반복문
반복문의 종류는 for, while, do-while
for문
for 사용법 및 순서
for( ①초기화식; ②조건식; ④증감식){
③실행문;
}
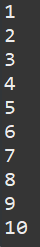
ex) Ch04_9_forPrintFrom1To10Example
public class Ch04_9_forPrintFrom1To10Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i =1; i <= 10; i++) {
// ①초기화식; ②조건식; ④증감식
System.out.println(i);
// ③실행문;
}
}
}
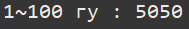
ex) Ch04_10_ForSumFrom1To100Example1
public class Ch04_10_ForSumFrom1To100Example1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("1~100 гу : " + sum);
}
}
ex)Ch04_10_ForSumFrom1To100Example2 (전역변수 지역변수 예제)
public class Ch04_10_ForSumFrom1To100Example2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int i = 0; //전역변수로 함수 외부에 선언해야됨
for(i=1; i<=100; i++) {
//위의 전역변수가 없다면 i는 for문 안에서만 활동하는 지역변수라 오류가 발생
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("1~" + (i-1) + " гу : " + sum);
}
}
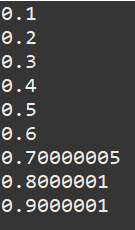
ex) flaot 타입 카운터 변수
public class ForFloatCounterExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(float x= 0.1f; x<=1.0f; x+=0.1f) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
ex) ForMultiplicationTableExample (중첩 for문으로 구구단 출력하기)
public class ForMultiplicationTableExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int m=2; m<=9; m++) {
System.out.println("*** " + m + "단 ***");
for(int n=1; n<=9; n++) {
System.out.println(m + " x " + n + " = " + (m*n));
}
}
}
}2단부터 9단까지 출력됩니다.
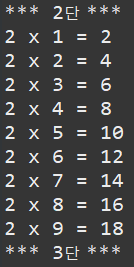

while
- while 사용법 및 순서
while( ①조건식 ) {
②실행문; //조건식이 true일 경우 (반복영역)
}
//조건식이 false일 경우 반복문을 빠져나옴
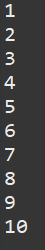
ex) WhilePrintFrom1To10Example (while문을 사용해서 1부터 100까지 출력)
public class WhilePrintFrom1To10Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i<=10) {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}
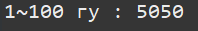
ex) Ch04_12_WhileSumForm1To100Example(while문을 사용해서 1부터 100까지 합을 출력)
public class Ch04_12_WhileSumForm1To100Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
while(i<=100) {
sum += i;
i++;
}
System.out.println("1~" + (i-1) + " гу : " + sum);
}
}
do-while
- do-while 사용법 및 순서
do{
① 실행문;//최초실행
} while ( ②조건식 );
- do-while문이 처음 실행될 때 실행문(①)을 우선 실행합니다.
- 실행문(①)이 모두 실행되면 조건식(②)을 평가합니다.
- 조건식의 결과가 true이면 실행문(①) -> 조건식(②)과 같이 반복 실행을 합니다.
- 조건식의 결과가 false이면 do-while문을 종료합니다.
break
- break문은 반복문인 for문, while문, do-while문의 실행을 중지 할 때 사용됩니다.
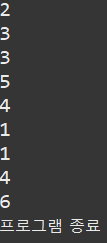
ex)Ch04_13_BreakExample
public class Ch04_13_BreakExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
while(true) {
int num = (int)(Math.random()*6) + 1; //무한대로 1~6까지 숫자를 출력
System.out.println(num); // 만약에 임의의 숫자가 6이면
if(num == 6) { //임의의 숫자가 6이 나오면 break를 만나서 종료
break;
}
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
}
}
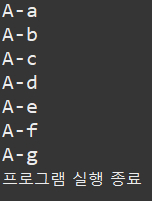
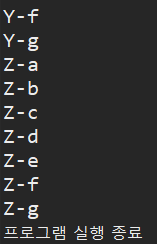
ex) Ch04_14_BreakOutterExample
public class Ch04_14_BreakOutterExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Outter:
for(char upper='A'; upper<='Z'; upper++) {
for(char lower='a'; lower<='z'; lower++) {
System.out.println(upper + "-" + lower);
if(lower=='g') { //lower=='g'면
break Outter; //break를 만나 :Outter를 빠져나감
//일반적인 break는 가장 가까이에 있는 반복문을 멈추게함 예제결과 2에서 확인
}
}
}
System.out.println("프로그램 실행 종료");
}
}
예제결과2 Outter가 없는 break문 작성시
continue
continue문은 반복문인 for문, while문, do-while문에서만 사용되고
블록 내부에서 continue문이 실행되면 for문의 증감식 또는 while문, do-while문의 조건식으로 이동한다.
ex)Ch04_15_ContinueExample
public class Ch04_15_ContinueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) { //ⓐ
if(i%2 != 0) { //i%2 나머지가 0이 아니면 -> 홀수면
continue; //continue문을 만나 조건식을 다시 시작함 ⓐ로 이동
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}