<SWEA> #1249 보급로_priority queue, compare, buffer vs scanner, bfs (c++, java)
SAMSUNG SW Test
목록 보기
36/39
이 문제는 예전에 c++로 풀었던 문젠데 java로 다시 풀려고 하니까 문법이 생각이 안 나서 애를 먹었다.. 그래서 이 문제에 필요한 java 문법 간단하게 (깊게 다루지는 않을 것임) 정리하면서 다시 풀어보자!
✍1. Scanner vs Buffer
Scanner
import java.util.Scanner; Scanner sc=new Scanner (System.in); int T=sc.nextInt();숫자를 입력 받을 때 Scanner를 사용해서 편리하게 입력을 받을 수 있지만 input 값이 작을 때만 사용하고 data의 값이 많아졌을 때는 Buffer을 사용해야 함 (속도가 느림)
Buffer
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); String s=br.readLine(); //String int T=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); //int : 형변환 필요Buffer는 String으로만 값을 입력받기 때문에, 큰 데이터에 있어서 Scanner보다 효율이 좋고 String이 아닌 다른 값으로 받을 때는 형변환이 필요
사용할 때 main에 throws Exception 해주거나 try-catch로 예외처리 필요
e.g.
이 문제에서는 '1234'처럼 공백없이 한 라인을 읽어들이고 1,2,3,4 를 각각 배열에 저장해야한다BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); for (int i=0; i<N; i++) { String[] line=br.readLine().split(""); for (int j=0; j<N; j++) { map[i][j]=Integer.parseInt(line[j]); } }
✍2. Priority Queue
Priority Queue 선언
import java.util.PriorityQueue; // int형 우선순위가 낮은 숫자 순 PriorityQueue<Integer> pq1 = new PriorityQueue<>(); // int형 우선순위가 높은 숫자 순 PriorityQueue<Integer> pq2 = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder()); // string형 우선순위가 낮은 글자 순 PriorityQueue<String> pq3 = new PriorityQueue<>(); // string형 우선순위가 높은 글자 순 PriorityQueue<String> pq4 = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
java에서 우선순위 큐를 사용하고 싶다면java.util.PriorityQueue를importPriorityQueue<Element> pq=new PriorityQueue<>()같은 형식으로 선언- 기본은 우선순위가 낮은 숫자가 부여되고 만약 높은 숫자가 우선순위가 되게 하고 싶다면
Collection.reverseOrder()메서드 활용
Priority Queue 사용
- 값 추가: add(value), offer(value)
- 값 제거:
poll() - 첫번째 값을 반환하고 제거, 비어있다면 null return,
remove() - 첫번째 값을 제거,
clear() - 초기화
✍3. Interface Comparable
정렬 수행 시 기본적으로 적용되는 정렬 기준이 되는 메서드를 정의하는 인터페이스
Comparable 구현
- 정렬할 객체에 Comparable interface를 implements
- compareTo() 메서드를 오버라이드
현재 객체 < 파라미터로 넘어온 객체 : 음수 리턴
현재 객체 > 파라미터로 넘어온 객체 : 양수 리턴
현재 객체 == 파라미터로 넘어온 객체 : 0 리턴
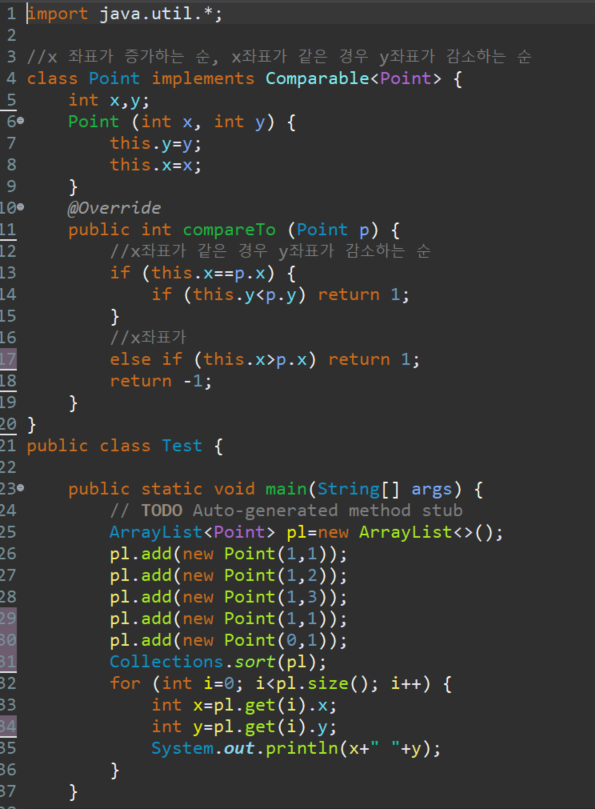
e.g. x좌표가 증가하는 순 (오름차순), x좌표가 같다면 y좌표가 감소하는 순(내림차순) 정렬
✍ C++ Sorce Code
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <string.h>
#define endl "\n"
const int dy[] = { 0,0,1,-1 };
const int dx[] = { 1,-1,0,0 };
const int MAX = 101;
using namespace std;
int C, N;
int map[MAX][MAX];
int dist[MAX][MAX];
int bfs() {
priority_queue<pair<pair<int, int>, int> >pq;
pq.push(make_pair(make_pair(0, 0), 0));
dist[0][0] = 0;
while (!pq.empty()) {
int d = -pq.top().first.first;
int y = pq.top().first.second;
