DFS 깊이 우선 탐색
📚 'DFS(Depth-First Search)' 란
- 그래프 전체를 탐색하는 방법 중 하나 → 완전 탐색
- 하나의 가지를 모두 탐색한 후에 다음 가지로 이동
- 재귀함수 또는 스택(stack)으로 구현
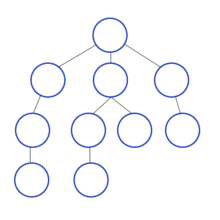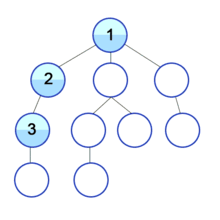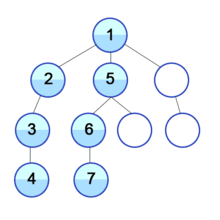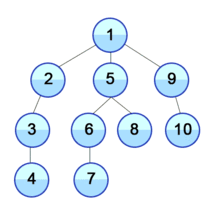
[출처] 위키피디아(깊이우선탐색)
📝 특징
- 정점 방문 시, 방문 여부(visited)를 검사
→ 방문 했다면 visited[node]를 true로 변경 후 가지치기
- 다양한 경로(다양한 방식)을 들려보는 탐색 시 유용!!
💻 코드 구현
입력이 아래와 같을 때
5
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
- 인접 행렬 저장
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int arr[10][10] = { 0, };
int N;
void dfs(int now)
{
for (int next = 1; next <= N; next++)
{
if (arr[now][next] == 0)
continue;
dfs(next);
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
int from, to;
cin >> from >> to;
arr[from][to] = 1;
}
dfs(1);
return 0;
}
- 인접 리스트 저장 (vector 활용)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int N;
vector<int> arr[10];
void dfsVector(int now)
{
cout << now << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < arr[now].size(); i++)
{
int next = arr[now][i];
dfsVector(next);
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
int from, to;
cin >> from >> to;
arr[from].push_back(to);
}
dfsVector(1);
return 0;
}
- 응용 코드
void dfs(int now)
{
if (~~~~~) {
끝나면서 무언가 처리
return;
}
for (int next = 1; next <= N; next++)
{
if (arr[now][next] == 0) continue;
used[next] = 1;
path.push_back(next);
dfs(next);
path.pop_back();
used[next] = 0;
}
}



SHE IS BACK TO C++
WELCOME NEW RICE👍👍