자료 추상화
// 구체적인 Point 클래스
public class Point1 {
public double x;
public double y;
}
// 추상적인 Point 클래스
public class Point2 {
double getX();
double getY();
void setCartesian(double x, double y);
double getR();
double getTheta();
void setPolar(double r, double theta);
}- 변수를 Private으로 선언하더라도 각 값마다 조회(get)함수와 설정(set)함수를 제공한다면,
구현을 외부로 노출하는 셈이에요. - 구현을 감추려면
추상화가 필요해요. 조회 함수와 설정 함수로 변수를 다룬다고 클래스가 되는게 아니라, 추상 인터페이스를 제공해 사용자가 구현을 모른 채 자료의 핵심을 조작할 수 있어야 진정한 의미의 클래스예요.
💡 추상화와 캡슐화의 차이?
- 자료를 세세하게 공개하기 보다는 추상적인 개념으로 표현하는 편이 좋아요. 인터페이스나 조회/설정 함수만으로 추상화가 이뤄지는게 아니에요.
- 개발자는 객체가 포함하는 자료를 표현할 가장 좋은 방법을 고민해야 해요.
// 구체적인 Vehicle 클래스
public interface Vehicle {
double getFuelTankCapacityInGallons(); // 변수값을 읽어 반환할 뿐
double getGallonsOfGasoline();
}
// 추상적인 Vehicle 클래스
public interface Vehicle {
double getPercentFuelRemaining(); // 정보가 어디서 오는지 드러나지 않는다
}- 아무 생각없이 조회/설정 함수를 추가하는 방법이 가장 나빠요. → 그럼 Java에서 많이 쓰던 getter/setter를 포함한 클래스들은요..?
자료 / 객체 비대칭
객체
추상화 뒤로 자료를 숨김. 자료를 다루는 함수만 공개
자료 구조
자료를 그대로 공개. 별다른 함수 제공하지 않음.
1. 절차적인 도형
각 도형 클래스는 간단한 자료 구조, 아무 메서드도 제공하지 않아요.
- 절차 지향적
- 도형의 동작은 Geometry 클래스에서 구현
- 함수를 추가할 때는 도형 클래스는 수정할 필요가 없어요.
- 도형을 추가할 때는 모든 함수를 수정해야 해요.
//// 도형 자료 구조
public class Square {
public Point topLeft;
public double side;
}
public class Rectangle {
public Point topLeft;
public double height;
public double width;
}
public class Circle {
public Point center;
public double radius;
}
public class Geometry {
public final double PI = 3.141592653589793;
public double area(Object shape) throws NoSuchShapeException {
if (shape instanceof Square) {
Square s = (Square)shape;
return s.side * s.side;
} else if (shape instanceof Rectangle) {
Rectangle r = (Rectangle)shape;
return r.height * r.width;
} else if (shape instanceof Circle) {
Circle c = (Circle)shape;
return PI * c.radius * c.radius;
}
throw new NoSuchShapeException();
}
//// 새로운 함수 추가 자유로움.
}2. 객체 지향적인 도형
각 도형 객체는 area()는 다형(polymorphic) 메서드를 제공합니다.
- 새 도형을 추가해도 기존 함수에 영향을 미치지 않음
- 새 함수를 추가할 때에는 도형 클래스 전부를 고쳐야 함.
public class Square implements Shape {
private Point topLeft;
private double side;
public double area() {
return side * side;
}
}
public class Rectangle implements Shape {
private Point topLeft;
private double height;
private double width;
public double area() {
return height * width;
}
}
public class Circle implements Shape {
private Point center;
private double radius;
public final double PI = 3.141592653589793;
public double area() {
return PI * radius * radius;
}
}3. 절차적인 코드 vs 객체 지향 코드
(자료 구조를 사용하는)절차적인 코드
- 기존 자료 구조를 변경하지 않으면서 새 함수(동작)를 추가하기 쉽다.
- 새로운 자료 구조(도메인)를 추가기 어렵다. 그러기 위해선 모든 함수를 고쳐야 한다.
