3주차: 5/15/2023 - 5/21/2023
Numbers
Divisors and primes
- Divisor of an integer n: an integer m that may be multiplied by some integer to produce n
# Divisor
inputNumber = int(input('Input an integer greater than 0: '))
for number in range(1, inputNumber+1):
if inputNumber % number == 0:
print('Divisor of {}: {}'.format(inputNumber, number))- Prime: a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers
# Prime
inputNumber = int(input('Input an integer greater than 0: '))
for number in range(2, inputNumber+1):
flag = True
for n in range(2, number):
if number % n == 0:
flag = False
break
if flag:
print('{}: prime'.format(number))
else:
print('{}: \t\t composite'.format(number))- Prime factorization: decomposition of a positive integer into a product of smaller primes
# Prime factors
inputNumber = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
n = 2
while n <= inputNumber:
if inputNumber % n == 0:
print('Prime factor: {}'.format(n))
inputNumber /= n
else:
n += 1
# Prime factorization
inputNumber = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
n = 2
searchNumbers = []
while n <= inputNumber:
if inputNumber % n == 0:
print('Prime factor: {}'.format(n))
if searchNumbers.count(n) == 0:
searchNumbers.append(n)
elif searchNumbers.count(n) == 1:
searchNumbers.remove(n)
inputNumber /= n
else:
n += 1
print('searchNumbers: {}'.format(searchNumbers))- Greatest common divisor (GCD): GCD of two or more integers, which are not all zero, is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers
# GCD of two numbers
num1 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
num2 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
gcd = 0
for i in range(1, num1+1):
if num1 % i == 0 and num2 % i == 0:
print('Common divisor: {}'.format(i))
gcd = i
print('Greatest common divisor: {}'.format(gcd))
# GCD of three numbers
num1 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
num2 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
num3 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
gcd = 0
for i in range(1, num1+1):
if num1 % i == 0 and num2 % i == 0 and num3 % i == 0:
print('Common divisor: {}'.format(i))
gcd = i
print('Greatest common divisor: {}'.format(gcd))
# Euclidean algorithm
num1 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
num2 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
temp1 = num1; temp2 = num2
while temp2 > 0:
temp = temp2
temp2 = temp1 % temp2
temp1 = temp
print('GCD of {} and {}: {}'.format(num1, num2, temp1))
for n in range(1, temp1+1):
if temp1 % n == 0:
print('Common divisor of {} and {}: {}'.format(num1, num2, n))- Least common multiple (LCM): LCM of two integers a and b is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both a and b
# LCM of two numbers
num1 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
num2 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
gcd = 0
for i in range(1, num1+1):
if num1 % i == 0 and num2 % i == 0:
print('Common divisor: {}'.format(i))
gcd = i
print('Greatest common divisor: {}'.format(gcd))
lcm = (num1 * num2) // gcd
print('Least common multiple: {}'.format(lcm))
# LCM of three numbers
num1 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
num2 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
num3 = int(input('Input an integer greater than 1: '))
gcd = 0
for i in range(1, num1+1):
if num1 % i == 0 and num2 % i == 0:
print('Common divisor: {}'.format(i))
gcd = i
print('Greatest common divisor: {}'.format(gcd))
lcm = (num1 * num2) // gcd
print('Least common multiple: {}'.format(lcm))
newNum = lcm
for i in range(1, newNum+1):
if newNum % i == 0 and num3 % i == 0:
gcd = i
print('Greatest common divisor: {}'.format(gcd))
lcm = (newNum * num3) // gcd
print('Least common multiple: {}'.format(lcm))
# Exercise
ship1 = 3; ship2 = 4; ship3 = 5
gcd = 0
for i in range(1, ship1+1):
if ship1 % i == 0 and ship2 % i == 0:
gcd = i
print('GCD: {}'.format(gcd))
lcm = (ship1 * ship2) // gcd
print('LCM of {} and {}: {}'.format(ship1, ship2, lcm))
newDay = lcm
for i in range(1, newDay+1):
if newDay % i == 0 and ship3 % i == 0:
gcd = i
print('GCD: {}'.format(gcd))
lcm = (newDay * ship3) // gcd
print('LCM of {} and {}: {}'.format(ship2, ship3, lcm))- Base: the number of unique digits, including the digit zero, used to represent numbers
dNum = 30
print('Binary: {}'.format(bin(dNum)))
print('Octal: {}'.format(oct(dNum)))
print('Hexadecimal: {}'.format(hex(dNum)))
print('Binary: {}'.format(type(bin(dNum))))
