2025.05.02 작성
OS : macOs
언어 : Java
실행환경(플랫폼): 백준 / 프로그래머스 (Programmers)
코딩 테스트 필수 역량
- 독해력 : 문제를 빠르고 정확하게 이해하는 능력
- 지식 : 자료구조, 알고리즘
- 문제해결능력 : 아이디어 + 경험
- 코딩능력 : 프로그래밍 언어 문법, 경험
- 검증, 디버깅 : 에러, 잘못된 부분 빠르게 찾아 수정
- 경험 : 반복, 노하우, 풀이방법
- 전략 : 시간배분, 문제 우선순위, 부분점수
디버깅
- 오류를 찾아 바로 잡는 과정
- 코딩 테스트에서 문법 오류는 실행 시 자동으로 찾아 주지만, 논리 오류는 사용자 의도와는 다르게 동작하므로 찾기 어려움.
- 주의 사항
- 반복문 범위
- 변수 사용 위치
- 자료형 선택(예: long 타입을 int로 정의)
자료구조
자료구조 (Data Structure)는 컴퓨터에서 데이터를 효율적으로 저장하고, 접근하기 위해, 특정 구조에 맞게 모아서 저장할 수 있도록 만들어 놓은 것.
자료구조는 각각의 데이터 자체도 중요하지만, 데이터 간의 관계, 상위/하위/중첩 구조를 파악하는 것이 중요.
각 자료구조 별로 제공하는 기능(함수나 메서드)를 숙지하고 있어야 함.
배열
꼭 알아둬야 할 자료 구조: 배열 (Array)
- 데이터를 나열하고, 각 데이터를 인덱스에 대응하도록 구성한 데이터 구조
- 파이썬에서는 리스트 타입이 배열 기능을 제공함
자바에서의 배열의 특징
- 초기화 시 길이 고정 (이후 길이 변경 불가)
- 전체 값들은 모두 같은 타입
- 길이는[], 값(요소)는 {} 사용
[ 배열 연습 문제 ]
숫자의 합 구하기
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11720
- 풀이
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); String[] str = br.readLine().split(""); int sum = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { sum+= Integer.parseInt(str[i]); } System.out.println(sum); } }
평균 구하기
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1546
- 풀이
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); // 시험 본 과목의 수 int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); String[] score = br.readLine().split(" "); double sum = 0; int max = 0; for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { if(max < Integer.parseInt(score[i])){ max = Integer.parseInt(score[i]); }else{ max = max; } } for (int k = 0 ; k < n ; k++) { sum += (double)Integer.parseInt(score[k])/max*100; } System.out.println(sum / n); } }
최대값
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2566
- 풀이
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.IOException; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); int x = 1, y = 1; int max = 0; int[][] arr = new int[9][9]; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { String[] input = br.readLine().split(" "); for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) { arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(input[j]); } } for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) { if (arr[i][j] > max) { max = arr[i][j]; x = i + 1; y = j + 1; } } } System.out.println(max); System.out.println(x + " " + y); } }
이웃한 칸
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/250125
- 풀이
class Solution { public int solution(String[][] board, int h, int w) { int answer = 0; int n = board.length; int count = 0; int[] dh = {0, 1, -1, 0}; int[] dw = {1, 0, 0, -1}; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ int h_check = h+dh[i]; int w_check = w+dw[i]; if(h_check >= 0 && h_check < n && w_check >= 0 && w_check < n){ if(board[h][w].equals(board[h_check][w_check])) { count ++; } } } return count; } }
행렬의 곱셈
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/12949
- 풀이
