다양한 방식으로 저장된 데이터를 읽고 쓰기 위한 공통된 방법을 제공
특징
- 외부 반복을 통해 작업하는 컬렉션과 달리 내부 반복(internal iteration)을 통해 작업을 수행한다.
- 재사용이 가능한 컬렉션과 달리 한 번만 사용할 수 있다.
- 원본 데이터를 변경하지 않는다.
- 필터-맵(filter-map) 기반의 API를 사용하여 지연(lazy) 연산을 통해 성능을 최적화한다.
- parallelStream() 메서드를 통한 손쉬운 병렬 처리를 지원한다.
- 배열, 컬렉션, 파일에 저장된 데이터도 모두 같은 방법으로 다룰 수 있다.
- 매개 변수로 함수형 인터페이스를 받는다.
- 람다식은 함수형 인터페이스를 반환한다.
동작 흐름
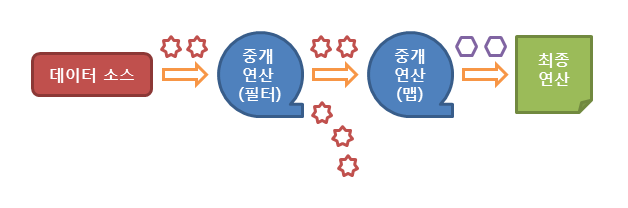
- 스트림의 생성
- 스트림의 중개 연산 (스트림의 변환)
- 스트림의 최종 연산 (스트림 사용)
1. 스트림 생성
컬렉션, 배열, 가변 매개변수, 지정된 범위의 연속된 정수, 특정 타입의 난수들, 람다 표현식, 파일, 빈 스트림 같은 다양한 데이터 소스에서 Stream API를 생성할 수 있다.
Collection
- 모든 컬렉션의 최고 상위 조상인
Collection인터페이스에는 스트림을 생성하는stream()이 정의되어 있다. parallelStream()으로 병렬 처리가 가능한 스트림을 생성할 수도 있다.
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(List.of(1, 4, 3, 2));
Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();
stream.forEach(System.out::println);<실행 결과>
1
4
3
2Stream.forEach(): 해당 스트림의 요소를 하나씩 소모해가며 순차적으로 접근한다.- 같은 스트림으로는 해당 메서드를 한 번밖에 호출할 수 없다.
- 원본 데이터를 소모하는 것이 아니다.
Array
Arrays클래스에 다양한stream()메서드가 클래스 메서드로 정의되어 있다.- 기본 타입을 저장할 수 있는 배열에 관한 스트림이 별도로 정의되어 있다.
- java.util.stream 패키지의 IntStream, LongStream, DoubleStream의 인터페이스로 각각 제공된다.
- 전체 배열뿐만 아니라 일부분의 스트림을 생성할 수 있다.
String[] array = new String[]{"하나", "넷", "셋", "둘"};
Stream<String> stream1 = Arrays.stream(array);
stream1.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e + " "));
System.out.println();
Stream<String> stream2 = Arrays.stream(array, 1, 3);
stream2.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e + " "));<실행 결과>
하나 넷 셋 둘
넷 셋Variable Parameter 가변 매개변수
Stream클래스의of()→ 가변 매개변수를 전달받아 스트림 생성 가능
Stream<Double> stream = Stream.of(4.2, 2.5, 3.1, 1.9)지정된 범위의 연속된 정수
IntStream과LongStream인터페이스에range(),rangeClosed()가 정의되어 있다.range(int begin, int end): begin ~ (end - 1)rangeClosed(int begin, int end): begin ~ end
IntStream stream1 = IntStream.range(1, 4);
stream1.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e + " "));
System.out.println();
IntStream stream2 = IntStream.range(1, 4);
stream2.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e + " "));<실행 결과>
1 2 3
1 2 3 4특정 타입의 난수
Random클래스의ints(),longs(),doubles()- 매개변수로 long 타입의 스트림의 크기를 전달받는다.
