Overview
디자인패턴 시작하기를 보고 정리하기
Memento
- '추억', '기억' 을 의미
- 객체 상태 기억했다가 필요할 때 꺼내 씀
- 기억 읽기는 다른 객체에서도 접근 가능
- 기억 생성은 해다 객체에서만 가능
다이어그램
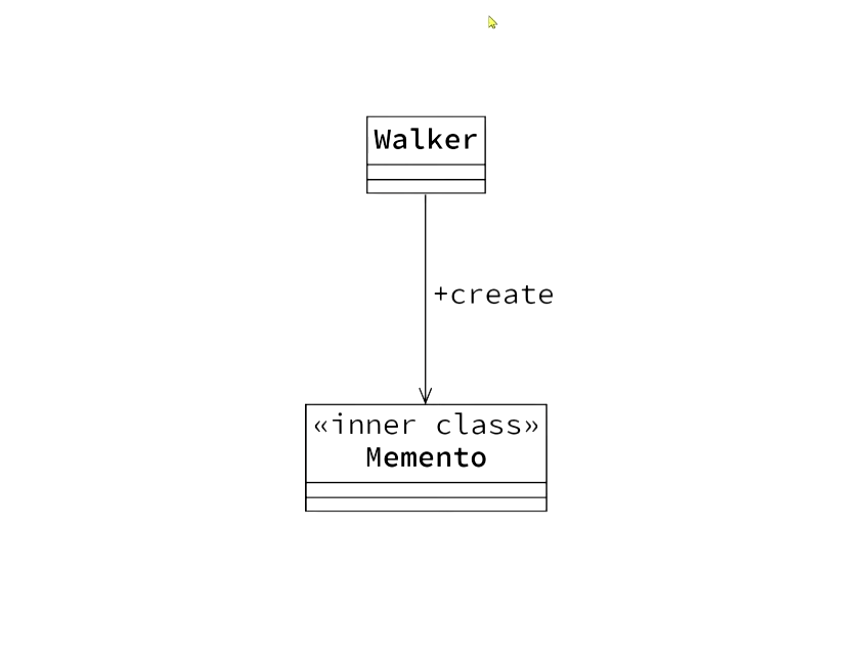
- Walker : 시작 지점에서 목표 지점까지 걸어가는 역할
- Memento : Walker 클래스에서만 생성하고, Walker 클래스만이 Memento 클래스 필드를 변경할 수 있게 하기 위해 내부 클래스로 선언. Walker에 대하여 어떤 기억을 저장할 지, 저장한 기억을 어떻게 사용할 지 정의
구현 코드
Walker
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Walker {
/// 워커의 현재 위치
private int currentX, currentY;
/// 목표 좌표
private int targetX, targetY;
/// 시작 > 목표까지 도달하기 위해 어떤 액션을 취해야 하는지, 순서
private ArrayList<String> actionList = new ArrayList<String>();
/// 생성자에서 시작 > 목표 좌표 설정
public Walker(int currentX, int currentY, int targetX, int targetY) {
this.currentX = currentX;
this.currentY = currentY;
this.targetX = targetX;
this.targetY = targetY;
}
/// 액션 인자를 통해 이동
public double walk(String action) {
actionList.add(action);
if (action.equals("UP")) {
currentY += 1;
} else if (action.equals("RIGHT")) {
currentX += 1;
} else if (action.equals("DOWN")) {
currentX -= 1;
} else if (action.equals("LEFT")) {
currentX -= 1;
}
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(currentX - targetX, 2) + Math.pow(currentY - targetY, 2));
}
/// Walker 에서만 생성, 변경 가능. 고록 내부 클래스로 생성함.
public class Memento {
private int x, y;
private ArrayList<String> actionList;
private Memento() {}
}
public Memento createMemento() {
// Walker의 인자 값을 Memento 에 저장
Memento memento = new Memento();
memento.x = this.currentX;
memento.y = this.currentY;
// !깊은 복사 필요! : clone을 하지 않으면 Walker 객체의 actionList가 변경될 때 함께 변경되기 때문
memento.actionList = (ArrayList<String>)this.actionList.clone();
return memento;
}
// Memento 객체를 사용해서 Walker 상태 변경
// 객체의 상태를 기억해 두었다가 필요할 때 기억한 상태로 되돌려 주는 역할
public void restoreMemento(Memento memento) {
this.currentX = memento.x;
this.currentY = memento.y;
this.actionList = (ArrayList<String>)memento.actionList.clone();
}
public String toString() {
return actionList.toString();
}
}Main
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
// 현재(0,0) 목표(10,10)
Walker walker = new Walker(0, 0, 10, 10);
String[] actions = { "UP", "RIGHT", "DOWN", "LEFT" };
Random random = new Random(); // 무작위 이동
double minDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE; // 최단 거리
Walker.Memento memento = null;
while (true) {
String action = actions[random.nextInt(4)];
double distance = walker.walk(action);
System.out.println(action + " " + distance);
if (distance == 0.0) {
break;
}
if (minDistance > distance) {
// 목표거리에 가까워지고 있다면 현재 거리를 최단 거리로 저장한다.
