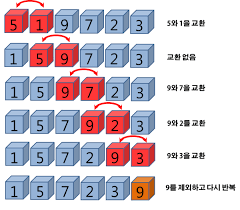
버블 정렬
두 인접한 데이터의 크기를 비교해 정렬하는 방법
시간 복잡도 - swap 여부를 판단 할 수 있는 변수를 두지 않고 하는 구현의 경우는 O(N2), swap여부를 판단할 수 있는 변수를 둔 경우 O(N)
import java.util.Arrays;
public class 버블정렬 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 10;
int[] arr = {7, 5, 9, 0, 3, 1, 6, 2, 4, 8};
Arrays.sort(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (arr[i] == arr[i + 1]) {
System.out.print("D");
return;
}
}
System.out.print("U");
}
}
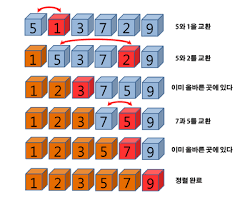
선택 정렬
대상 데이터에서 최대나 최소 데이터를 데이터가 나열된 순으로 찾아가며 선택하는 방법
시간복잡도 - O(N^)
정렬 된 상태 최선의 경우 O(N)의 시간 복잡도를 갖게 됨
public class 선택정렬 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 10;
int[] arr = { 7, 5, 9, 0, 3, 1, 6, 2, 4, 8 };
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int min_index = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[min_index] > arr[j]) {
min_index = j;
}
}
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[min_index];
arr[min_index] = temp;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
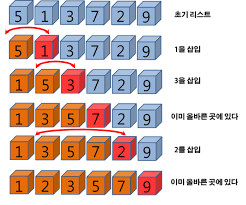
삽입 정렬
이미 정렬된 데이터 범위에 종렬되지 않은 데이터를 적절한 위치에 삽입 시켜 정렬하는 방식
시간 복잡도 - O(N^)
public class 삽입정렬 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 10;
int[] arr = { 7, 5, 9, 0, 3, 1, 6, 2, 4, 8 };
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j - 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
arr[j - 1] = temp;
} else
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
