팩토리 메서드 패턴
객체 생성을 공장 클래스로 캡슐화 처리해 대신 생성하게 하는 생성 디자인 패턴
즉, 클라이언트에서 직접 new 연산자를 통해 제품 객체를 생성하는 것이 아닌, 제품 객체들을 도맡아 생성하는 공장 클래스를 만들고, 이를 상속하는 서브 공장 클래스의 메서드에서 여러 제품 객체 생성을 각각 책임지는 것이다.
또한 객체 생성에 필요한 과정을 템플릿처럼 미리 구성해놓고, 객체 생성에 관한 전처리나 후처리를 통해 생성 과정을 다양하게 처리해 객체를 유연하게 정할 수 있다.
🔶 팩토리 메서드 패턴 구조
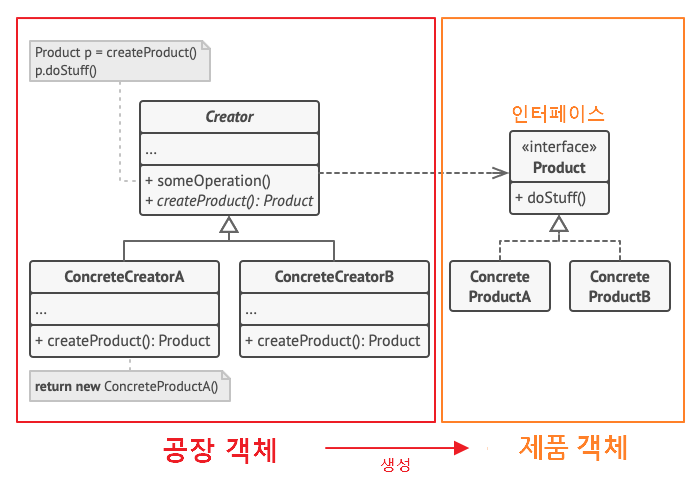
💠 Creator : 최상위 공장 클래스로, 팩토리 메서드를 추상화해 서브 클래스로 하여금 구현하도록 함
- 객체 생성 처리 메서드(someOperation) : 객체 생성에 관한 전처리, 후처리를 템플릿화 한 메서드
- 팩토리 메서드(createProduct) : 서브 공장 클래스에서 재정의할 객체 생성 추상 메서드
💠 ConcreteCreator : 각 서브 공장 클래스들은 이에 맞는 제품 객체를 반환하도록 생성 추상 메서드를 재정의한다. 즉, 제품 객체 하나 당 그에 걸맞는 생산 공장 객체가 위치된다.
💠 Product : 제품 구현체를 추상화
💠 ConcreteProduct : 제품 구현체
정리하자면, 팩토리 메서드 패턴은 객체를 만들어내는 공장을 만드는 패턴이라고 생각하면 된다.
그리고 어떤 클래스의 인스턴스를 만들지는 미리 정의한 공장 서브 클래스에서 결정한다.
