DFS 예제
기본 예제
얼음트레이에서 만들어지는 얼음 개수
내 초기답안
import sys
import time
sys.stdin = open('input_01.txt')
current = time.time()
# U, D, R, L
dx = (0, 0, 1, -1)
dy = (-1, 1, 0, 0)
def dfs(graph, vertex, visited, N, M):
x, y = vertex
if x < 0 or x >= M or y < 0 or y >= N or visited[y][x] or graph[y][x] == 1:
return False
visited[y][x] = True
for dx_, dy_ in zip(dx, dy):
dfs(graph, (x+dx_, y+dy_), visited, N, M)
return True
N, M = map(int, input().split())
graph = [list(map(int, input())) for _ in range(N)]
visited = [[False] * M for _ in range(N)]
cnt = 0
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if not graph[i][j] and not visited[i][j]:
if dfs(graph, (j, i), visited, N, M):
cnt += 1
# print(graph)
# print(visited)
print(cnt)
print(time.time() - current)참고 답안
import sys
import time
sys.stdin = open('input_01.txt')
current = time.time()
# N, M을 공백을 기준으로 구분하여 입력 받기
n, m = map(int, input().split())
# 2차원 리스트의 맵 정보 입력 받기
graph = []
for i in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int, input())))
# DFS로 특정한 노드를 방문한 뒤에 연결된 모든 노드들도 방문
def dfs(x, y):
# 주어진 범위를 벗어나는 경우에는 즉시 종료
if x <= -1 or x >= n or y <= -1 or y >= m:
return False
# 현재 노드를 아직 방문하지 않았다면
if graph[x][y] == 0:
# 해당 노드 방문 처리
graph[x][y] = 1
# 상, 하, 좌, 우의 위치들도 모두 재귀적으로 호출
dfs(x - 1, y)
dfs(x, y - 1)
dfs(x + 1, y)
dfs(x, y + 1)
return True
return False
# 모든 노드(위치)에 대하여 음료수 채우기
result = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
# 현재 위치에서 DFS 수행
if dfs(i, j) == True:
result += 1
print(result) # 정답 출력
print(time.time() - current)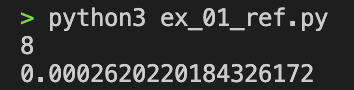
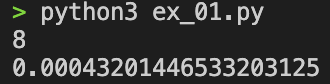
실행시간이 꽤 많이 차이난다. 알고리즘 문제를 수학문제처럼 통일된 방법으로 풀고 싶었는데 시간 복잡도를 스스로 해칠 수는 없으니깐 visited 리스트를 제거하고 분기점을 최소화하는 방향으로 수정하고자 한다.
백준 1012
배추밭 흰지렁이 개수 구하기
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(100000)
sys.stdin = open('input_bj_1012.txt')
input = sys.stdin.readline
# U, D, L, R
d = [(0, -1), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (1, 0)]
def dfs(v):
x, y = v
graph[y][x] = 0
for dx, dy in d:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if nx < 0 or nx >= M or ny < 0 or ny >= N or not graph[ny][nx]:
continue
dfs((nx, ny))
for _ in range(int(input())):
# input
M, N, K = map(int, input().split())
graph = [[0] * M for _ in range(N)]
for _ in range(K):
x, y = map(int, input().split())
graph[y][x] = 1
# traverse
cnt = 0
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if graph[i][j]:
dfs((j, i))
cnt += 1
print(cnt)회고
입력 받는 값 중, N, M의 최대값은 50이다. 파이썬에 recursion max는 1500으로 탐색 횟수 최대값 2500보다 작기 때문에 recursion max값을 조정할 필요가 있다.
BFS 예제
백준 1260
단순한 bfs, dfs 적용 traverse
from collections import deque
import sys
sys.stdin = open('input_bj_1260.txt')
def dfs(graph, vertex, visited):
if visited[vertex]:
return
print(vertex, end=' ')
visited[vertex] = True
for v in graph[vertex]:
dfs(graph, v, visited)
def bfs(graph, vertex, visited):
q = deque([vertex])
visited[vertex] = True
while q:
vertex = q.popleft()
print(vertex, end=' ')
for v in graph[vertex]:
if not visited[v]:
visited[v] = True
q.append(v)
N, M, start = map(int, input().split())
visited = [False] * (N+1)
graph = [[] for _ in range(N+1)]
for m in range(M):
x, y = map(int, input().split())
if y not in graph[x]:
graph[x].append(y)
if x not in graph[y]:
graph[y].append(x)
graph = [sorted(element) for element in graph]
dfs(graph, start, visited)
print()
visited = [False] * (N+1)
bfs(graph, start, visited)회고
readline과 그냥 input의 시간 차이가 크다.
