1. font
css에서 font를 꾸며주는 데에는 굉장히 많은 속성이 있다.
그중 몇가지 주로 사용되는 것만 작성해보겠다.
font-size
말 그대로 해당 폰트의 크기를 결정해주는 속성이다.
line-height
줄의 높이를 정해주는 속성이다.
단위(px,rem)으로 사용할 수 있고 실수를 통해 사용할 수도 있다.
p.normal{
font-size:15px;
color:red;
line-height: normal;
}
p.lineheight1{
font-size:15px;
color:blue;
line-height: 20px;
}
p.lineheight2{
font-size:30px;
color:black;
line-height:4;
}
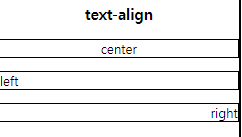
text-align
text-align 속성으로 문자의 좌우/가운데정렬이 가능하다.
p.center{
text-align: center;
}
p.left{
text-align: left;
}
p.right{
text-align: right;
}
letter-spacing / word-spacing
letter-spacing은 글자 간 간격을 설정해주고, word-spacing은 단어 사이의 간격을 설정해준다.
p.letter{
letter-spacing: 20px;
/* 글자 간 간격 */
}
p.word{
word-spacing: -10px;
/* 단어 사이의 간격 */
}
text-transform : upper/lower case
text-transform을 uppercase로 설정 해주면 무조건 대문자만 입력이 가능하다. 반대로 lowercase는 소문자만 출력 해준다.
input.upper{
text-transform: uppercase;
}
input.lower{
text-transform: lowercase;
}
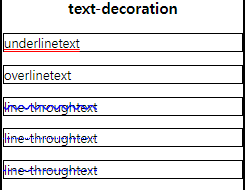
text-decoration
text-decoration으로 글자에 선을 긋는 등의 꾸며주기가 가능하다.
여러 속성을 통해 글자 꾸며주기 가능.
p.underline{
text-decoration: underline double red;
}
p.overline{
text-decoration: overline;
}
p.linethrough1{
text-decoration: line-through wavy blue;
}
p.linethrough2{
text-decoration: line-through dotted blue;
}
p.linethrough3{
text-decoration: line-through dashed blue;
}
2.selector(선택자)
선택자를 통해 특정 요소를 스타일링 할 수 있다.
tag[attr]
attr속성만 가진 태그를 가리킨다.
.property input[alt]{
color:red;
}tag[attr=value]
해당 속성의 값이 value인 태그만 가르킨다.
.property input[type=text]{
text-decoration:line-through;
}tag[attr^=value]
해당 속성의 값이 value 시작하는 태그
.property input[alt^=start]{
color:blue;
}tag[attr$=value]
해당 속성의 값이 value로 끝나는 태그
.property input[alt$=end]{
color:aqua;
}tag[attr*=value]
value값을 가지고 있는 태그
.property input[alt*=all]{
color:brown;
}tag:first-child,tag:last-child,tag:nth-child(n)
부모 기준 첫번째,마지막 자식 태그,n번째 태그 반환
tag:first-of-type,tag:last-of-type,tag:nth-of-type(n)
전체 코드내의 타입들 중 첫번째,마지막,n번째 요소
tag:link
아직 선택되지 않은 링크
tag:active
마우스를 꾹 누를때 선택
tag:[type="radio"]:checked
라디오 버튼류가 checked될 때 선택
tag:hover
마우스를 올려놨을 때 선택
tag:before{content:""}
해당 태그의 앞쪽에 가상요소 content를 삽입한다.
tag:after{content:""}
해당 태그의 뒤쪽에 가상요소 content를 삽입한다.
tag1~tag2
tag1과 tag2는 동일한 부모와 동일한 레벨상에 있고 코드상 tag1이 tag2 위에 있다.
위 조건에서 tag2를 선택한다.
tag1+tag2
tag1에 바로 인접한 tag2를 선택한다.
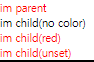
상속
initial : 부모의 속성을 받고싶지 않을때 사용
inherit : 부모에게 무조건 상속받아야 함
unset :
ㄴ 1. 부모로부터 상속받을 값이 있을 때 : inherit
ㄴ 2. 부모로부터 상속받을 값이 없을 때 : initial
.inheritance .parent{
color:red;
}
.inheritance .child:first-of-type{
color:initial;
}
.inheritance .child:nth-child(2){
color:inherit;
}
.inheritance .child:nth-child(3){
color:unset;
}
Layout
layout 속성은 요소의 위치를 결정해주는 속성이다.
float:left
해당 요소가 왼쪽에 둥둥 떠있다는 느낌으로 생각하면 된다. right도 마찬가지.