🔶 팩토리 메서드 패턴 흐름
클래스 구성
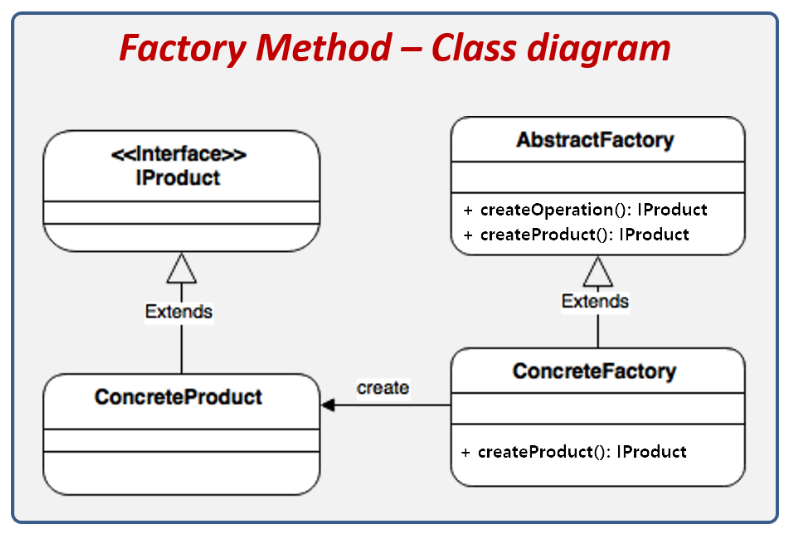
제품(Product) 클래스
// 제품 객체 추상화 (인터페이스)
interface IProduct {
void setting();
}
// 제품 구현체
class ConcreteProductA implements IProduct {
public void setting() {
}
}
class ConcreteProductB implements IProduct {
public void setting() {
}
}공장(Factory) 클래스
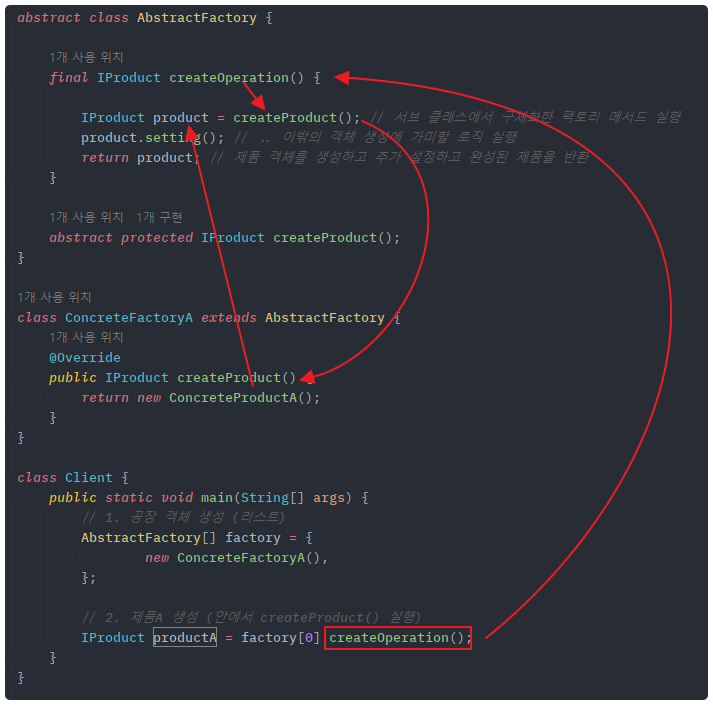
// 공장 객체 추상화 (추상 클래스)
abstract class AbstractFactory {
// 객체 생성 전처리 후처리 메소드 (final로 오버라이딩 방지, 템플릿화)
final IProduct createOperation() {
IProduct product = createProduct(); // 서브 클래스에서 구체화한 팩토리 메서드 실행
product.setting(); // .. 이밖의 객체 생성에 가미할 로직 실행
return product; // 제품 객체를 생성하고 추가 설정하고 완성된 제품을 반환
}
// 팩토리 메소드 : 구체적인 객체 생성 종류는 각 서브 클래스에 위임
// protected 이기 때문에 외부에 노출이 안됨
abstract protected IProduct createProduct();
}
// 공장 객체 A (ProductA를 생성하여 반환)
class ConcreteFactoryA extends AbstractFactory {
@Override
public IProduct createProduct() {
return new ConcreteProductA();
}
}
// 공장 객체 B (ProductB를 생성하여 반환)
class ConcreteFactoryB extends AbstractFactory {
@Override
public IProduct createProduct() {
return new ConcreteProductB();
