Relational Databases
Databases
- Relational Databases
: Define relationships between tables of data inside the database
- More storage
- Secured with encryption(암호화)
- Many people can use at once
- A database can be a relational database even if not all tables are related to all other tables.
- 예시
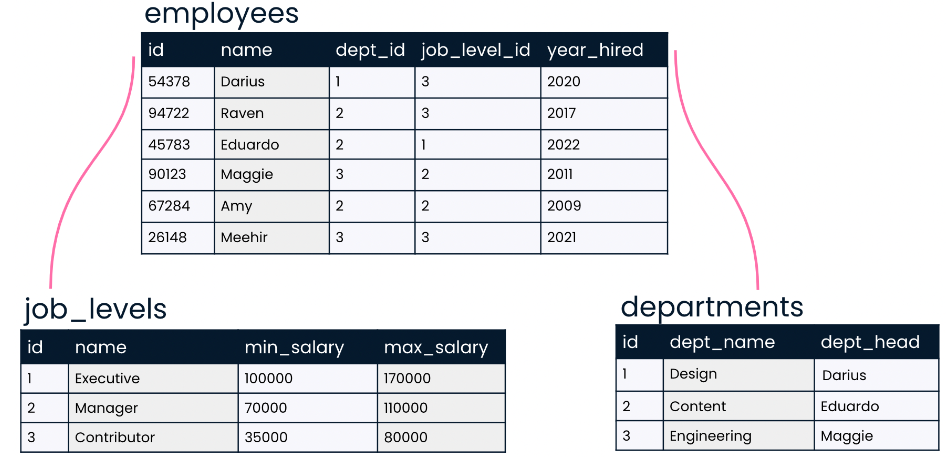
- This is a relational database containing three tables: employees, job_levels, and departments.
- SQL(Structured Query Language)
Tables
- rows(records), columns(fields)
Good table name
- 소문자
- 공백 X. _ 를 사용할 것
- 집합접 그룹 이름 혹은 복수
Good filed name
- 소문자
- 공백 X. _ 를 사용할 것
- 단수형: 단일 record에 대해 해당 field에 포함된 정보를 나타내기 때문
- table 이름과 같아서는 안된다
unique identifier(고유 식별자)
Data
데이터 유형을 지정
- string: VARCHAR
- integer: INT
- float: NUMERIC
Querying
Introducing queries
SELECT name, card_num
FROM patrons;
- 키워드: 대문자, 테이블 및 필드명: 소문자
- 쿼리 마지막:
; 로 끝내기
- 쉼표로 구분
- 모든 필드 선택:
*
Writting queries
- Aliasing:
AS
- 중복 제거:
DISTINCT
- View:
CREATE VIEW ... AS
- refer to it later, or allow others to access and use the results.
- 쿼리의 결과를 가상의 테이블로 만드는 것. 데이터베이스에 존재하는 일종의 가상 테이블.
- 실제 테이블처럼 행과 열을 가지고 있지만, 실제로 데이터를 저장하고 있지는 않는다. 즉 다른 테이블이나 다른 뷰에 저장되어 있는 데이터를 보여주는 역할만을 수행.
- 장점
- 특정 사용자에게 테이블 전체가 아닌 필요한 필드만을 보여줄 수 있습니다.
- 복잡한 쿼리를 단순화해서 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 쿼리를 재사용할 수 있습니다.
- 단점
- 한 번 정의된 뷰는 변경할 수 없습니다.
- 삽입, 삭제, 갱신 작업에 많은 제한 사항을 가집니다.
- 자신만의 인덱스를 가질 수 없습니다.
- 참고: http://www.tcpschool.com/mysql/mysql_view_createReplace
CREATE VIEW employee_hire_yerars AS
SELECT id, name, year_hired
FROM employees;
SQL flavors