- 새로운 자료 타입이 아니라
새로운 함수가 필요한 경우에 더 유리
객체 지향 코드
- 기존 함수를 변경하지 않으면서 새 클래스를 추가하기 쉽다.
- 새로운 함수를 추가하기 어렵다. 그러기 위해선 모든 클래스를 고쳐야 한다.
- 새로운 함수보다는
새로운 자료 타입이 필요한 경우 더 유리
💡 모든 문제를 객체로 해결하려는 생각은 좋지 않다.
디미터 법칙(Law of Demeter)
모듈은 자신이 조작하는 객체의 속사정을 몰라야 한다.
즉, 객체는 조회 함수로 내부 구조를 공개하면 안된다.
→ private 변수, public 메서드로 구현하면 되는 것 아닌가요?? ❌😵❌
💡 핵심은 객체 구조의 경로를 따라 멀리 떨어져 있는 낯선 객체에 메시지를 보내는 설계는 피하라는 것.
노출 범위를 제한하기 위해 객체의 모든 메서드는 다음에 해당하는 메서드만을 호출해야 한다
- 객체 자신의 메서드
- 메서드의 파라미터로 넘어온 객체들의 메서드
- 메서드 내부에서 생성, 초기화된 객체의 메서드
- 인스턴스 변수로 가지고 있는 객체가 소유한 메서드
class Demeter {
private Member member;
public myMethod(OtherObject other) {
// do sth
}
public okLawOfDemeter(Paramemter param) {
myMethod(); // 1. 객체 자신의 메서드
param.paramMethod(); // 2. 메서드의 파라미터로 넘어온 객체들의 메서드
Local local = new Local();
local.localMethod(); // 3. 메서드 내부에서 생성, 초기화된 객체의 메서드
member.memberMethod(); // 4. 인스턴스 변수로 가지고 있는 객체가 소유한 메서드
}
}나쁜 예
//// 줄줄이 사탕
final String outputDir = ctxt.getOptions().getScratchDir().getAbsolutePath();리팩토링
STEP 1. 디미터 법칙을 만족하기 위해
/// 디미터 법칙을 만족하기 위해
Options opts = ctxt.getOptions();
File scratchDir = opts.getScratchDir();
final String outputDir = scratchDir.getAbsolutePath();→ 함수 하나가 아는 지식이 너무 많아요. 의존 관계를 모두 알아야해요.
Q.
이 예시가 디미터 법칙을 위반하는 것일까요?
A.
ctxt, opts, scratchDir이 어떤 형태인지에 따라 다르다!
Reason
객체라면,
위의 예시는 내부 구조를 그대로 드러내기 때문에 디미터 법칙을 위반해요.
자료 구조라면,
당연히 내부 구조를 드러내야 하기 때문에 디미터 법칙이 적용 되지 않아요.
이렇게 구현 하면 더 좋았겠죠..final String outputDir = ctxt.options.scratchDir.absolutePath;
STEP 2. 구조체 감추기
//// 후보 1
ctxt.getAbsolutePathOfScratchDirectoryOption();
//// 후보 2
ctxt.getScratchDirectoryOption().getAbsolutePath()후보 1: ctx객체에 공개해야 하는 메서드가 너무 많다. = 응집도가 낮아진다.
후보 2: getScratchDirectoryOption()가 자료 구조를 반환함을 가정한다.
ctxt가 객체라면 뭔가를 하라고 말해야지 속을 드러내라고 말하면 안 된다.
STEP 3. 객체에게 일을 시키기
- 왜 절대 경로가 필요한가요? 임시 파일을 생성하기 위해서!
- 목적을 달성하기 위해 객체에게 일을 시키자!
BufferedOutputStream bos = ctxt.createScratchFileStream(classFileName);Kotlin data class는 왜 상속이 안될까?? listing-api에서 data class 받을때 중복되는 것들 있는데
중복되는 변수들을 모아서 interface화 하고 data class에서 overriding해서 사용하는게 좋은 일일까?
interface가 하는 역할은 뭘까???