- 매개변수가 없다면 크기가 정해지지 않은 무한 스트림(infinite stream) 반환
- 이때 limit() 메서드로 따로 스트림의 크기를 제한해야 한다.
Random random = new Random();
IntStream stream = random.ints(4);
stream.forEach(System.out::println);<실행 결과>
1072176871
-649065206
133298431
-616174137Lambda Expression
- 매개변수로 전달받은 람다식의 반환값을 요소로 하는 무한 스트림
Stream클래스의iterate(),generate()iterate(): seed로 명시된 값을 람다식에 사용하여 반환된 값을 다시 시드로 사용하는 방식generate(): 매개변수가 없는 람다 표현식을 사용하여 반환된 값으로 무한 스트림 생성
IntStream stream = Stream.iterate(2, n -> n + 2); // 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, ..File
jva.nio.file.Files클래스의lines(): 파일의 한 행(line)을 요소로 하는 스트림java.nio.BufferedReader클래스의lines(): 파일뿐만 아니라 다른 입력으로부터도 데이터를 행 단위로 읽어올 수 있다.
Stream<String> stream = Files.lines(Path path);Empty Stream
- 아무 요소도 가지지 않는다.
Stream<Object> stream = Stream.empty();
System.out.println(stream.count());<실행 결과>
02. 중개 연산 intermediate operation
초기 스트림은 중개 연산을 통해 또 다른 스트림으로 변환된다.
연속으로 연결해서 사용할 수 있다.
filter-map 기반 API 사용 → 지연(lazy) 연산을 통해 성능 최적화한다.
- 스트림 필터링:
filter(),distinct() - 스트림 변환:
map(),flatMap() - 스트림 제한:
limit(),skip() - 스트림 정렬:
sorted() - 스트림 연산 결과 확인:
peek()
필터링
Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate): 주어진 조건(predicate)에 맞는 요소로만 구성된 새로운 스트림 반환Stream<T> distinct(): 중복된 요소가 제거된 새로운 스트림 반환- Object 클래스의 equals() 사용
IntStream stream1 = IntStream.of(7, 5, 5, 2, 1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 6);
IntStream stream2 = IntStream.of(7, 5, 5, 2, 1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 6);
stream1.distinct()
.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e + " "));
System.out.println();
stream2.filter(n -> n % 2 != 0)
.forEach(e -> System.out.print(e + " "));<실행 결과>
7 5 2 1 3 4 6
7 5 5 1 3 5변환
<R> Stream<R> map(Function<? super T, ? extends R> mapper): 요소들을 주어진 함수 인수로 전달하여 그 반환값들로 이루어진 새로운 스트림 반환<R> Stream<R> flatMap(Function<? super T, ? extends Stream<? extends R>> mapper): 스트림의 요소가 배열일 경우 배열의 각 요소의 반환값을 하나로 합친 새로운 스트림 반환
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("HTML", "CSS", "JAVA", "JAVASCRIPT");
stream.map(s -> s.length())
.forEach(System.out::println);<실행 결과>
4
3
4
10String[] array = {"Woowahan study", "clean architecture"};
Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(array);
stream.flatMap(s -> Stream.of(s.split(" ")))
.forEach(System.out::println);<실행 결과>
Woowahan
study
clean
architecture제한
Stream<T> limit(long maxSize): 첫 번째 요소부터 전달된 개수만큼의 요소만으로 이루어진 새로운 스트림 반환Stream<T> skip(long n): 첫 번째 요소부터 전달된 개수만큼의 요소를 제외한 나머지 요소만으로 이루어진 새로운 스트림 반환
IntStream stream1 = IntStream.range(0, 10);
IntStream stream2 = IntStream.range(0, 10);
IntStream stream3 = IntStream.range(0, 10);
stream1.limit(5)
.forEach(n -> System.out.print(n + " "));
System.out.println();
stream1.skip(4)
.forEach(n -> System.out.print(n + " "));
System.out.println();
stream1.skip(3)
.limit(5)
.forEach(n -> System.out.print(n + " "));<실행 결과>
0 1 2 3 4
4 5 6 7 8 9
3 4 5 6 7정렬
Stream<T> sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator): 주어진 비교자(comparator)를 이용하여 정렬한다.Stream<T>sorted(): 비교자를 전달하지 않으면 사전 편찬 순(natural order)으로 정렬한다.
Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of("JAVA", "HTML", "JAVASCRIPT", "CSS");
Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of("JAVA", "HTML", "JAVASCRIPT", "CSS");
stream1.sorted()
.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + " "));
System.out.println();
stream1.sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder())
.forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + " "));<실행 결과>
CSS HTML JAVA JAVASCRIPT
JAVASCRIPT JAVA HTML CSS연산 결과 확인
Stream<T> peek(Consumer<? super T> action): 원본 스트림이 아닌 결과 스트림으로부터 요소를 소모하여 추가로 명시된 동작을 수행한다.- 연산과 연산 사이 결과를 확인하고 싶을 때 사용한다. (디버깅)
IntStream stream = IntStream.of(7, 5, 5, 2, 1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 6);
stream1.peek(s -> System.out.println("원본 스트림: " + s))
.skip(2)
.peek(s -> System.out.println("skip(2) 실행 후: " + s))
.limit(5)
.peek(s -> System.out.println("limit(5) 실행 후: " + s))
.sorted()
.peek(s -> System.out.println("sorted() 실행 후: " + s))
.forEach(System.out::println);<실행 결과>
원본 스트림 : 7
원본 스트림 : 5
원본 스트림 : 5
skip(2) 실행 후 : 5
limit(5) 실행 후 : 5
원본 스트림 : 2
skip(2) 실행 후 : 2
limit(5) 실행 후 : 2
원본 스트림 : 1
skip(2) 실행 후 : 1
limit(5) 실행 후 : 1
원본 스트림 : 2
skip(2) 실행 후 : 2
limit(5) 실행 후 : 2
원본 스트림 : 3
skip(2) 실행 후 : 3
limit(5) 실행 후 : 3
sorted() 실행 후 : 1
1
sorted() 실행 후 : 2
2
sorted() 실행 후 : 2
2
sorted() 실행 후 : 3
3
sorted() 실행 후 : 5
53. 최종 연산 terminal operation
중개 연산을 통해 변환된 스트림은 최종 연산을 통해 각 요소를 소모하며 결과를 표시한다.
지연(lazy)되었던 모든 중개 연산들이 모두 수행되는 것
최종 연산 시 모든 요소를 소모한 스트림은 더는 사용할 수 없다.
- 요소의 출력:
forEach() - 요소의 소모:
reduce() - 요소의 검색:
findFirst(),findAny() - 요소의 검사:
anyMatch(),allMatch(),nonMatch() - 요소의 통계:
count(),min(),max() - 요소의 연산:
sum(),average() - 요소의 수집:
collect()
출력
void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action): 각 요소를 소모하여 명시된 동작 수행- 반환 타입이 void이므로 보통 요소를 출력하는 용도로 쓰인다.
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("JAVA", "HTML", "JAVASCRIPT", "CSS");
stream..forEach(System.out::println);<실행 결과>
JAVA
HTML
JAVASCRIPT
CSS소모
Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator): 첫 번째 요소와 두 번째 요소로 연산을 수행한 뒤, 그 결과와 세 번째 요소로 또다시 연산을 수행한다.T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator): 인수로 전달받은 초기값과 첫 번째 요소와 연산을 한 뒤, 그 결과와 두 번째 요소를 가지고 계속해서 연산을 수행한다.- 빈 스트림과 연산할 경우 초깃값을 그대로 반환한다.
Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of("JAVA", "HTML", "JAVASCRIPT", "CSS");
Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of("JAVA", "HTML", "JAVASCRIPT", "CSS");
Optional<String> result1 = stream1.reduce(s1, s2) -> s1 + "_" + s2);
result1.ifPresent(System.out::println);
String result2 = stream2.reduce("PYTHON", (s1, s2) -> s1 + "_" + s2);
System.out.println(result2);<실행 결과>
JAVA_HTML_JAVASCRIPT_CSS
PYTHON_JAVA_HTML_JAVASCRIPT_CSS검색
Optional<T> findFirst(),Optional<T> findAny(): 첫 번째 요소 참조- 빈 스트림에서는 비어있는 Optional 객체 반환
- 병렬 스트림의 경우
findAny()를 사용해야 정확한 연산 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
IntStream stream1 = IntStream.of(4, 2, 7, 3, 5, 1, 6);
IntStream stream2 = IntStream.of(4, 2, 7, 3, 5, 1, 6);
OptionalInt result1 = stream1.sorted().findFirst();
System.out.println(result1.getAsInt());
OptionalInt result2 = stream2.findAny();
System.out.println(result2.getAsInt());<실행 결과>
1
4검사
boolean anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate): 특정 조건을 만족하는 요소가 있는가boolean allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate): 특정 조건을 모두 만족하는가boolean noneMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate): 특정 조건을 모두 만족하지 않는가
IntStream stream1 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
IntStream stream2 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
System.out.println(stream1.anyMatch(n -> n == 70));
System.out.println(stream2.allMatch(n -> n > 80));<실행 결과>
true
false통계
long count(): 요소의 개수 반환Optional<T> max(Comparator<? super T> comparator),Optional<T> min(Comparator<? super T> comparator): 요소 중 가장 큰 값과 가장 작은 값의 요소를 참조하는 Optional 객체 반환
IntStream stream1 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
IntStream stream2 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
long result1 = stream1.count();
OptionalInt result2 = stream2.max();
System.out.println(result1);
System.out.println(result2.getAsInt());<실행 결과>
4
90연산
IntStream,DoubleStream같은 기본 타입 스트림의 제공 메서드T sum(): 모든 요소의 합 반환Optional<T> average(): 모든 요소의 평균값 반환
IntStream stream1 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
DoubleStream stream2 = DoubleStream.of(30.3, 90.9, 70.7, 10.1);
int result1 = stream1.sum();
OptionalDouble result2 = stream2.average();
System.out.println(result1);
System.out.println(result2.getAsDouble());<실행 결과>
200
50.5수집
<R,A> R collect(Collector<? super T,A,R> collector): 인수로 전달되는 Collectors 객체에 구현된 방법대로 스트림의 요소를 수집한다.Collector클래스에는 미리 정의된 다양한 방법이 정적 메서드로 정의되어 있다.- 스트림을 배열이나 컬렉션으로 변환:
toArray()toCollection()toList()toSet()toMap() - 요소의 통계, 연산:
counting()maxBy()minBy()summingInt()averagingInt() - 요소의 소모:
reducing()joining() - 요소의 그룹화와 분할:
groupingBy()partitioningBy()
- 스트림을 배열이나 컬렉션으로 변환:
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("JAVA", "HTML", "JAVASCRIPT", "CSS");
List<String> list = stream.collect(Collectors.toList());
Iterator<String> iter = list.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iter.next() + " ");
}<실행 결과>
JAVA HTML JAVASCRIPT CSSStream<String> stream = Stream.of("JAVA", "PHP", "JAVASCRIPT", "CSS");
Map<Boolean, List<String>> partition = stream.collect(
Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.length() % 2 == 0));
List<String> oddLengthList = partition.get(false);
System.out.println(oddLengthList);
List<String> evenLengthList = partition.get(true);
System.out.println(evenLengthList);<실행 결과>
[PHP, CSS]
[JAVA, JAVASCRIPT]