정수원님의 강의 스프링 시큐리티 완전 정복 [6.x 개정판] 보면서 공부한 내용입니다.
인증
Authentication
-
시큐리티 인증 / 인가 흐름도
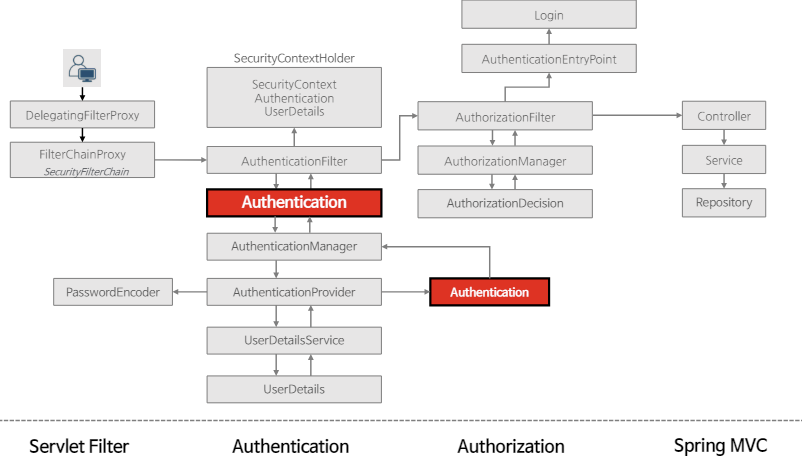
-
특정 자원에 접근하려는 사람의 신원을 확인하는 방법
EX) 당신은 누구인가? => 시스템에 존재 => 신원 보증 -
일반적인 사용자 인증 방법은 이름, 비밀번호를 입력하는 것(인증)으로 신원이 인증되면 권한 부여(인가)를 할 수 있다
-
Authentication은 사용자의 인증 정보를 저장하는 토큰 개념의 객체로 활용되며 인증 이후 SecuirtyContext에 저장디어 전역적으로 참조 가능하다
💡 Authentication 개념
- getPrincipal() : 인증 주체를 의미하며 인증 요청이 들어왔을 경우 => 사용자 이름
인증 후 => UserDetails 타입의 객체
- getCredentials() : 사용자 인증 후 인증 주체가 올바른 것을 증명하는 자격 증명(ex : 비밀번호)
- getAuthorities() : 사용자(principal)에게 부여된 권한
- getDetails() : 인증 요청에 대한 추가적인 세부 사항을 저장한다. IP 주소, 인증서 일련 번호 등이 된다
- isAuthenticated() : 인증 상태 반환 (인증 받았는지, 안받았는지)
- setAuthenticated(boolean) : 인증 상태를 설정
인증 컨텍스트
SecurityContext
- Authentication 저장 : 현재 인증된 사용자의 Authentication 객체를 저장한다
- ThreadLocal 저장소 사용 : SecurityContextHolder 를 통해 접근되며 ThreadLocal안에 SecurityContext가 저장되어 각 스레드가 자신만의 보안 컨텍스트를 유지한다
💡 ThreadLocal의 특징
: 각각 클라이언트마다 스레드 생성 => 각 스레드마다 ThreadLocal 존재
=> ThreadLocal에 SecurityContext가 존재
즉, 각 스레드마다 독립적으로 SecurityContext 객체를 가지고 있기 때문에 자신이 가지고 있는 SecurityContext값을 사용할 수 있지만 다른 스레드의 SecurityContext값을 가지고 오거나 저장할 수 없다 - 애플리케이션 전반에 걸친 접근성 : 애플리케이션의 어느 곳에서나 접근 가능(전역적으로 사용 가능)하며 현재 사용자의 인증 상태나 권한을 확인하는 데 사용됨
SecurityContextHolder
- SecurityContext 저장 : 현재 인증된 사용자의 Authentication 객체를 담고 있는 SecurityContext 객체를 저장
- 전략 패턴 사용 : 다양한 저장 전략을 지원하기 위해 SecurityContextHolderStrategy 인터페이스를 사용
- 기본 전략 : MODE_THREADLOCAL
- 전략 모드 직접 지정 가능 : SecurityContextHolder.setStrategyName(String)
SecurityContextHolder 저장 모드
- MODE_THREADLOCAL(ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy) : 기본 전략 모드이다. 각 스레드가 독립적인 보안 컨텍스트를 가진다. 대부분의 서버 환경에 적합
- MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL(InheritableThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy) : 부모 스레드로부터 자식 스레드로 보안 컨텍스트가 상속되며 작업을 스레드 간 분산 실행하는 경우 유용 할 수 있다
💡 메인 스레드 안에서 별도의 스레드를 생성할 수 있는데, 새롭게 생성된 스레드를 메인 스레드의 자식 스레드가 된다.