상속이 안되는 문제점을 어떻게 해결하면 좋을까???
잡종 구조
- 절반은 객체, 절반은 자료 구조
- 자료구조에 비즈니스 로직을 담는 경우
- 공개 변수
- 공개 getter/setter 함수
그럼 ctxt 안에있는 2번째 객체는 모든 것을 다 알아야하지 않을까?
어차피 ctxt의 일을 2번째 객체에게 넘긴 것이 아닐까??
final String outputDir = ctxt.getOptions().getModule().getAbsolutePath();
Options options = ctxt.getOptions();
File scratchDir = opts.getScratchDir();
final String outputDir = scratchDir.getAbsolutePath();
String outFile = outputDir + "/" + className.replace('.', '/') + ".class";
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fout);
BufferedOutputStream bos = ctxt.createScartchFileStream(classFileName);
새로운 예제 1
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class PostService {
private final PostRepository messageRepository;
public Mono<Void> deletePost(final DeletePostCommand command) {
return postRepository.findByPostId(command.getPostId())
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.error(new PostNotFoundException()))
.flatMap(post -> {
**if (!post.getUser().getId().equals(command.getDeleter().getUserId())) {
return Mono.error(new AccessDeniedException());
}**
return postRepository.save(post.deleteAndCopy());
})
.then();
}
}
// **작성자와 삭제 요청자가 일치하는 지 확인**하기 위해 여러 객체들에게 정보를 묻고 있음
// **객체가 객체를 탐색하므로 결합이 강하게 생겨있다.**public class PostService {
private final PostRepository messageRepository;
public Mono<Void> deletePost(final DeletePostCommand command) {
return postRepository.findByPostId(command.getPostId())
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.error(new PostNotFoundException()))
.flatMap(post ->
postRepository.save(post.deleteAndCopy(command.getDeleter())))
.then();
}
}
// **게시글을 삭제하기 위해서는 작성자와 수정자가 일치해야한다는 지식을 Post 에게로 옮겼기** 때문에
// deletePost 메소드 내에서 여러 객체를 탐색하지 않는다.
public class Post {
private final String id;
private final PostWriter user;
private final Boolean deleted;
...
public Post deleteAndCopy(final PostWriter deleter) {
**verifyDeletePermission(deleter); // 권한 체크**
return copyFromThis()
.deleted(true)
.build();
}
**// 작성자와 삭제 요청자가 일치하지 않을 경우 예외 반환**
private void verifyDeletePermission(final PostWriter deleter) {
if (!this.user.equals(deleter)) { // id 기준 equals and hashcode 생성되어 있음
throw new AccessDeniedException();
}
}
}왜 이런 모양이 나왔을지 생각해보기
- 추상화 수준 분리
- 책임의 분리
- 결합도 낮추기
public class Post {
private final String id;
private final PostWriter user;
private final Boolean deleted;
...
public Post deleteAndCopy(final PostWriter deleter) {
**this.user.checkDeletePermission(deleter); // 권한 체크**
return copyFromThis()
.deleted(true)
.build();
}
}
public class PostWriter {
private final Long id;
...
public void checkDeletingPermission(final PostWriter performer) {
if (getId().equals(performer.getId())) {
return;
}
throw new AccessDeniedException();
}
}새로운 예제2
@Getter
public class Employee {
private final String name;
private final Enterprise enterprise;
public int getEnterprisePostalCode() {
return this.enterprise.getAddressPostalCode();
}
}
@Getter
public class Enterprise {
private final int employeeNumber;
private final String domain;
private final Address address;
public int getAddressPostalCode() {
return this.address.getPostalCode();
}
}
@Getter
public class Address {
private final String street;
private final int postalCode;
private final String city;
}public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Address address = new Address("종로구 청와대로 1", 03054, "서울특별시");
final Enterprise enterprise = new Enterprise(100, "청와대", address);
final Employee employee = new Employee("안주형", enterprise);
// 1번
**System.out.println(employee.getEnterprise().getAddress().getPostalCode());**
// 2번
**System.out.println(employee.getEnterprisePostalCode());**
}
}자료 전달 객체
DTO
- Martin Fowler, EAA
The main purpose of DTO pattern, which is to reduce the number of roundtrips between a client and a server by sending multiple parameters in a single call.