print('Octal: {}'.format(type(oct(dNum))))
print('Hexadecimal: {}'.format(type(hex(dNum))))
print('Binary: {}'.format(format(dNum, '#b')))
print('Binary: {}'.format(format(dNum, '#o')))
print('Binary: {}'.format(format(dNum, '#x')))
print('{0:#b}, {0:#o}, {0:#x}'.format(dNum))
print('Binary: {}'.format(format(dNum, 'b')))
print('Binary: {}'.format(format(dNum, 'o')))
print('Binary: {}'.format(format(dNum, 'x')))
print('Binary (0b11110) -> Decimal ({})'.format(int('0b11110', 2)))
print('Octal (0o36) -> Decimal ({})'.format(int('0o36', 8)))
print('Hexadecimal (0x1e) -> Decimal ({})'.format(int('0x1e', 16)))Exercises
import random
rNum = random.randint(100, 1000)
print(f'rNum: {rNum}')
for num in range(1, rNum+1):
primeFactor = 0
# Divisor
if rNum % num == 0:
print(f'[Divisor]: {num}')
primeFactor += 1
# Prime
if num != 1:
flag = True
for n in range(2, num):
if num % n == 0:
flag = False
break
if flag:
print(f'[Prime]: {num}')
primeFactor += 1
# Prime factor
if primeFactor >= 2:
print(f'[Prime factor]: {num}')import random
rNum = random.randint(100, 1000)
print(f'rNum: {rNum}')
primeFactorList = []
n = 2
while n <= rNum:
if rNum % n == 0:
print(f'Prime factor: {n}')
primeFactorList.append(n)
rNum /= n
else:
n += 1
print(f'primeFactorList: {primeFactorList}')
tempNum = 0
for p in primeFactorList:
if tempNum != p:
print(f'{p}\'s count: {primeFactorList.count(p)}')
tempNum = p
import random
rNum1 = random.randint(100, 1000)
rNum2 = random.randint(100, 1000)
print(f'rNum1: {rNum1}')
print(f'rNum2: {rNum2}')
maxNum = 0
for n in range(1, min(rNum1, rNum2)+1):
if rNum1 % n == 0 and rNum2 % n == 0:
print(f'Common divisor: {n}')
maxNum = n
print(f'GCD: {maxNum}')
if maxNum == 1:
print(f'{rNum1} and {rNum2} are coprime')import random
rNum1 = random.randint(100, 1000)
rNum2 = random.randint(100, 1000)
print(f'rNum1: {rNum1}')
print(f'rNum2: {rNum2}')
maxNum = 0
for n in range(1, min(rNum1, rNum2)+1):
if rNum1 % n == 0 and rNum2 % n == 0:
print(f'Common divisor: {n}')
maxNum = n
print(f'GCD: {maxNum}')
minNum = (rNum1 * rNum2) // maxNum
print(f'LCM: {minNum}')
Sequences
- Sequence: an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters
- Arithmetic sequence: a sequence of numbers such that the difference from any succeeding term to its preceding term remains constant throughout the sequence
- where is the common difference
-
-
# Find the nth term: using the common difference
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputD = int(input('Input common difference d: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = 0
n = 1
while n <= inputN:
if n == 1:
valueN = inputA1
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(n, valueN))
n += 1
continue
valueN += inputD
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(n, valueN))
n += 1
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(inputN, valueN))
# Find the nth term: using the formula an = a1 + (n-1)d
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputD = int(input('Input common difference d: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = 0
valueN = inputA1 + (inputN - 1) * inputD
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(inputN, valueN))# Find the sum: using the common difference
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputD = int(input('Input common difference d: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = 0
sumN = 0
n = 1
while n <= inputN:
if n == 1:
valueN = inputA1
sumN = valueN
print('Value of the sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(n, sumN))
n += 1
continue
valueN += inputD
sumN += valueN
print('Value of the sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(n, sumN))
n += 1
print('Value of the sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, sumN))
# Find the sum: using the formula
# - an = a1 + (n-1)d
# - sn = n(a1 + an) / 2
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputD = int(input('Input common difference d: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = inputA1 + (inputN - 1) * inputD
sumN = inputN * (inputA1 + valueN) / 2
print('Value of the sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, int(sumN)))- Geometric sequence: a sequence of non-zero numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous one by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio
- where is the common ratio
-
-
# Find the nth term: using the common ratio
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputR = int(input('Input common ratio r: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = 0