다만, 각 스레드는 독립적으로 SecurityContext 객체를 저장하기 때문에 부모가 가지고 있는 스레드는 자식에게 자동으로 저장이 되지 않는다.
=> 즉, 자식 스레드도 부모 스레드의 SecurityContext를 사용하기 위해서는 해당 모드를 사용하면 된다 - MODE_GLOBAL(GlobalSecurityContextHolderStrategy) : 전역적으로 하나의 보안 컨텍스트(SecurityContext)를 공유한다. 서버 환경에서는 부적합하지만 주로 간단한 애플리케이션에 적합하다
SecurityContext 참조 및 삭제
- SecurityContext 참조 : SecurityContexHolder.getContextHolderStrategy().getContext()
- SecurityContext 삭제 : SecurityContexHolder.getContextHolderStrategy().clearContext()
SecurityContextHolder & SecurityContext 구조
- 각 스레드 마다 할당 되는 전용 저장소에 SecurityContext 를 저장
=> 동시성 문제 발생 (X) - 기존의 ThreadLocal이 재사용될 수 있기 때문에 클라이언트로 응답 직전에 항상 SecurityContext 를 삭제함
=> clearContext() 호출

SecurityContextHolderStrategy 사용하기
- SecurityContextHolderStrategy를 자동 주입 될 수 있도록 설정하여 각 애플리케이션 컨텍스트가 자신에게 적합한 보안 전략을 사용할 수 있도록 한다 (여러 애플리케이션 컨텍스트 운용하는 상황에 적합)
SecurityContextHolderStrategy securityContextHolderStrategy = SecurityContextHolder.getContextHolderStrategy();
SecurityContext context = securityContextHolderStrategy.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(authentication);
securityContextHolderStrategy.setContext(context); 인증 관리자
AuthenticationManager
- 인증 필터로부터 Authenticaion 객체를 전달 받아 인증을 시도하며 성공할 경우 사용자 정보, 권한 등을 완전히 채워진 Authentication 객체를 반환한다
- 사용자가 인증 처리 요청
- Authentication Filter(인증 필터)가 요청 받아 Authenticaion 객체(사용자가 입력한 UserName/Password 저장)를 만든다
- Authentication Manager에게 인증 객체를 전달하면서 인증 처리를 맡기면 Authentication Manager 내부적으로 인증 처리를 수행한다
- 인증에 성공하면 User 객체/Authority 권한 정보를 저장한 새로운 인증 객체를 만든다
- 새롭게 만들어진 인증 객체를 Authentication Filter로 다시 반환한다
- AuthenticationProvider을 관리하며 해당 목록들을 순차적으로 순회하며 인증 요청을 처리한다
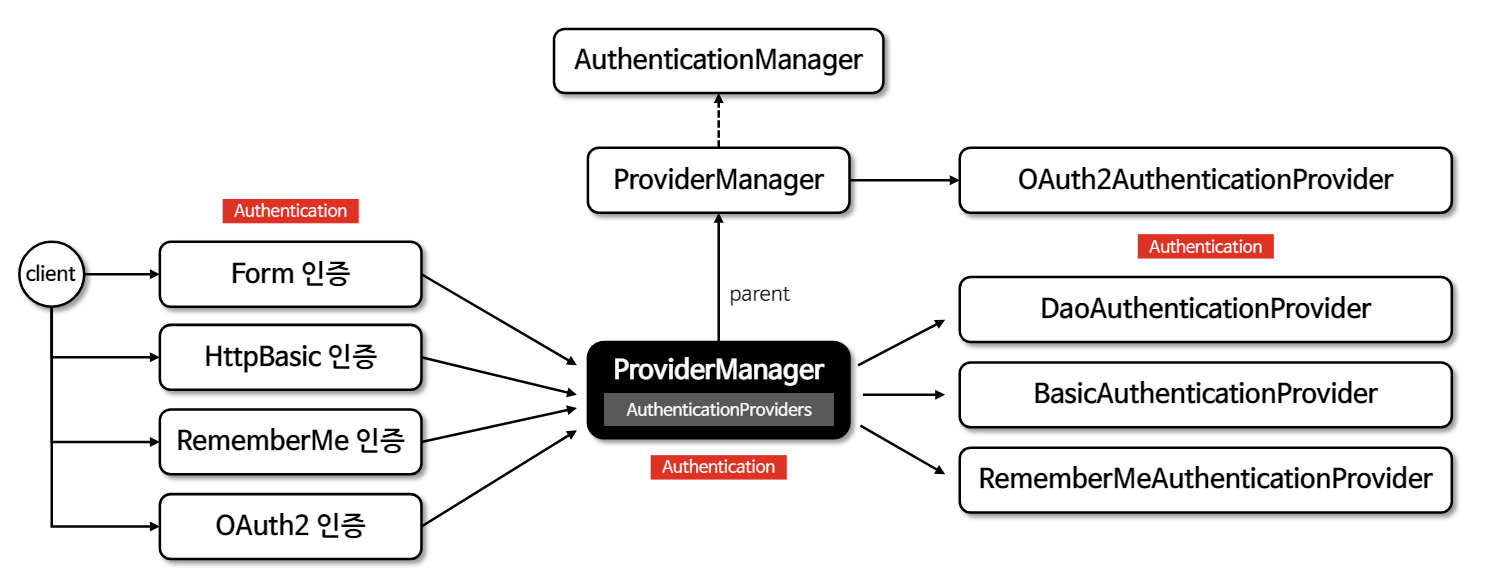
선택적으로 부모격인 ProviderManager를 구성할 수 있으며 자식인 ProviderManager가 인증 처리를 못하면 부모인 ProviderManager가 가지고 있는 인증 처리를 대신 할 수 있다
- AuthenticationProvider 목록 중에서 인증 처리 요건에 맞는 AuthenticationProvider를 찾아 인증 처리를 위임한다
즉, 인증 관리자는 인증 처리 전 Authentication Filter로 부터 인증 객체를 받아 AuthenticationProvider에게 넘겨주면 인증에 성공한 뒤 다시 객체를 받아 인증 필터에게 전달하는 역할을 한다
