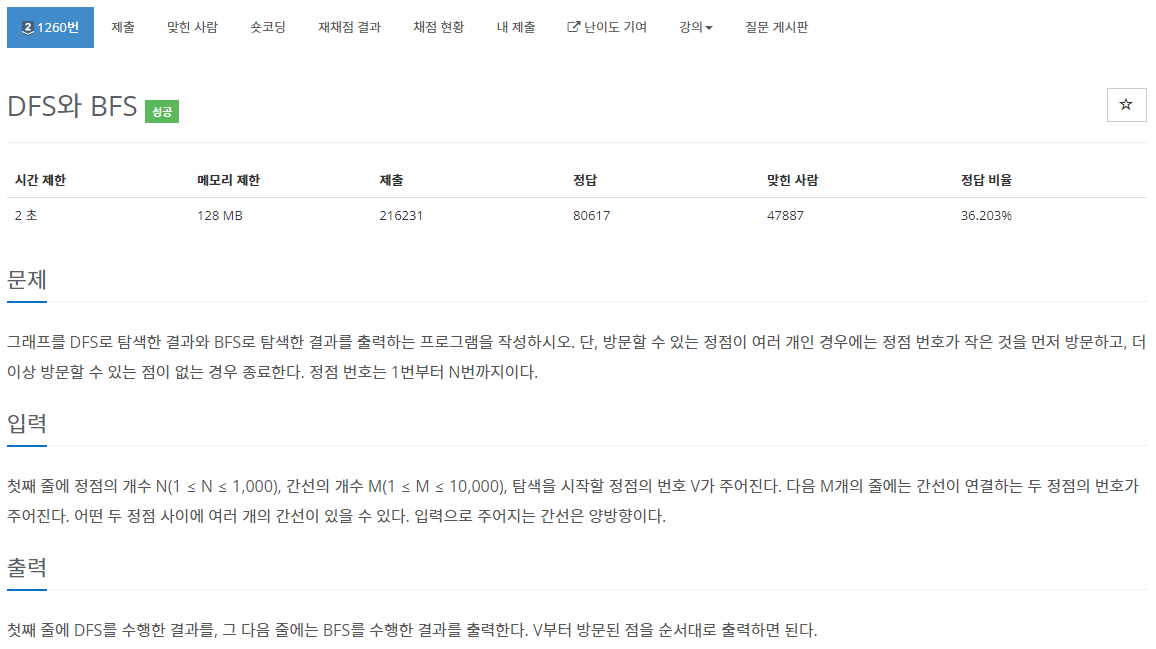
💡 문제
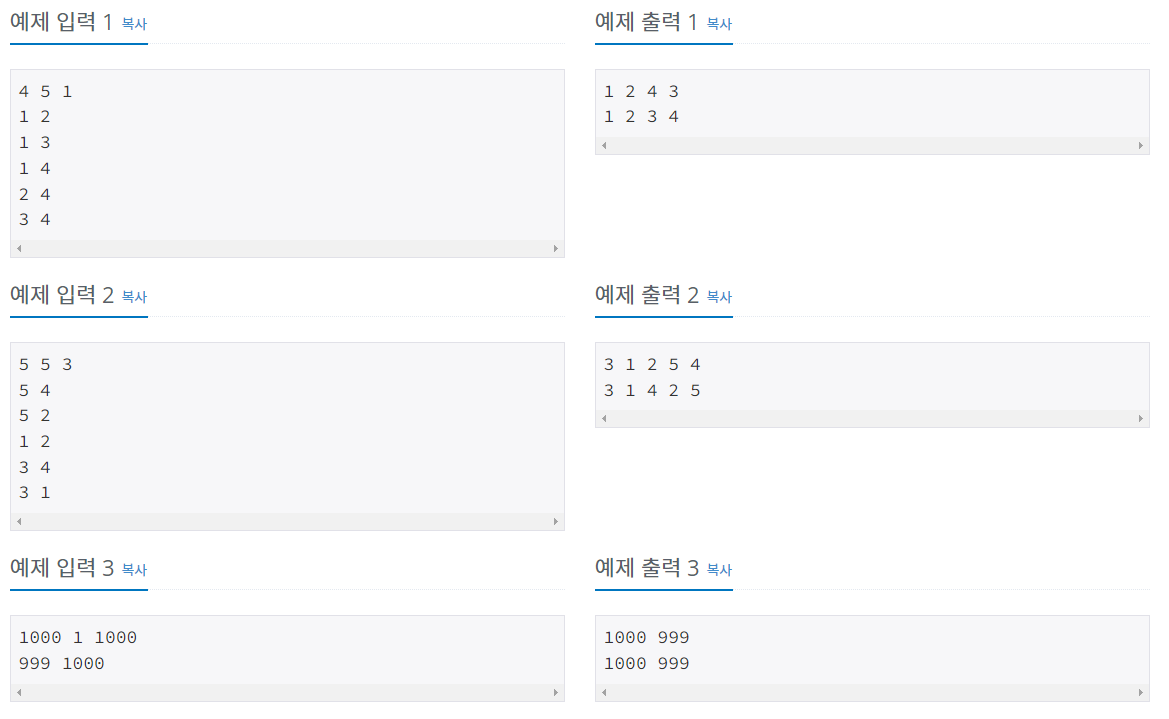
💬 입출력 예시
📌 풀이(소스코드)
import static java.util.Collections.sort;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int n, m, v;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph;
static boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
v = sc.nextInt();
graph = new ArrayList<>();
visited = new boolean[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
graph.get(a).add(b);
graph.get(b).add(a);
}
for (ArrayList<Integer> list: graph) {
sort(list);
}
dfs(v);
System.out.println();
visited = new boolean[n+1];
bfs(v);
}
static void dfs(int x) {
visited[x] = true;
System.out.print(x + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(x).size(); i++) {
int y = graph.get(x).get(i);
if (!visited[y]) dfs(y);
}
}
static void bfs(int start) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(start);
visited[start] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int x = q.poll();
System.out.print(x + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(x).size(); i++) {
int y = graph.get(x).get(i);
if (!visited[y]) {
q.offer(y);
visited[y] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
📄 해설
- DFS, BFS 알고리즘을 사용하여 해결하는 문제, 정점 번호가 작은 것을 먼저 방문하기 위해 리스트를 정렬해준 뒤 진행
- DFS, BFS 알고리즘에 대한 자세한 설명은 [작성자의 글] 에 정리되어있음