-
domain model과 presentation layer의 분리
-
직렬화 로직의 캡슐화
By encapsulating the serialization logic within a DTO, any changes to the serialization process can be made in a single location, making it easier to manage and maintain. -
비즈니스 로직을 포함하지 않는 순수 객체
The purpose of the pattern is to optimize the data transfer and the structure of the contracts. -
로컬 DTO
도메인간의 데이터 전달에 사용되는 DTO. 도메인 로직을 노출할 가능성 높아져요. -
DTO는 명확하게 Immutable해야한다!
-
MVC 계층간 이동할때 객체 이름 고민해보기.
-
controller → service 넘길때는 requestDTO 그대로하면 어떨까?
Entity
In general, an entity is something that exists as a distinct and independent unit. In the context of computer science and information technology, an entity refers to an object or thing that can be distinguished from other objects based on its attributes or characteristics.
Entity에 대한 오해들
- Confusing entities with database tables:
✔️ entities와 database tables을 동일시.
✔️ Hibernate나 Entity Framework와 같은 ORM tool이 entity와 database를 direct하게 mapping하기 때문.
✔️ An entity is a logical abstraction that represents a real-world object or concept, while a database table is a physical representation of that entity in a database. - Treating entities as data containers:
✔️ properties 또는 attributes만 가지고 있는 단순 데이터 객체라고 생각
✔️ attribute: 상태를 나타냄 + methods: 행동을 정의 = entity
✔️ Entities are not just data containers; they represent real-world objects or concepts with complex behaviors and interactions. - 엔티티를 올바르게 식별하고 정의하지 못하는 문제:
✔️ 애플리케이션과 사용자의 요구에 기반하여 엔티티를 정확하게식별하고 정의하는 것이 중요 - Overloading entities with too much responsibility:
✔️ 엔티티에 너무 많은 책임이 부여되어 복잡하고 비대한 객체 모델이 발생
✔️ 하나의 엔티티 내에서 너무 많은 개념 또는 동작을 표현하려고 할 때 발생
✔️ 각 엔티티틔 책임을 올바르게 식별하고 복잡한 동작을 더 작고 집중된 엔티티로 분해하는 것이 중요
다양한 방식으로 표현 될 수 있는 Entity
OOP: objects with properties and methods(define their attributes and behaviors)
public class Customer {
private String name;
private String email;
public Customer(String name, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}Database: tables with columns(correspond to their attributes)

RESTful API: resources that can be accessed and manipulated using HTTP methods.
- resource: 현실세계의 물체나 개념을 표현하는 개념적 실체(Entity)
GET /api/customers // Retrieve a list of all customers
GET /api/customers/{id} // Retrieve a specific customer by ID
POST /api/customers // Create a new customer
PUT /api/customers/{id} // Update an existing customer by ID
DELETE /api/customers/{id} // Delete an existing customer by ID- RESTful API에서 API 리소스들은 일반적으로 Entity에 대응한다.
- ‘customer’ entity는 RESTful API를 통해서 노출된다.
- Each endpoint corresponds to a different action that can be performed on the customer entity, using the HTTP methods and parameters specified in the RESTful API.
VO
- DDD(Eric Evans)에서 처음 소개된 개념
- 소프트웨어 시스템의 기반이 되는 비즈니스 개념과 규칙을 나타내는 도메인 모델의 Building Block 중 하나.