}
}클래스 흐름
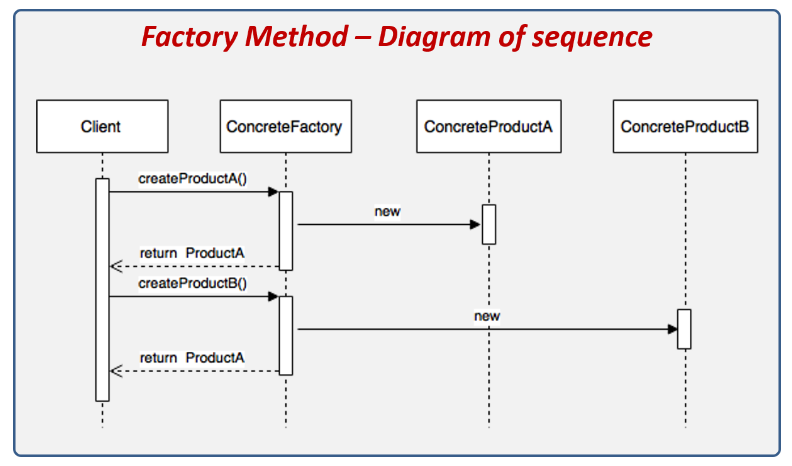
class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 공장 객체 생성 (리스트)
AbstractFactory[] factory = {
new ConcreteFactoryA(),
new ConcreteFactoryB()
};
// 2. 제품A 생성 (안에서 createProduct() 와 생성 후처리 실행)
IProduct productA = factory[0].createOperation();
// 3. 제품B 생성 (안에서 createProduct() 와 생성 후처리 실행)
IProduct productB = factory[1].createOperation();
}
}
🔶 팩토리 메서드 패턴 특징
패턴 사용 시기
💠 클래스 생성과 사용의 처리 로직을 분리해 결합도를 낮추고자 할 때
💠 코드가 동작해야 하는 객체의 유형과 종속성을 캡슐화를 통해 정보 은닉 처리 할 경우
💠 라이브러리 혹은 프레임워크 사용자에게 구성 요소를 확장하는 방법을 제공하려는 경우
💠 기존 객체를 재구성하는 대신 기존 객체를 재사용하여 리소스를 절약하고자 하는 경우
패턴 장점
💠 생성자와 구현 객체의 강한 결합을 피할 수 있다.
💠 객체의 생성 후 공통으로 할 일을 수행하도록 지정해줄 수 있다.
💠 캡슐화, 추상화를 통해 생성되는 객체의 구체적인 타입을 감출 수 있다.
💠 단일 책임 원칙 준수 : 객체 생성 코드를 한 곳으로 이동해 코드를 유지보수하기 쉽게 할 수 있다.
💠 개방/폐쇄 원칙 준수 : 기존 코드를 수정하지 않고 새로운 유형의 제품 인스턴스를 프로그램에 도입할 수 있다.
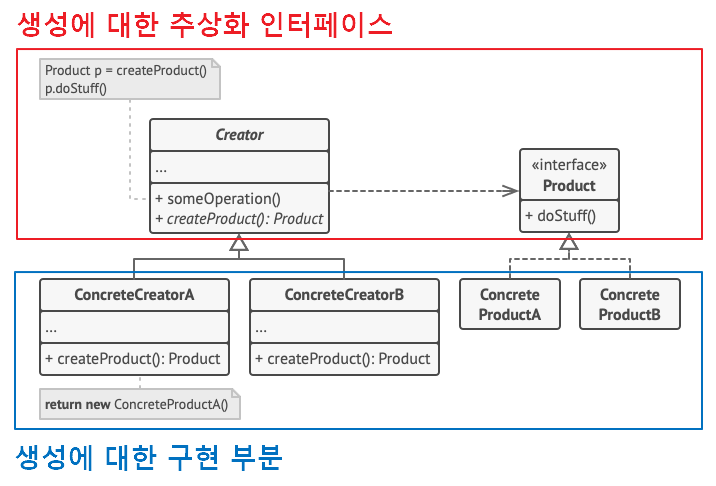
💠 생성에 대한 인터페이스 부분과 생성에 대한 구현 부분을 따로 나뉘었기 때문에 패키지 분리하여 개별로 여러 개발자가 협업을 통해 개발 가능하다.
패턴 단점
💠 각 제품 구현체마다 팩토리 객체들을 모두 구현해주어야 하기 때문에, 구현체가 늘어날 때마다 팩토리 클래스가 증가해 서브 클래스 수가 폭발한다.
💠 코드의 복잡성이 증가한다.