어려울 것 없이 기계마냥 바로 써내려갔다 ㅋ
백준 2667
아파트 단지 개수와 구성 아파트 개수
from collections import deque
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
# sys.stdin = open('input_bj_2667.txt')
# U, D, L, R
dx = (0, 0, -1, 1)
dy = (-1, 1, 0, 0)
def bfs(x, y):
cnt = 0
q = deque([(x, y)])
graph[y][x] = 0
while q:
# print(q)
cnt += 1
x, y = q.popleft()
for dx_, dy_ in zip(dx, dy):
tmp_x = x + dx_
tmp_y = y + dy_
if tmp_x < 0 or tmp_x >= N or tmp_y < 0 or tmp_y >= N or not graph[tmp_y][tmp_x]:
continue
q.append((tmp_x, tmp_y))
graph[tmp_y][tmp_x] = 0
# print()
return cnt
# input
N = int(input())
graph = [list(map(int, input().strip())) for _ in range(N)]
block_cnt = 0
arr_cnt = []
# traverse
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if not graph[i][j]:
continue
# print(*graph, sep='\n')
# print()
arr_cnt.append(bfs(j, i))
block_cnt += 1
arr_cnt.sort()
# output
print(block_cnt)
print(*arr_cnt, sep='\n')회고
if tmp_x < 0 or tmp_x >= N or tmp_y < 0 or tmp_y >= N or not graph[tmp_y][tmp_x]:-
이 조건문에서 걸러지는 비중이 높은
not graph[tmp_y][tmp_x]를 앞에 두면 안된다. index error를 피해가기 위해서는 앞의 조건을 먼저 따져야하기 때문. -
readline은
\n도 받아버리기 때문에 strip() 필수.
어려웠던 것
백준 1987 문제
겹치지 않게 알파벳 바닥에서 최대한 멀리 가기
import sys
import time
sys.stdin = open('./search/input_bj_1987.txt')
input = sys.stdin.readline
current = time.time()
# U, D, L, R
d = [(0, -1), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (1, 0)]
def dfs(v, alphas=[], cnt=0):
x, y = v
cnt += 1
alphas.append(graph[y][x])
for dx, dy in d:
nx, ny = x+dx, y+dy
if nx < 0 or nx >= C or ny < 0 or ny >= R or (graph[ny][nx] in alphas):
continue
v = nx, ny
dfs(v, alphas, cnt)
alphas.pop()
global max_cnt
max_cnt = max(max_cnt, cnt)
# input
R, C = map(int, input().split())
graph = [list(input().strip()) for _ in range(R)]
start = (0, 0)
# output
max_cnt = 0 # global variable
dfs(start)
print(max_cnt)
# print(time.time() - current)시간 초과로 안된다.
import sys
import time
sys.stdin = open('./search/input_bj_1987.txt')
input = sys.stdin.readline
current = time.time()
# U, D, L, R
d = [(0, -1), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (1, 0)]
def dfs(v, cnt=0):
x, y = v
cnt += 1
alphas[ord(graph[y][x]) - ord('A')] = 1
for dx, dy in d:
nx, ny = x+dx, y+dy
if nx < 0 or nx >= C or ny < 0 or ny >= R or (alphas[ord(graph[ny][nx]) - ord('A')]):
continue
v = nx, ny
dfs(v, cnt)
alphas[ord(graph[ny][nx]) - ord('A')] = 0
global max_cnt
max_cnt = max(max_cnt, cnt)
# input
R, C = map(int, input().split())
graph = [list(input().strip()) for _ in range(R)]
alphas = [0] * 26
start = (0, 0)
# output
max_cnt = 0 # global variable
dfs(start)
print(max_cnt)
# print(time.time() - current)정답 처리가 됐을 뿐, 사실상 시간 초과
우수 코드
비트 연산을 활용하고 memoization으로 불필요한 연산 제거
R,C = map(int,input().split())
arr = [list(input()) for _ in range(R)]
check = [[0]*C for _ in range(R)]
A = ord('A')
stack = [(0,0,1,1<<(ord(arr[0][0])-A))]
result = 0
dx = [-1,1,0,0]
dy = [0,0,1,-1]
while stack:
x,y,cnt,total = stack.pop()
if result < cnt:
result = cnt
if result == 26:
break
for i in range(4):
nx = x + dx[i]
ny = y + dy[i]
if 0 <= nx < R and 0<= ny <C:
if (total & (1<<ord(arr[nx][ny])- A)) == 0:
temp = total | (1<<(ord(arr[nx][ny])-A))
if check[nx][ny] != temp:
check[nx][ny] = temp
stack.append((nx,ny,cnt+1,temp))
print(result)감격스러운 우수코드.
씹고 뜯고 내 것으로 만들자.
