
Introducing BloombergGPT
Introducing BloombergGPT, Bloomberg’s 50-billion parameter large language model, purpose-built from scratch for finance
BloombergGPT outperforms similarly-sized open models on financial NLP tasks by significant margins — without sacrificing performance on general LLM benchmarks
NEW YORK – Bloomberg today released a research paper detailing the development of BloombergGPTTM, a new large-scale generative artificial intelligence (AI) model. This large language model (LLM) has been specifically trained on a wide range of financial data to support a diverse set of natural language processing (NLP) tasks within the financial industry.
Recent advances in Artificial Intelligence (AI) based on LLMs have already demonstrated exciting new applications for many domains. However, the complexity and unique terminology of the financial domain warrant a domain-specific model. BloombergGPT represents the first step in the development and application of this new technology for the financial industry. This model will assist Bloomberg in improving existing financial NLP tasks, such as sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, news classification, and question answering, among others. Furthermore, BloombergGPT will unlock new opportunities for marshalling the vast quantities of data available on the Bloomberg Terminal to better help the firm’s customers, while bringing the full potential of AI to the financial domain.
For more than a decade, Bloomberg has been a trailblazer in its application of AI, Machine Learning, and NLP in finance. Today, Bloomberg supports a very large and diverse set of NLP tasks that will benefit from a new finance-aware language model. Bloomberg researchers pioneered a mixed approach that combines both finance data with general-purpose datasets to train a model that achieves best-in-class results on financial benchmarks, while also maintaining competitive performance on general-purpose LLM benchmarks.
To achieve this milestone, Bloomberg’s ML Product and Research group collaborated with the firm’s AI Engineering team to construct one of the largest domain-specific datasets yet, drawing on the company’s existing data creation, collection, and curation resources. As a financial data company, Bloomberg’s data analysts have collected and maintained financial language documents over the span of forty years. The team pulled from this extensive archive of financial data to create a comprehensive 363 billion token dataset consisting of English financial documents.
This data was augmented with a 345 billion token public dataset to create a large training corpus with over 700 billion tokens. Using a portion of this training corpus, the team trained a 50-billion parameter decoder-only causal language model. The resulting model was validated on existing finance-specific NLP benchmarks, a suite of Bloomberg internal benchmarks, and broad categories of general-purpose NLP tasks from popular benchmarks (e.g., BIG-bench Hard, Knowledge Assessments, Reading Comprehension, and Linguistic Tasks). Notably, the BloombergGPT model outperforms existing open models of a similar size on financial tasks by large margins, while still performing on par or better on general NLP benchmarks.
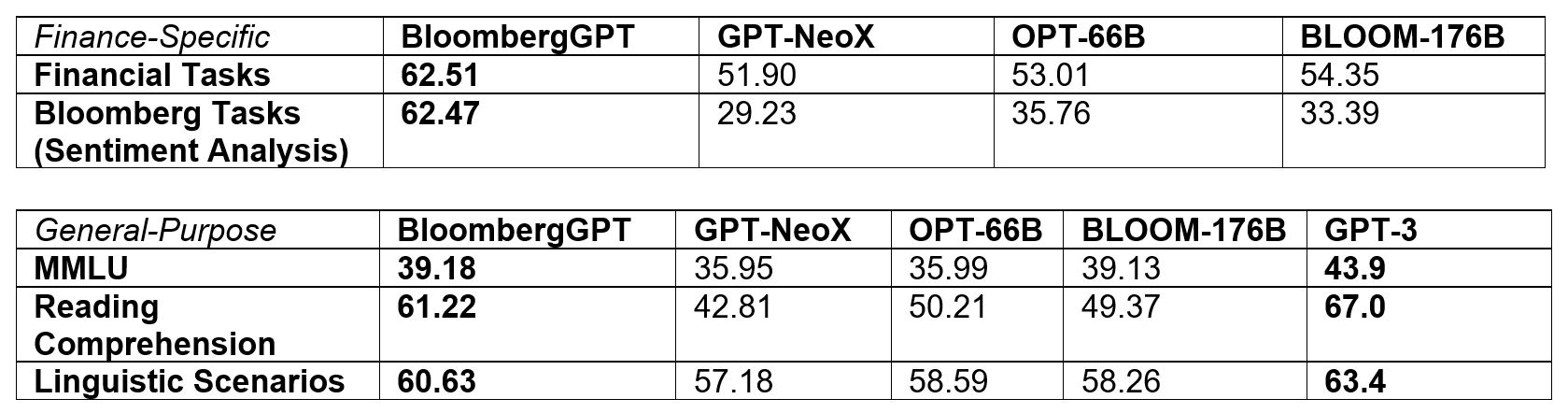
Table 1. How BloombergGPT performs across two broad categories of NLP tasks: finance-specific and general-purpose.