팩토리 메서드 패턴을 잘 적용한 코드 - java
제품 객체
class Ship {
String name, color, capacity;
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("Ship { name: '%s', color: '%s', logo: '%s' }\n", name, color, capacity);
}
}
class ContainerShip extends Ship {
ContainerShip(String name, String capacity, String color) {
this.name = name;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.color = color;
}
}
class OilTankerShip extends Ship {
OilTankerShip(String name, String capacity, String color) {
this.name = name;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.color = color;
}
}공장 객체
abstract class ShipFactory {
// 객체 생성 전처리 / 후처리 메서드 (상속 불가)
final Ship orderShip(String email) {
validate(email);
Ship ship = createShip(); // 선박 객체 생성
sendEmailTo(email, ship);
return ship;
}
// 팩토리 메서드
abstract protected Ship createShip();
private void validate(String email) {
if (email == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("이메일을 남겨주세요");
}
}
private void sendEmailTo(String email, Ship ship) {
System.out.println(ship.name + " 다 만들었다고 " + email + "로 메일을 보냈습니다.");
}
}
class ContainerShipFactory extends ShipFactory {
@Override
protected Ship createShip() {
return new ContainerShip("ContainerShip", "20t", "green");
}
}
class OilTankerShipFactory extends ShipFactory {
@Override
protected Ship createShip() {
return new OilTankerShip("OilTankerShip", "15t", "blue");
}
}클라이언트
class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 전용 선박 생산 공장 객체를 통해 선박을 생성
Ship containerShip = new ContainerShipFactory().orderShip("inpa.naver.com");
System.out.println(containerShip);
Ship oilTankerShip = new OilTankerShipFactory().orderShip("inpa.naver.com");
System.out.println(oilTankerShip);
}
}팩토리 메서드 패턴을 잘 적용한 코드 - typescript
제품 객체
// 제품(Ship) 인터페이스
interface Ship {
name: string;
color: string;
capacity: string;
toString(): string;
}
// 구체적인 제품(선박) 클래스들
class ContainerShip implements Ship {
name: string;
color: string;
capacity: string;
constructor(name: string, capacity: string, color: string) {
this.name = name;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.color = color;
}
toString(): string {
return `Ship { name: '${this.name}', color: '${this.color}', capacity: '${this.capacity}' }`;
}
}
class OilTankerShip implements Ship {
name: string;
color: string;
capacity: string;
constructor(name: string, capacity: string, color: string) {
this.name = name;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.color = color;
}
toString(): string {
return `Ship { name: '${this.name}', color: '${this.color}', capacity: '${this.capacity}' }`;
}
}공장 객체
// 추상 팩토리 클래스
abstract class ShipFactory {
// 템플릿 메서드: 생성 전/후 처리
public orderShip(email: string): Ship {
this.validate(email);
const ship = this.createShip(); // 선박 객체 생성
this.sendEmailTo(email, ship);
return ship;
}
// 팩토리 메서드 (구체적인 제품 생성은 서브 클래스에 위임)
protected abstract createShip(): Ship;
private validate(email: string): void {
if (!email) {
throw new Error("이메일을 남겨주세요");
}
}
private sendEmailTo(email: string, ship: Ship): void {
console.log(`${ship.name} 다 만들었다고 ${email}로 메일을 보냈습니다.`);
}
}
// 구체적인 팩토리 클래스들
class ContainerShipFactory extends ShipFactory {
protected createShip(): Ship {
return new ContainerShip("ContainerShip", "20t", "green");
}
}
class OilTankerShipFactory extends ShipFactory {
protected createShip(): Ship {
return new OilTankerShip("OilTankerShip", "15t", "blue");
}
}클라이언트
// 클라이언트 코드
class Client {
public static main() {
// 전용 선박 생산 공장을 통해 선박 생성
const containerShipFactory = new ContainerShipFactory();
const containerShip = containerShipFactory.orderShip("inpa@naver.com");
console.log(containerShip.toString());
const oilTankerShipFactory = new OilTankerShipFactory();
const oilTankerShip = oilTankerShipFactory.orderShip("inpa@naver.com");
console.log(oilTankerShip.toString());
}
}
// 클라이언트 코드 실행
Client.main();