n = 1
while n <= inputN:
if n == 1:
valueN = inputA1
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(n, valueN))
n += 1
continue
valueN *= inputR
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(n, valueN))
n += 1
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(inputN, valueN))
# Find the nth term: using the formula an = a1 * r^(n-1)
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputR = int(input('Input common ratio r: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = inputA1 * (inputR ** (inputN - 1))
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(inputN, valueN))
# Find the sum: using the common ratio
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputR = int(input('Input common ratio r: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = 0
sumN = 0
n = 1
while n <= inputN:
if n == 1:
valueN = inputA1
sumN += valueN
print('Value of the sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(n, sumN))
n += 1
continue
valueN *= inputR
sumN += valueN
print('Value of the sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(n, sumN))
n += 1
print('Value of the sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, sumN))
# Find the sum: using the formula sn = a1 * (1 - r^n) / (1 - r)
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputR = int(input('Input common ratio r: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
sumN = inputA1 * (1 - inputR ** inputN) / (1 - inputR)
print('Value of the sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, int(sumN)))
# Exercise: arithmetic sequence
# an = a1 + (n - 1) * d
# sn = n * (a1 + an) / 2
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputD = int(input('Input common difference d: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = inputA1 + (inputN - 1) * inputD
sumN = inputN * (inputA1 + valueN) / 2
print('Value of the sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, int(sumN)))
# Exercise: geometric sequence
# sn = a1 * (1 - r^n) / (1 - r)
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputR = int(input('Input common ratio r: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
sumN = inputA1 * (1 - inputR ** inputN) / (1 - inputR)
print('Value of the sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, int(sumN)))- Difference sequence: a sequence that consists of terms that are differences of adjacent terms in another sequence
# a_n = {3, 7, 13, 21, 31, 43, 57}
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputAN = int(input('Input n of an: '))
inputB1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputBD = int(input('Input the common difference d for bn: '))
valueAN = 0
valueBN = 0
n = 1
while n <= inputAN:
if n == 1:
valueAN = inputA1
valueBN = inputB1
print('Value of {}th term of an: {}'.format(n, valueAN))
print('Value of {}th term of bn: {}'.format(n, valueBN))
n += 1
continue
valueAN += valueBN
valueBN += inputBD
print('Value of {}th term of an: {}'.format(n, valueAN))
print('Value of {}th term of bn: {}'.format(n, valueBN))
n += 1
print('Value of {}th term of an: {}'.format(inputAN, valueAN))
print('Value of {}th term of bn: {}'.format(inputAN, valueBN))
# bk = 2k + 2
# sn = n(b1 + bn) / 2
# s(n-1) = (n-1)(4 + 2(n-1) + 2) / 2 = (n-1)(2n + 4) / 2 = (n-1)(n+2) = n^2 + n - 2 = an - a1 = an - 3
# an = n^2 + n + 1
inputA1 = int(input('Input first term a1: '))
inputAN = int(input('Input n of an: '))
valueAN = inputAN ** 2 + inputAN + 1
print('Value of {}th term of an: {}'.format(inputAN, valueAN))- Fibonacci sequence: a sequence in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = 0
sumN = 0
valuePreN2 = 0
valuePreN1 = 0
n = 1
while n <= inputN:
if n == 1 or n == 2:
valueN = 1
valuePreN2 = valueN
valuePreN1 = valueN
sumN += valueN
n += 1
else:
valueN = valuePreN2 + valuePreN1
valuePreN2 = valuePreN1
valuePreN1 = valueN
sumN += valueN
n += 1
print('Value of {}th term: {}'.format(inputN, valueN))
print('Sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, sumN))- Factorial of a non-negative integer : the product of all positive integers less than or equal to
# Using the for loop
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
result = 1
for n in range(1, inputN + 1):
result *= n
print('{}!: {}'.format(inputN, result))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
# Using recursion
def factorialFun(n):
if n == 1:
return 1
return n * factorialFun(n - 1)
print('{}!: {}'.format(inputN, factorialFun(inputN)))