class Solution { public int[][] solution(int[][] arr1, int[][] arr2) { int n = arr1.length; // arr1 행 개수 int m = arr2[0].length; // arr2 열 개수 int k = arr1[0].length; // arr1 열 개수 int[][] answer = new int[n][m]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { for (int l = 0; l < k; l++) { answer[i][j] += arr1[i][l] * arr2[l][j]; } } } return answer; } }
[1차] 프렌즈4블록
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/17679
- 풀이
class Solution { public int solution(int m, int n, String[] board) { int answer = 0; char[][] map = new char[m][n]; // toCharArray()로 쪼개서 한 줄 한 줄 문자 배열로 변환 for(int i = 0; i < m ; i++) { map[i] = board[i].toCharArray(); } // 1) 4개의 블록 체크 // 2) 체크된 블록 삭제 // 3) 블록을 아래로 떨어뜨림 // 4) 더 이상 없을 때 까지 반복 // 지워지는 블록은 총 몇 개인지 while(true) { int cnt = checkBlock(m, n, map); if (cnt == 0) break; answer += cnt; dropBlock(m, n, map); } return answer; } // 1) 4개의 블록 체크 private void checkFour(char[][] map, boolean[][] isChecked, int i, int j) { char block = map[i][j]; for(int r = i; r < i+2; r++){ for(int c = j; c < j+2; c++){ // 실패 if (map[r][c] != block) return; } } for(int r = i; r < i+2; r++){ for(int c = j; c < j+2; c++){ // 맞음 > true isChecked[r][c] = true; } } } // 2) 체크된 블록 삭제 private int checkBlock(int m, int n, char[][] map) { int cnt = 0; boolean[][] isChecked = new boolean[m][n]; for (int i = 0; i < m-1; i++){ for (int j = 0; j < n-1; j++){ // 빈칸이면 스킵 if(map[i][j] == '.') continue; checkFour(map, isChecked, i, j); } } for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ // isChecked가 true이면 if(isChecked[i][j]){ cnt++; map[i][j] = '.'; } } } return cnt; } // 3) **블록을 아래로 떨어뜨림 private void dropBlock(int m, int n, char[][] map) { for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) { for(int i = m-1; i >= 0; i--){ if(map[i][j] == '.') { for(int k = i-1; k >= 0; k--) { if (map[k][j] != '.') { map[i][j] = map[k][j]; map[k][j] = '.'; break; } } } } } } }
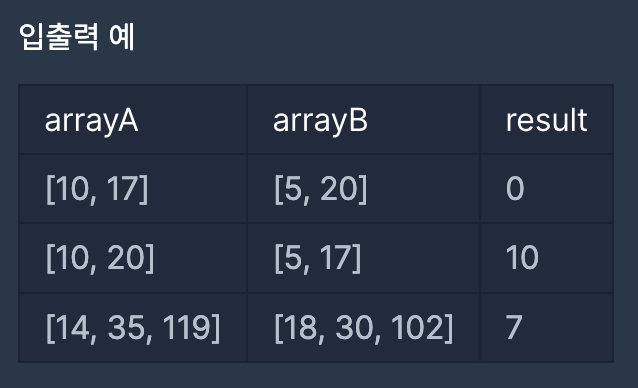
숫자 카드 나누기
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/135807
- 풀이
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] arrayA, int[] arrayB) {
int answer = 0;
int a = arrayA[0];
int b = arrayB[0];
for(int i = 0; i < arrayA.length; i++) {
// 나누어 떨어지면 공약수 > a값 그대로 유지
if(arrayA[i] == 0) continue;
int max = Math.max(arrayA[i], a);
int min = Math.min(arrayA[i], a);
a = gcd(max, min);
}
for(int i = 0; i < arrayB.length; i++) {
if(arrayB[i] == 0) continue;
int max = Math.max(arrayB[i], b);
int min = Math.min(arrayB[i], b);
b = gcd(max, min);
}
for(int i : arrayB) {
if(i % a == 0){
a = 0;
break;
}
}
for(int i : arrayA) {
if(i % b == 0) {
b = 0;
break;
}
}
answer = Math.max(a, b);
return answer;
}
static int gcd(int a, int b) {
if(b == 0) return a;
return gcd(b, a%b);
}
}유클리드 호제법을 이용한 최대공약수(GCD) 계산
두 수 a, b의 최대공약수(GCD)를 구하는 알고리즘
gcd(a, b) = gcd(b, a % b)
→ b가 0이 될 때까지 반복 → 그때 a가 GCD(예시)
gcd(18, 12)
= gcd(12, 18 % 12) → gcd(12, 6)
= gcd(6, 12 % 6) → gcd(6, 0)
= 6GCD 함수
static int gcd(int a, int b) {
if(b == 0) return a;
return gcd(b, a%b);
}