- AuthenticationManagerBuilder에 의해 객체가 생성되며 주로 사용하는 구현체는 ProviderManager이다
@Bean //@Bean으로 선언이 가능하다
publicCustomAuthenticationFiltercustomFilter(){
List<AuthenticationProvider>list1=List.of(newDaoAuthenticationProvider());
ProviderManagerparent=newProviderManager(list1); // 부모 생성
List<AuthenticationProvider>list2=List.of(newAnonymousAuthenticationProvider("key"), newCustomAuthenticationProvider());
ProviderManagerauthenticationManager=newProviderManager(list2,parent); // 자식, 부모
CustomAuthenticationFiltercustomAuthenticationFilter=newCustomAuthenticationFilter();
customAuthenticationFilter.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager); // 필터를 통해 인증 요청 수행
returncustomAuthenticationFilter;
}인증 방법
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
int currentPosition = 0;
int size = this.providers.size();
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authenticating request with %s (%d/%d)",
provider.getClass().getSimpleName(), ++currentPosition, size));
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) { // null 이 아닌 경우 for문을 빠져나옴
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
// 한 번 인증에 성공하면 결과를 return함
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
prepareException(ex, authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
lastException = ex;
}
}
if (result == null && this.parent != null) {
// result가 null이지만 parent가 null이 아닌 경우
try {
parentResult = this.parent.authenticate(authentication);
// parent에게 인증을 수행하게 함
result = parentResult;
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException ex) {
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
parentException = ex;
lastException = ex;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
if (parentResult == null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
}
return result;
}
if (lastException == null) {
// 인증에 모두 실패해서 결과값이 null인 경우
