1.문제
You are given an array of characters letters that is sorted in non-decreasing order, and a character target. There are at least two different characters in letters.
Return the smallest character in letters that is lexicographically greater than target. If such a character does not exist, return the first character in letters.
영어 알파벳이 오름차순으로 정렬되어있는 배열이 주어지고 특정 영어 알파벳인 target이 주어질 때 letters에서 사전 순서에서 target보다 큰 철자들 중 가장 사전 순서로 앞에 있는 철자를 리턴하는 문제이다. 만약 target보다 사전 순서가 뒤 인 알파벳이 없다면 letters[0]을 리턴하면 된다.
Example 1
Input: letters = ["c","f","j"], target = "a"
Output: "c"
Explanation: The smallest character that is lexicographically greater than 'a' in letters is 'c'.
Example 2
Input: letters = ["c","f","j"], target = "c"
Output: "f"
Explanation: The smallest character that is lexicographically greater than 'c' in letters is 'f'.
Example 3
Input: letters = ["x","x","y","y"], target = "z"
Output: "x"
Explanation: There are no characters in letters that is lexicographically greater than 'z' so we return letters[0].
Constraints:
- 2 <= letters.length <= 10^4
- letters[i] is a lowercase English letter.
- letters is sorted in non-decreasing order.
- letters contains at least two different characters.
- target is a lowercase English letter.
2.풀이
- letters를 반복 하면서 target보다 사전 순서가 뒤인 알파벳인지 확인한다.
/**
* @param {character[]} letters
* @param {character} target
* @return {character}
*/
const nextGreatestLetter = function (letters, target) {
let result = letters[0];
for (let i = 0; i < letters.length; i++) {
// target 보다 사전 순서가 크다면 result 에 저장 후 break
if (letters[i] > target) {
result = letters[i];
break;
}
}
return result;
};
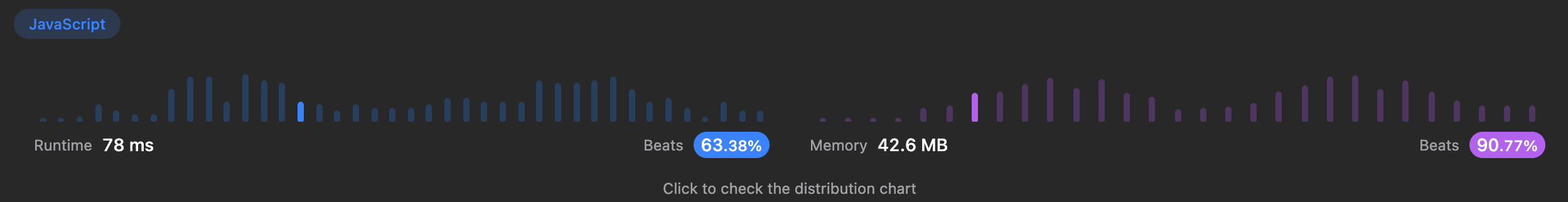
3.결과