minDistance = distance;
memento = walker.createMemento();
} else {
// 멀어진다면 이전 상태로 되돌림
if (memento != null) {
walker.restoreMemento(memento);
}
}
}
System.out.println("Walker's path: " + walker);
}
}결과
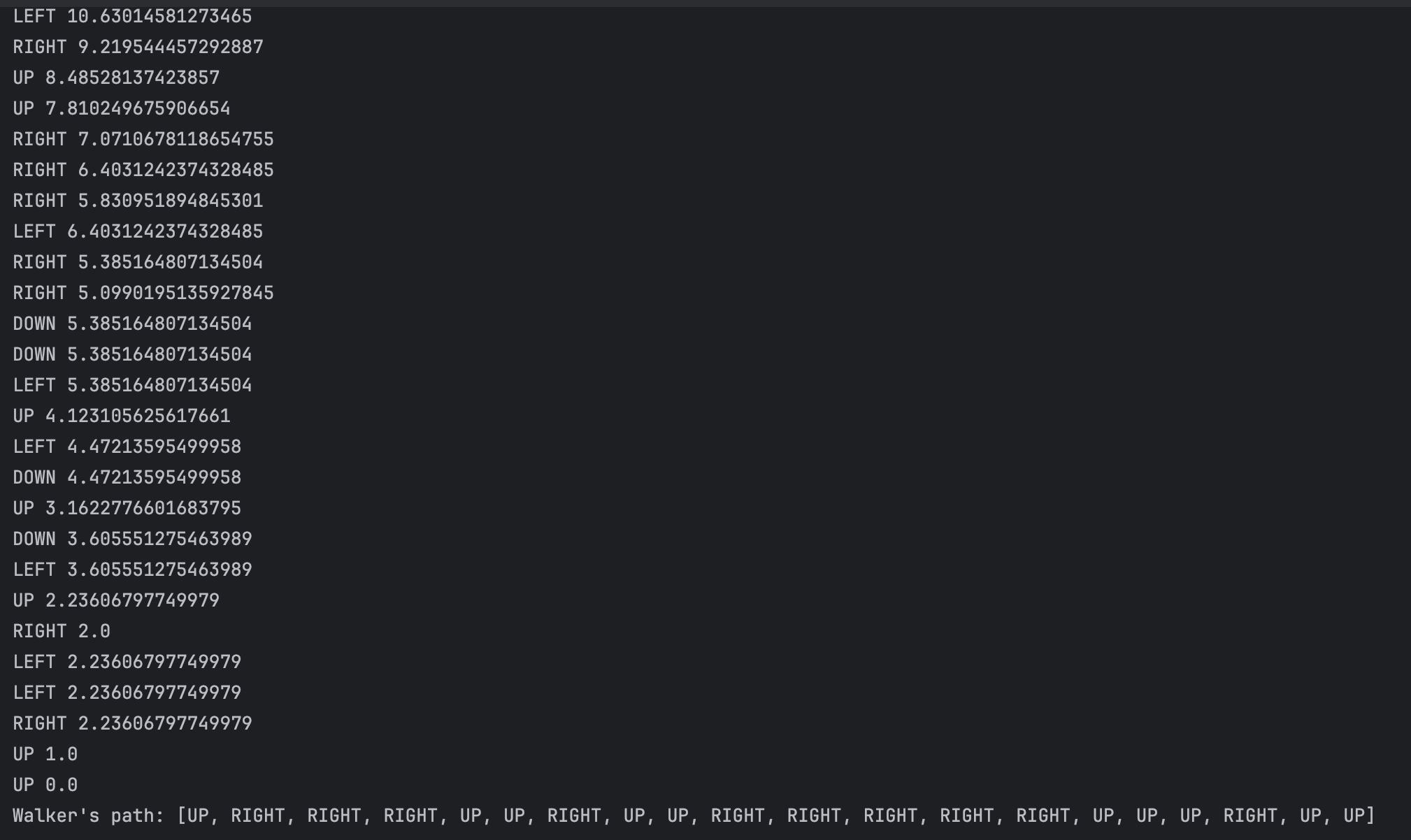
점점 목표 지점과 가까워짐, 그러기 위해 실행한 액션 히스토리 확인 가능