.layout .image{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background-color: hotpink;
float:left;
/* 이 영역은 왼쪽에 둥둥 떠있다는 느낌으로 생각하면 된다. */
margin:10px;
}
.layout p{
border:initial;
}
float를 끊기 위해서는
.firstsection::after{ content:''; display:block; clear:both; }이렇게 after를 취한뒤 해당 속성을 사용해주면 된다.
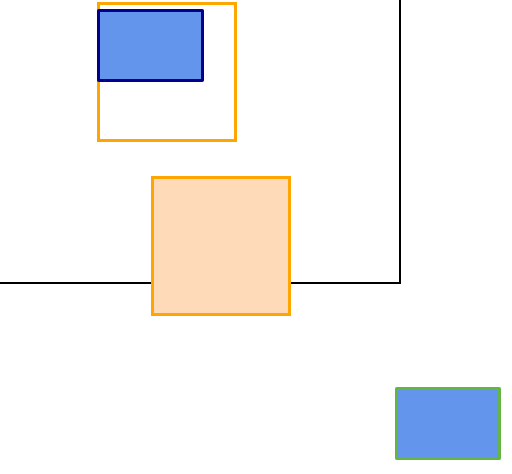
position:static,relative,absoulte,fixed
static : 기본값(normal flow)이므로 top/bottom/left/right 옵션을 사용할 수 없다.
relative : 자기 자신을 기준으로 top/right/left/bottom값에 따라 오프셋 적용
absolute : 일반적인 문서 흐름에서 제거하고 레이아웃에 공간도 배정하지 않음,부모 중에서 position이 static이 아닌 요소를 찾아 기준점을 삼는다.
fixed : 뷰포트를 기준으로 동작한다. 스크롤을 해도 그자리에 그대로 있음,페이지 우측하단의 플로팅버튼을 구현할때 주로 쓰임
.layout .relative{
position:relative;
}
.layout .relative>div{
width:200px;
height:200px;
border : 5px solid orange;
margin-left:150px;
}
#box1{
background-color:peachpuff;
position:relative;
top:50px;
left:80px;
}
#box2{
width:150px;
height:100px;
border-color:darkblue;
background-color:cornflowerblue;
border-radius: 3px;
position:absolute;
top:10px;
}
#box3{
width:150px;
height:100px;
border-color:rgb(98, 182, 65);
background-color:cornflowerblue;
border-radius: 3px;
position:fixed;
bottom:40px;
right:40px;
}
flex
flex는 유연하게 동작하는 속성으로 부모 container에 display:flex를 설정해주고 시작한다.
.container1{
display:flex;
}flex는 주축인 main axis와 cross axis를 기반으로 두고 요소를 이동시킨다.
flex-direction
컨테이너 속성으로 주축의 방향을 설정할 수 있다.
row/row-reverse/column/column-reverse
flex-wrap
컨테이너 속성으로 요소들이 강제로 한 줄에 배치되도록 할 것인지, 여러 행으로 배치되도록 할 것인지 정해준다.
nowrap이 default이며 wrap은 분할되어 여러 행에 걸쳐서 배치하며, wrap-reverse는 역순으로 배치한다.
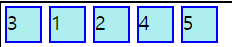
order
아이템 속성으로 해당 아이템의 정렬 순서를 정해준다. 낮을수록 앞에 배치된다.
.item1:nth-child(3){
order:-1;
}
flex-grow
컨테이너의 남은 공간을 item들이 가지게 된다.
.item2{
flex-grow:1;
}
.item2:nth-child(2){
flex-grow:3
}2번째 요소와 나머지 요소의 비율은 3:1

flex-basis
flex-grow에서 요소의 크기가 다를 경우의 너비차이를 잡아준다.
보통 basis를 0으로 두고 flex-grow를 통해 비율을 설정한다.
.item3{
width:initial;
flex-grow:1;
flex-basis:0;
}너비를 고정시키지 않으면 요소의 내용에 맞춰서 너비가 결정된다.
여기서 flex-grow를 사용하면 요소의 내용을 베이스로 flex-grow가 설정되는데
flex-basis를 0으로 초기화하면 전부 똑같아진다.