# Using the math library
import math
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
print('{}!: {}'.format(inputN, math.factorial(inputN)))- Group sequence: a sequence which exhibits a pattern when its terms are grouped
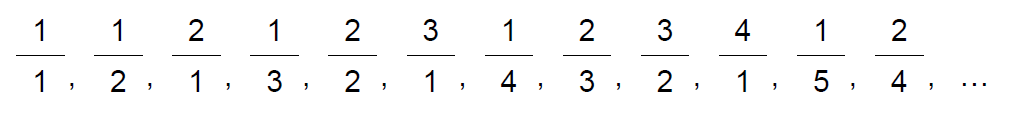
# Exercise 1
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
flag = True
n = 1; nCnt = 1; searchN = 0
while flag:
for i in range(1, n+1):
if i == n:
print('{} '.format(i), end='')
else:
print('{}, '.format(i), end='')
nCnt += 1
if nCnt > inputN:
searchN = i
flag = False
break
print()
n += 1
print('{}th term: {}'.format(inputN, searchN))
# Exercise 2
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
flag = True
n = 1; nCnt = 1; searchNC = 0; searchNP = 0
while flag:
for i in range(1, n+1):
if i == n:
print('{}/{} '.format(i, (n-i+1)), end='')
else:
print('{}/{}, '.format(i, (n-i+1)), end='')
nCnt += 1
if nCnt > inputN:
searchNC = i
searchNP = n - i + 1
flag = False
break
print()
n += 1
print('{}th term: {}/{}'.format(inputN, searchNC, searchNP))Exercises
# inputA1 = int(input('Input a1: '))
# inputD = int(input('Input d: '))
# inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = 0; sumN = 0
n = 1
while n <= inputN:
if n == 1:
valueN = inputA1
sumN += valueN
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(n, valueN))
print('Sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(n, sumN))
n += 1
continue
valueN += inputD
sumN += valueN
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(n, valueN))
print('Sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(n, sumN))
n += 1
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(inputN, valueN))
print('Sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, sumN))
# Formula
inputA1 = int(input('Input a1: '))
inputD = int(input('Input d: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = inputA1 + (inputN - 1) * inputD
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(inputN, valueN))
sumN = inputN * (inputA1 + valueN) / 2
print('Sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, int(sumN)))
# inputA1 = int(input('Input a1: '))
# inputR = int(input('Input r: '))
# inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = 0; sumN = 0
n = 1
while n <= inputN:
if n == 1:
valueN = inputA1
sumN += valueN
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(n, valueN))
print('Sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(n, sumN))
n += 1
continue
valueN *= inputR
sumN += valueN
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(n, valueN))
print('Sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(n, sumN))
n += 1
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(inputN, valueN))
print('Sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, sumN))
# Formula
inputA1 = int(input('Input a1: '))
inputR = int(input('Input r: '))
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = inputA1 * (inputR ** (inputN - 1))
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(inputN, valueN))
sumN = inputA1 * (1 - inputR ** inputN) / (1 - inputR)
print('Sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, int(sumN)))- where
where and
# Fibonacci
# an = a(n-2) + a(n-1)
inputN = int(input('Input n: '))
valueN = 0; sumN = 0
valuePreN2 = 0
valuePreN1 = 0
n = 1
while n <= inputN:
if n == 1 or n == 2:
valueN = 1
valuePreN2 = valueN
valuePreN1 = valueN
sumN += valueN
n += 1
else:
valueN = valuePreN2 + valuePreN1
valuePreN2 = valuePreN1
valuePreN1 = valueN
sumN += valueN
n += 1
print('Value of the {}th term: {}'.format(inputN, valueN))
print('Sum of the first {} terms: {}'.format(inputN, sumN))flag = True
# Group number
n = 1
nCnt = 1; searchNC = 0; searchNP = 0
sumN = 0
while flag:
for i in range(1, n+1):
print('{}/{} '.format(i, n - i + 1), end='')
sumN += i / (n - i + 1)
nCnt += 1
if sumN > 100:
searchNC = i
searchNP = n - i + 1
flag = False
break
print()
n += 1
print('Term at which the sum exceeds 100 for the first time: {}th term = {}/{}'.format(nCnt, searchNC, searchNP))
print('Sum of the values of which the sum exceeds 100 for the first time: {}'.format(round(sumN, 2)))
Probability
- Permutation of a set: an arrangement of its members into a sequence or linear order, or if the set is already ordered, a rearrangement of its elements
- where
-
# Permutation
numN = int(input('Input numN: '))
numR = int(input('Input numR: '))
result = 1
for n in range(numN, (numN - numR), -1):
print('n: {}'.format(n))
result *= n
print('result: {}'.format(result))