int x = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int ny = y + dy[i];
int nx = x + dx[i];
if (ny < 0 || nx < 0 || ny >= N || nx >= N) continue;
if (dist[ny][nx] == -1) {
dist[ny][nx] = dist[y][x] + map[ny][nx];
pq.push(make_pair(make_pair(-dist[ny][nx], ny), nx));
//print();
}
if (dist[ny][nx] > dist[y][x] + map[ny][nx]) {
dist[ny][nx] = dist[y][x] + map[ny][nx];
//print();
}
}
}
return dist[N-1][N-1];
}
void input() {
cin >> C;
for (int i=1; i<=C; i++) {
cin >> N;
memset(dist, -1, sizeof(dist));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
string line;
cin >> line;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = line[j] - '0';
}
}
cout << "#" << i <<" "<< bfs() << endl;
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
input();
return 0;
}✍Java Source code
package org.swea.eclipse;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class Pos implements Comparable<Pos> {
int time;
int y,x;
Pos (int time, int y, int x) {
this.time=time;
this.y=y;
this.x=x;
}
public int compareTo (Pos p) {
if (this.time>p.time) return 1;
return -1;
}
}
public class Solution {
public static final int[] dy= {0,0,1,-1};
public static final int[] dx= {1,-1,0,0};
static int N;
static int[][] map;
static int min;
static int[][] dist;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in));
int T=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int tc=1; tc<=T; tc++) {
N=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map=new int[N][N];
dist=new int[N][N];
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
Arrays.fill(dist[i], -1);
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
String[] line=br.readLine().split("");
for (int j=0; j<N; j++) {
map[i][j]=Integer.parseInt(line[j]);
}
}
bfs();
System.out.printf("#%d %d\n", tc, dist[N-1][N-1]);
}
}
private static void bfs () {
PriorityQueue<Pos> pq=new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(new Pos(0,0,0));
dist[0][0]=0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Pos p=pq.poll();
int time=p.time;
int y=p.y;
int x=p.x;
for (int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int ny=y+dy[i];
int nx=x+dx[i];
if (ny<0 || nx<0 || ny>=N || nx>=N) continue;
if (dist[ny][nx]==-1) {
dist[ny][nx]=time+map[ny][nx];
pq.offer(new Pos(dist[ny][nx], ny, nx));
}
if (dist[ny][nx]>time+map[ny][nx])
dist[ny][nx]=time+map[ny][nx];
}
}
}
}
Reference
https://coding-factory.tistory.com/603
https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/09/06/java-comparable-and-comparator.html
https://velog.io/@camel-man-ims/Java-%EC%A0%95%EB%A6%AC-1-Scanner-vs-Buffer