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(this.messages.getMessage("ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() }, "No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
if (parentException == null) {
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
}
throw lastException;
// 인증에 실패했다고 최종 통보함
}인증 제공자
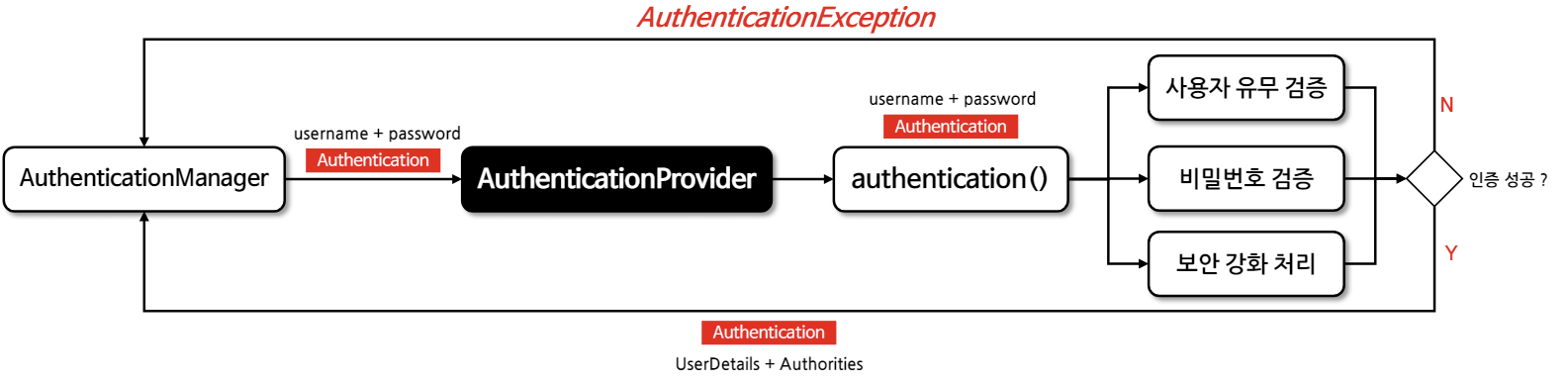
AuthenticationProvider
- 사용자가 시스템에 액세스하기 위해 제공한 정보가 유효한지 검증하는 과정
- 표준 사용자 이름과 비밀번호를 기반으로 한 인증, 토큰 인증, 지문 인식 등 다양한 인증 메커니즘을 지원한다
- 성공적으로 인증하면 Authentication 객체를 반환하며 사용자의 신원 정보와 인증된 자격 증명을 포함한다
- 예외가 발생하면 AuthenticationException과 같은 예외를 발생하여 문제를 알리는 역할을 한다
사용방법
하나의 Bean
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http
, AuthenticationManagerBuilder builder, AuthenticationConfiguration configuration) throws Exception {
AuthenticationManagerBuilder managerBuilder = http.getSharedObject(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);
managerBuilder.authenticationProvider(customAuthenticationProvider());
ProviderManager authenticationManager = (ProviderManager)configuration.getAuthenticationManager();
authenticationManager.getProviders().remove(0); // 첫 번째꺼를 삭제
// 원래 DaoAuthenticationProvider을 추가
builder.authenticationProvider(new DaoAuthenticationProvider());
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.anyRequest().authenticated())
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults());
return http.build();
}
/**
* 한 개의 Bean 정의할 때
*/
@Bean
public AuthenticationProvider customAuthenticationProvider() {
return new CustomAuthenticationProvider();
}두 개의 Bean
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http
, AuthenticationManagerBuilder builder, AuthenticationConfiguration configuration) throws Exception {
AuthenticationManagerBuilder managerBuilder = http.getSharedObject(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);
managerBuilder.authenticationProvider(customAuthenticationProvider());