Entity와 VO
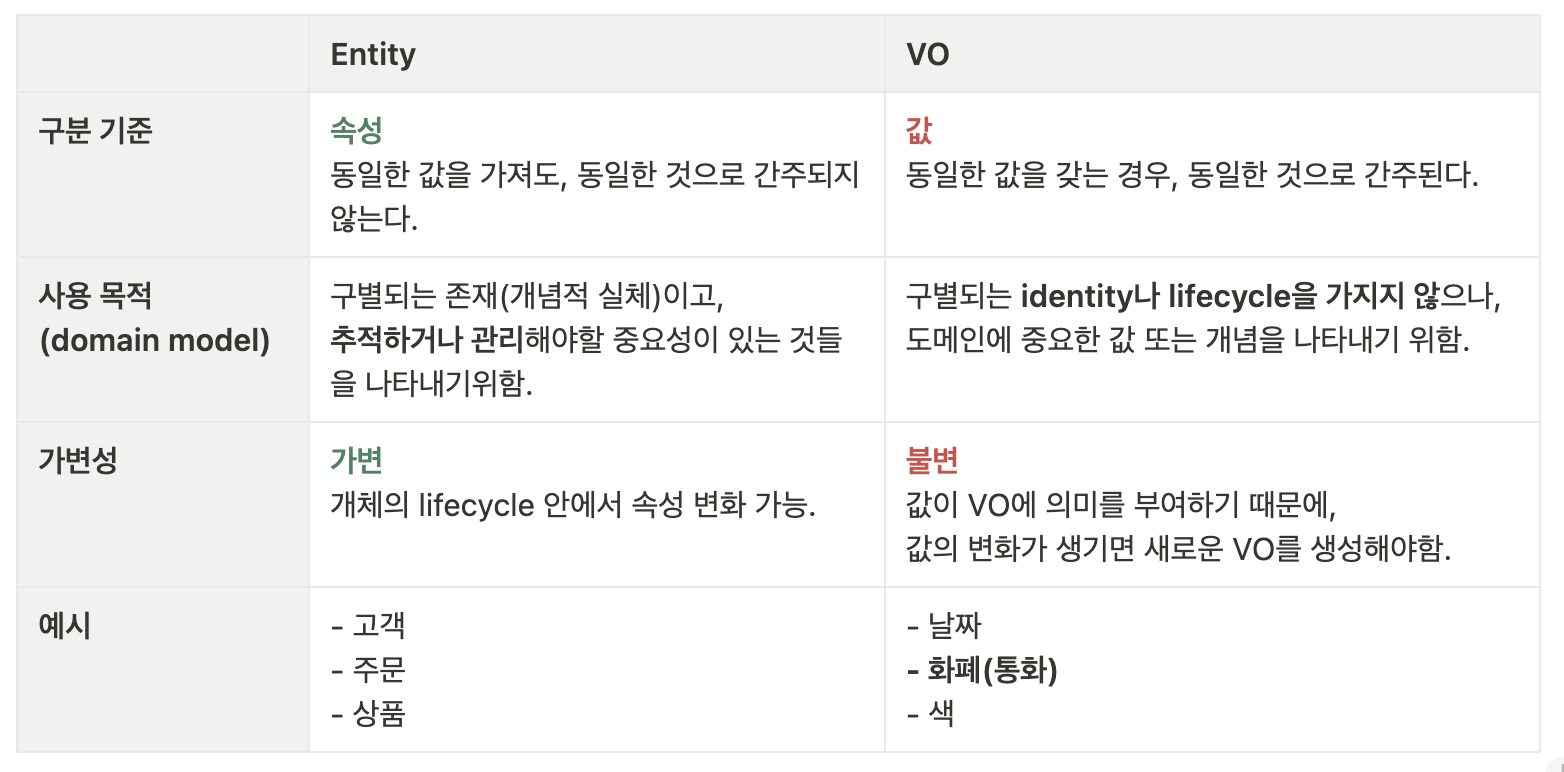
DTO와 VO
- 공통점
- Encapsulate Data
- Immutable
🤚 그렇다면, DTO를 VO의 한 종류로 볼 수 있나요??
아니요.
- DTO는 📦택배 포장📦한 Data
*Data = Entity, VO, Parameter들의 조합체 - VO는 값이나 개념의 Constant화.
