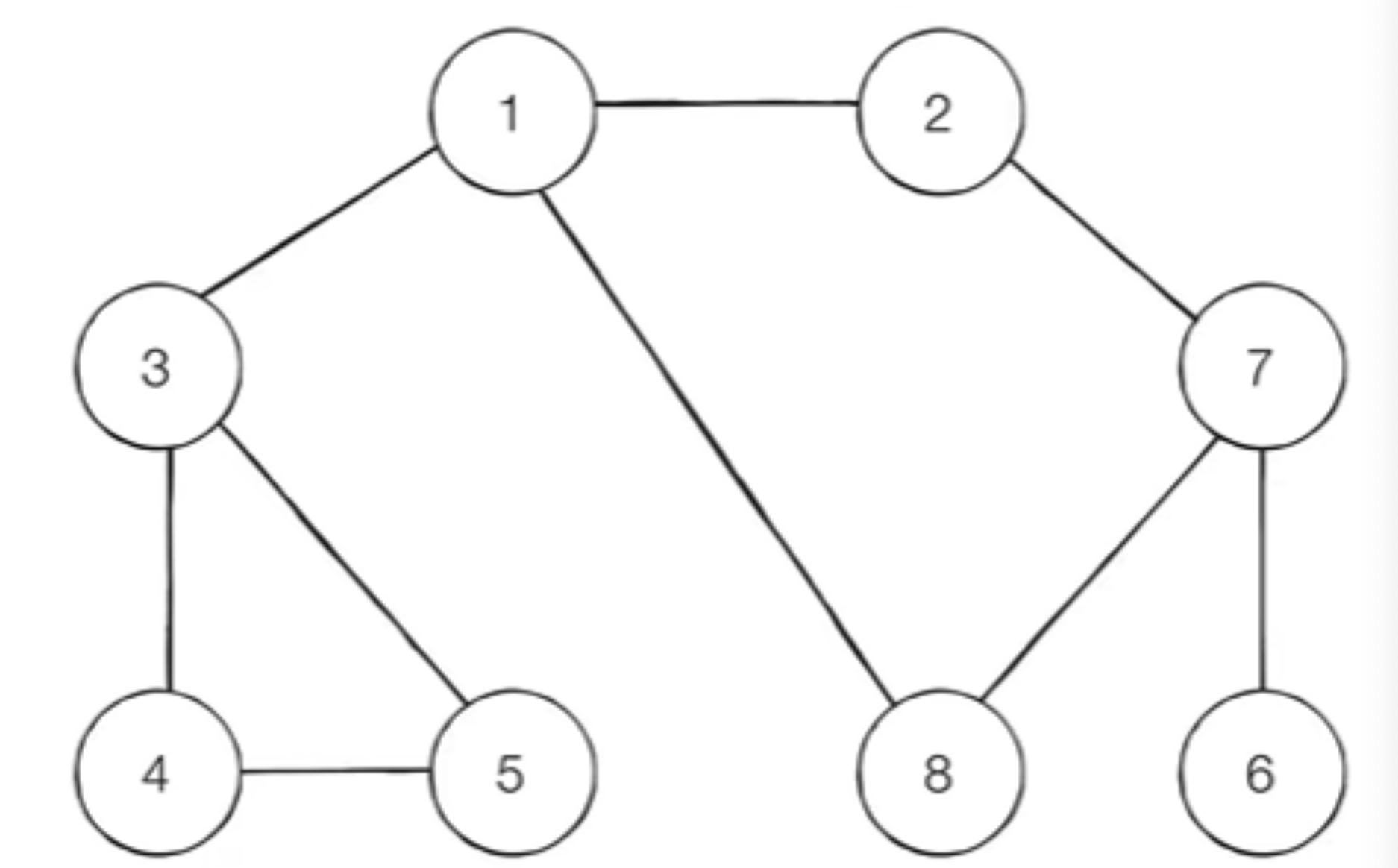
깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)
- 동작 원리 : 스택
- 구현 방법 : 재귀 함수 사용
- 탐색 순서 : 1 -> 2 -> 7 -> 6 -> 8 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
- 수행 과정
- 탐색 시작 노드를 스택에 삽입하고 방문 처리를 한다.
- 스택의 최상단 노드에 방문하지 않은 인접한 노드가 하나라도 있으면 그 노드를 스택에 넣고 방문 처리하고 방문하지 않은 인접 노드가 없으면 스택에서 최상단 노드를 꺼낸다.
- 2번의 과정을 더 이상 수행할 수 없을 때까지 반복한다.
