.so.cache) which contains a compiled list of candidate libraries previously found in the augmented library path (set by/etd/ld.so.conf). if, however, the binary was linked with the-z nodefaultliblinker option, libraries in the default library paths are skipped. - In the trusted default path
/lib, and then/usr/lib. if the binary was linked with the-z nodefaultliblinker option, this step is skipped. - Failing to find the shared library in all these locations will raise the "cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory" error.
- The (colon-separated)paths in the
- The dynamic linker of the GNU C Lib searches for shlibs in the following location in order.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rpath 참고
.so를 사용하기 위해서는 명시적으로 dlopen을 이용 혹은 해당 라이브러리의 이름만 링크되어 있는 라이브러리들을 이용해서 실제 자동적으로 실행시에 해당 .so가 로드되도록 하는 방법
.so를 사용하기 위해서 경로 지정에 보통 두가지 방법 사용
1. /etc/ld.so.conf 수정해 /sbin/ldconfig를 이용해 전역적으로 지정하는 방법
2. LD_LIBRARY_PATH를 셋팅해 해당 유저만 사용
자 근데 위에 2가지 방법 모두 문제가 있다. 사용자가 .so의 위치를 어떻게든 지정해야한다.
이는 배포 시 생각보다 큰 문제이다.
-rpath는 프로그램이 빌드될 때, 자동적으로 .so의 위치를 부여 (절대/상대 경로 이용가능)
-rpath .so 경로 -Wl- 이렇게하면 지정된 경로에서 바로
.so파일을 찾는다.