“For all the reasons generative LLMs are attractive – few-shot learning, text generation, conversational systems, etc. – we see tremendous value in having developed the first LLM focused on the financial domain,” said Shawn Edwards, Bloomberg’s Chief Technology Officer. “BloombergGPT will enable us to tackle many new types of applications, while it delivers much higher performance out-of-the-box than custom models for each application, at a faster time-to-market.”
“The quality of machine learning and NLP models comes down to the data you put into them,” explained Gideon Mann, Head of Bloomberg’s ML Product and Research team. “Thanks to the collection of financial documents Bloomberg has curated over four decades, we were able to carefully create a large and clean, domain-specific dataset to train a LLM that is best suited for financial use cases. We’re excited to use BloombergGPT to improve existing NLP workflows, while also imagining new ways to put this model to work to delight our customers.”
For more details about the development of BloombergGPT, read the paper on arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.17564.
Introducing BloombergGPT... (Bloomberg, March 30, 2023)
Bloomberg plans to integrate GPT-style A.I. into its terminal
How it could be used
Bloomberg says that Bloomberg GPT, an internal AI model, can more accurately answer questions like “CEO of Citigroup Inc?”, assess whether headlines are bearish or bullish for investors, and even write headlines based on short blurbs.
One early application would be to transform human language into the specific database language that Bloomberg’s software uses.
For example, it would transform “Tesla price” into ”(get(px_last) for([‘TSLA US Equity’])”.
Another possibility would be for the model to do behind-the-scenes work cleaning data and doing other errands on the application’s back end.
But Bloomberg is also looking at using artificial intelligence to power features that could help financial professionals save time and stay on top of the news.
Bloomberg plans to integrate GPT-style A.I. into its terminal (CNBC, APR 13 2023)
Paper Review: BloombergGPT: A Large Language Model for Finance
BloombergGPT is
BloombergGPT, a 50 billion parameter language model that supports a wide range of tasks within the financial industry.
Dataset are
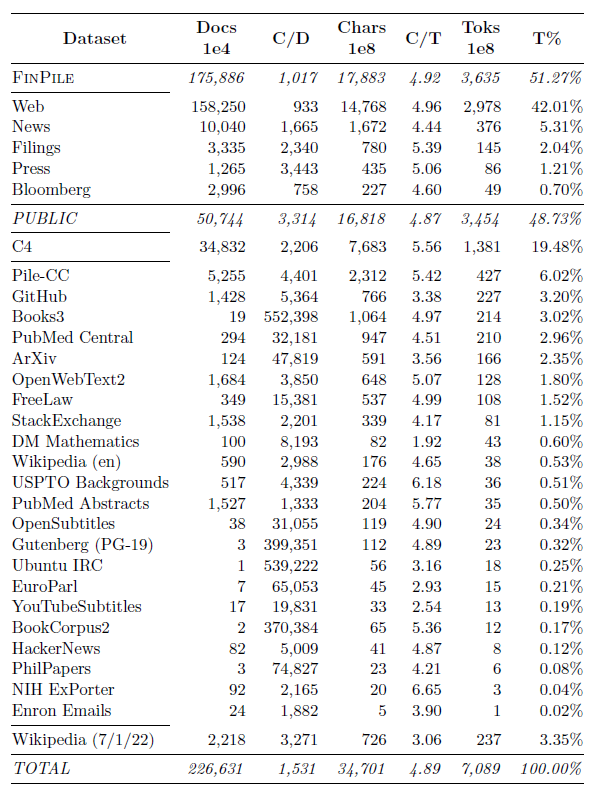
"FinPile" :
a comprehensive dataset consisting of a range of English financial documents including news, filings, press releases, web-scraped financial documents, and social media drawn from the Bloomberg archives.
Note that each document in FinPile is time-stamped, with dates ranging from 2007-03-01 to 2022-07-31; the quality and quantity of documents increase over this time range.
The Pile :
the dataset used in GPT-Neo (Black et al., 2021), GPTJ
(Wang and Komatsuzaki, 2021), and GPT-NeoX (20B) (Black et al., 2022).