깊이 우선 탐색
public class Main
{
public final static int GRAPH_LIST_SIZE = 9;
public static boolean[] visitedFlag = new boolean[GRAPH_LIST_SIZE];
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 리스트 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < GRAPH_LIST_SIZE; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
// 노드 1에 연결된 노드 정보를 저장
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(1).add(3);
graph.get(1).add(8);
// 노드 2에 연결된 노드 정보를 저장
graph.get(2).add(1);
graph.get(2).add(7);
// 노드 3에 연결된 노드 정보를 저장
graph.get(3).add(1);
graph.get(3).add(4);
graph.get(3).add(5);
// 노드 4에 연결된 노드 정보를 저장
graph.get(4).add(3);
graph.get(4).add(5);
// 노드 5에 연결된 노드 정보를 저장
graph.get(5).add(3);
graph.get(5).add(4);
// 노드 6에 연결된 노드 정보를 저장
graph.get(6).add(7);
// 노드 7에 연결된 노드 정보를 저장
graph.get(7).add(2);
graph.get(7).add(6);
graph.get(7).add(8);
// 노드 8에 연결된 노드 정보를 저장
graph.get(8).add(1);
dfs(1);
}
public static void dfs(int point) {
// 현재 노드 방문 처리하기
visitedFlag[point] = true;
System.out.print(point + " ");
// 인접 노드 방문
for(int node : graph.get(point)) {
if(!visitedFlag[node]) {
dfs(node);
}
}
}
}너비 우선 탐색(BFS)
- 동작 원리 : 큐
- 구현 방법 : 큐 자료 구조 사용
- 탐색 순서 : 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 8 -> 7 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6
- 수행 과정
1. 탐색 시작 노드를 큐에 삽입하고 방문 처리를 한다.- 큐에서 노드를 꺼낸 뒤에 해당 노드의 인접 노드 중에서 방문하지 않은 노드를 모두 큐에 삽입하고 방문 처리를 한다.
- 2번의 과정을 더 이상 수행할 수 없을 때 까지 반복한다.
너비 우선 탐색
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public final static int GRAPH_LIST_SIZE = 9;
public static boolean[] visitedFlag = new boolean[GRAPH_LIST_SIZE];
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 리스트 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < GRAPH_LIST_SIZE; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
// 노드 1에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(1).add(3);
graph.get(1).add(8);
// 노드 2에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(2).add(1);
graph.get(2).add(7);
// 노드 3에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(3).add(1);
graph.get(3).add(4);
graph.get(3).add(5);
// 노드 4에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(4).add(3);
graph.get(4).add(5);
// 노드 5에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(5).add(3);
graph.get(5).add(4);
// 노드 6에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(6).add(7);
// 노드 7에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(7).add(2);
graph.get(7).add(6);
graph.get(7).add(8);
// 노드 8에 연결된 노드 정보 저장
graph.get(8).add(1);
graph.get(8).add(7);
bfs(1);
}
// BFS 탐색을 위한 재귀함수
public static void bfs(int point){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
// 현재 노드 방문 처리
queue.offer(point);
visitedFlag[point] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int target = queue.poll();
System.out.print(target + " ");
// 인접 노드 방문
for(int node : graph.get(target)){
if(!visitedFlag[node]){
queue.offer(node);
visitedFlag[node] = true;
}
}
}
}
}DFS와 다르게 재귀 함수 로직이 존재하지 않고
초기 점을 큐에 넣고 그 뒤부터는 큐가 empty 될 때까지 반복문을 돌려 큐에 남아있는 노드와 인접한 노드들을 다 방문하는 구조입니다.
예시 문제
백준의 촌수계산 문제가 DFS로 표현하기 좋은 문제라 예시로 가져왔습니다.
백준 촌수계산 (https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2644)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
static boolean[] visitedFlag;
static int answer = -1;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
// 부모 - 자식 1촌
// 나 - 할아버지 2촌
// 나 - 아버지 형제 - 3촌
// 나를 기준으로 촌수 정하기
// 할아버지(2촌)
// 아버지(1촌) 아버지 형제(3촌)
// 나
// 입력 파일의 첫째 줄에는 전체 사람의 수 n이 주어지고,
// 둘째 줄에는 촌수를 계산해야 하는 서로 다른 두사람의 번호가 주어진다
// 셋째 줄에는 부모 자식들 간의 관계수 m이 주어진다.
// 넷째 줄부터는 부모 자식간의 관계를 나타내는 두 번호 x, y
// 이때 앞에 나오는 번호 x는 뒤에 나오는 정수 y의 부모 번호를 나타낸다.
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); // 전체 사람의 수
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int person1 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int person2 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 촌수를 계산해야 하는 서로 다른 두 사람의 번호
int m = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); // 부모 자식들 간의 관계 수 m
visitedFlag = new boolean[n+1];
// 리스트 초기화
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 부모
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 자식
graph.get(x).add(y);
graph.get(y).add(x);
}
dfs(person1,person2,0);
bw.write(answer+"");
bw.flush();
br.close();
bw.close();
}
static void dfs(int start, int end, int count) {
if (start == end) {
answer = count;
}
// 현재 노드 방문 처리
visitedFlag[start] = true;
for (int node : graph.get(start)) {
// 방문을 안 한
if (!visitedFlag[node]) {
dfs(node, end, count+1);
}
}
}
}초기점(자식)과 끝점(부모)를 지정해주고 인접리스트에 자식노드와 부모노드를 넣어준 뒤에, 자식에서 부모까지 깊이 우선 탐색 방식으로 몇 회 이동하는지에 대한 로직으로 구성했습니다.