# Circular permutation
# - With repetition: n! / (n-r)!
# - Without repetition: n! / r(n-r)!
n = int(input('Input the number of friends: '))
result = 1
for i in range(1, n):
result *= i
print('result: {}'.format(result))- Combination of a set: a selection of items from a set that has distinct members, such that the order of selection does not matter (unlike permutations)
- where
# Exercise 1
numN = int(input('Input numN: '))
numR = int(input('Input numR: '))
resultP = 1
resultR = 1
resultC = 1
for n in range(numN, numN-numR, -1):
print('n: {}'.format(n))
resultP *= n
print('resultP: {}'.format(resultP))
for n in range(numR, 0, -1):
print('n: {}'.format(n))
resultR *= n
print('resultR: {}'.format(resultR))
resultC = int(resultP / resultR)
print('resultC: {}'.format(resultC))
# Exercise 2
numN = int(input('Input numN: '))
numR = int(input('Input numR: '))
resultP = 1
resultR = 1
resultC = 1
for n in range(numN, numN-numR, -1):
print('n: {}'.format(n))
resultP *= n
print('resultP: {}'.format(resultP))
for n in range(numR, 0, -1):
print('n: {}'.format(n))
resultR *= n
print('resultR: {}'.format(resultR))
resultC = int(resultP / resultR)
print('resultC: {}'.format(resultC))
result = (1/resultC) * 100
print('{}%'.format(round(result, 2)))- Probability of an event: a number that indicates how likely the event is to occur
# 7C3 = 35
# 4C2 * 3C1 / 35 = 6 * 3 / 35 = 18/35
def proFun():
numN = int(input('Input numN: '))
numR = int(input('Input numR: '))
resultP = 1
resultR = 1
resultC = 1
for n in range(numN, numN-numR, -1):
resultP *= n
print('resultP: {}'.format(resultP))
for n in range(numR, 0, -1):
resultR *= n
print('resultR: {}'.format(resultR))
resultC = int(resultP / resultR)
print('resultC: {}'.format(resultC))
return resultC
sample = proFun()
print('sample: {}'.format(sample))
event1 = proFun()
print('event1: {}'.format(event1))
event2 = proFun()
print('event2: {}'.format(event2))
probability = event1 * event2 / sample
print('probability: {}%'.format(round(probability * 100, 2)))Exercises
def proFun():
numN = int(input('Input numN: '))
numR = int(input('Input numR: '))
resultP = 1
resultR = 1
resultC = 1
# Permutation
for n in range(numN, numN-numR, -1):
resultP *= n
print('resultP: {}'.format(resultP))
# R!
for n in range(numR, 0, -1):
resultR *= n
print('resultR: {}'.format(resultR))
# Combination
resultC = int(resultP / resultR)
print('resultC: {}'.format(resultC))
return resultC
sample = proFun()
print('sample: {}'.format(sample))
event1 = proFun()
print('event1: {}'.format(event1))
event2 = proFun()
print('event2: {}'.format(event2))
probability = event1 * event2 / sample
print('probability: {}%'.format(round(probability * 100, 2)))