The Colossal Clean Crawled Corpus (C4) :
a common dataset used to train LLMs, and C4 was introduced to support training T5 (Raffel et al., 2020).
Wikipedia :
Both The Pile and C4 include out-of-date copies of Wikipedia.
Tokenization is
Unigram Tokenizer
Base Model is
Our model is a decoder-only causal language model based on BLOOM (Scao et al., 2022).
BigScience Large Open-science Open-access Multilingual Language Model (BLOOM) is a transformer-based large language model. It was created by over 1000 AI researchers to provide a free large language model for everyone who wants to try. Trained on around 176 billion parameters over March through July 2022, it is considered an alternative to OpenAI's GPT-3 trained on 176 billion parameters. BLOOM uses a decoder-only transformer model architecture modified from Megatron-LM GPT-2.
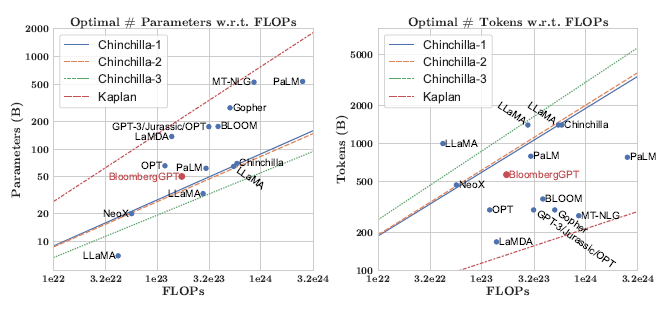
Model Size is
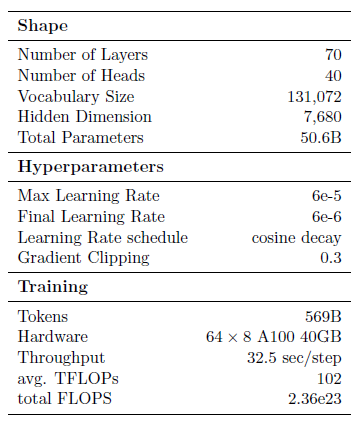
Model Shape is
Training Method is
BloombergGPT is a PyTorch model trained with a standard left-to-right causal language modeling objective.
Optimization Method is
We use the AdamW optimizer (Loshchilov and Hutter, 2019). We set
β₁ to 0.9, β₂ to 0.95, and weight decay to 0.1.
Training Result is
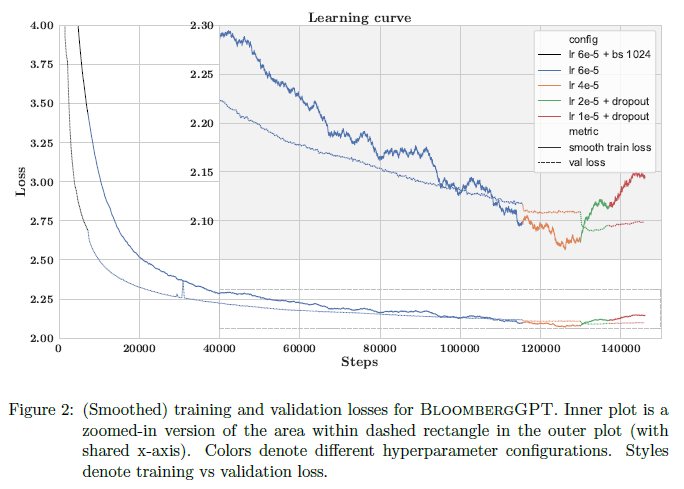

Evaluation
We evaluated the performance of BloombergGPT on two broad categories of tasks:
finance-specific and general purpose.
Finance-Specific :
The finance-specific tasks help us test our hypothesis that training on high-quality finance-specific data will yield better results on financial tasks.
->
다양한 사례와 결과 이후 These results further underscore the advantage of BloombergGPT for financial tasks.
General Purpose :
The general purpose tasks investigate whether the performance of our model is directly comparable to previously published results.
->
BIG-bench Hard, Knowledge Assessments, Reading Comprehension, Linguistic Tasks 등등 다양한 주제로 BloombergGPT, GPT-NeoX, OPT66B, BLOOM176B, GPT-3 등 비교함.
Summary :
Among the models with tens of billions of parameters that we compare to, BloombergGPT performs the best. Furthermore, in some cases, it is competitive or exceeds the performance of much larger models (hundreds of billions of parameters).
암튼 모델 잘 만들었다는 소리.