managerBuilder.authenticationProvider(customAuthenticationProvider2());
ProviderManager authenticationManager = (ProviderManager)configuration.getAuthenticationManager();
authenticationManager.getProviders().remove(0); // 첫 번째꺼를 삭제
// 원래 DaoAuthenticationProvider을 추가
builder.authenticationProvider(new DaoAuthenticationProvider());
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.anyRequest().authenticated())
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults());
return http.build();
}
/**
* 한 개의 Bean 정의할 때
*/
@Bean
public AuthenticationProvider customAuthenticationProvider() {
return new CustomAuthenticationProvider();
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationProvider customAuthenticationProvider2() {
return new CustomAuthenticationProvider();
}사용자 상세 서비스
UserDetailService
- 사용자의 존재 여부와 데이터를 검색하고 인증 과정을 수행한다
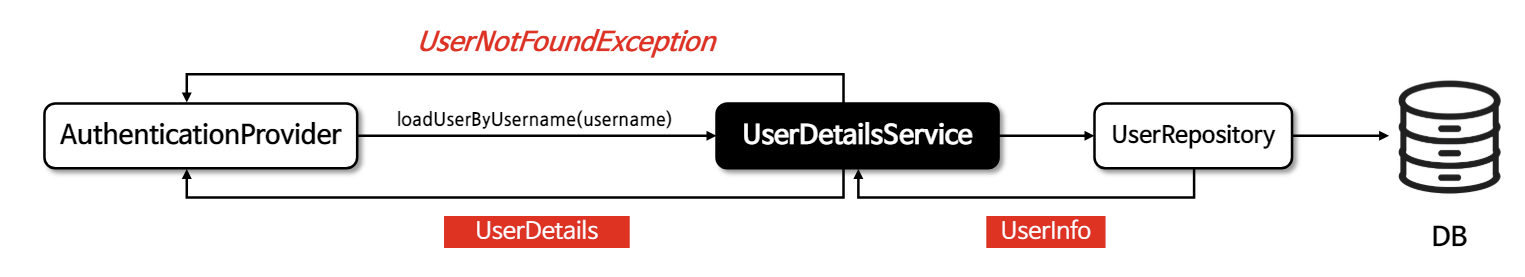
- 사용자 정보가 들어오면 내부적으로 UserRepository를 사용하여 사용자 정보를 가져온다
- UserInfo라는 도메인을 통해 객체를 전달하는데 그대로 전달하는 것이 아닌 UserDetails 타입의 도메인 객체에 매핑한 후 UserDetails의 객체로 AuthenticationProvider에게 전달이 된다
💡 사용자 정보가 없는 경우 UserNotFoundException 예외를 날린다
public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException{
UserDetails user = User.withUsername("user")
.password("{noop}1111")
.roles("USER").build();
return user;
}
}
/**
* SecurityConfig
*/
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
return new CustomUserDetailsService();
}
/**
* CustomAuthenticationProvider
*/
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
String loginId = authentication.getName();
String password = (String)authentication.getCredentials();
// 아이디 검증
UserDetails user = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(loginId);
if(user == null){
// 인증실패
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("UserNotFoundException");
}
// 비밀번호 검증
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
(user.getUsername(),user.getPassword(), user.getAuthorities());
}