📌relational data model
-
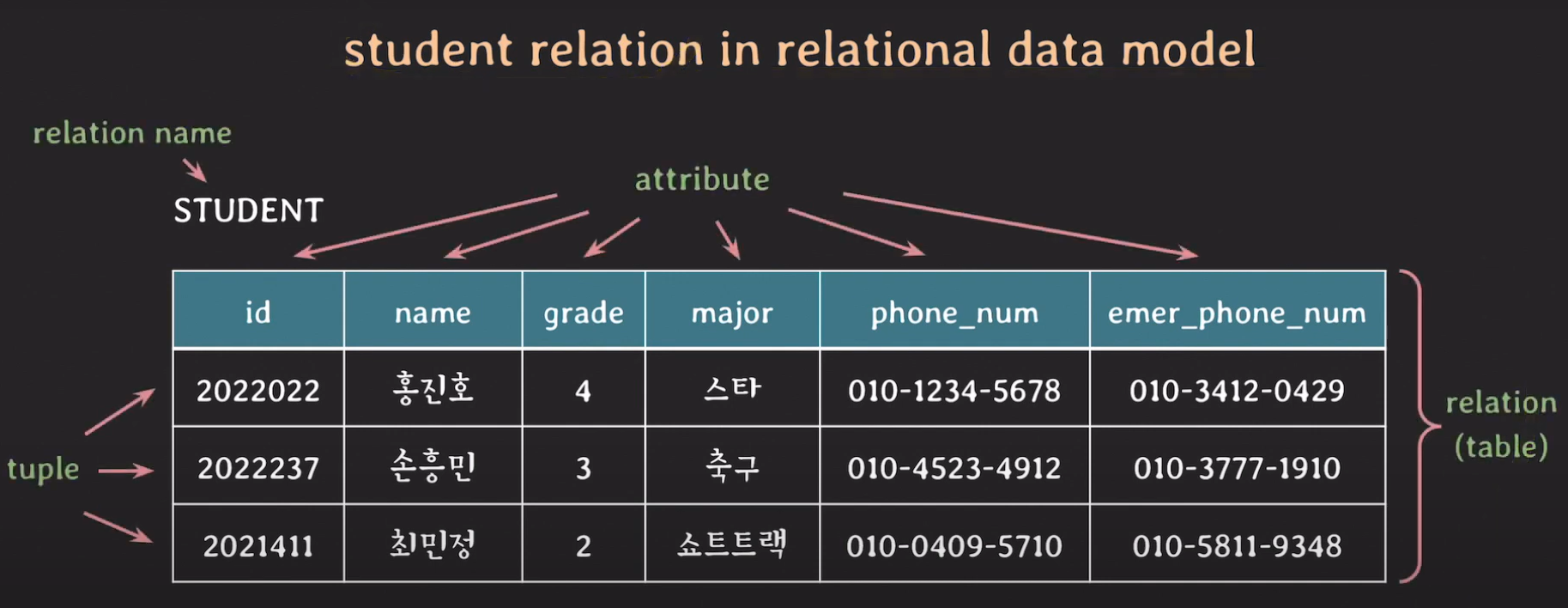
위의 표 전체를 relation 혹은 table이라고 한다.
-
추상적인 의미에서의 relation이 아니라 실제 데이터인 tuple들만의 집합을 relation(or relation state)이라고도 부른다.
주요 개념
| 주요 개념 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| domain | set of atomic values - 더 이상 나누어질 수 없는 값들의 집합 |
| domain name | domain 이름 |
| attribute | domain이 relation에서 맡은 역할 이름 |
| tuple | 각 attribute의 값으로 이루어진 리스트. 일부 값은 NULL일 수 있다. |
| relation | set of tuples- tuple들의 집합 |
| relation name | relation의 이름 |
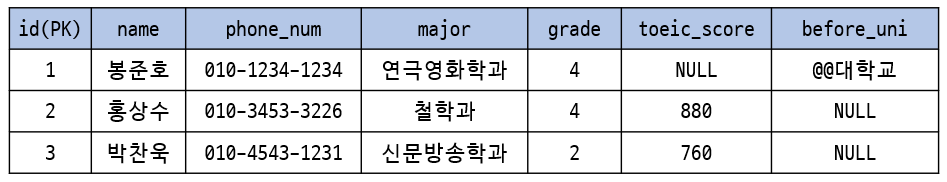
NULL의 의미
1.값이 존재하지 않는다.
2. 값이 존재하나 아직 그 값이 무엇인지 알지 못한다.
3. 해당 사항과 관련이 없다.
-
봉준호의 toeic_score가 NULL인 이유는 1. 아직 토익을 안봐서 값이 존재하지 않을 수 있고 2. 토익을 봤지만 아직 테이블에 수정이 안되서 그 값을 알지 못할 수 있다.
-
홍상수와 박찬욱의 before_uni 값이 NULL인 이유는 해당 attribute는 편입하기 전의 대학교에 관련된 값인데 두 사람 모두 편입한게 아니기 때문에 해당 attribute와 관련이 없기 때문이다.
relation schema
-
relation의 구조를 나타낸다.
-
relation의 이름과 attributes 리스트로 표기된다.
- ex) STUDENT(id, name, grade, major, phone_num, emer_phone_num)
-
attributes와 관련된 constraints(제약사항)도 포함한다.
degree of a relation
-
relation schema에서 attributes의 수를 말한다.
-
ex) STUDENT(id, name, grade, major, phone_num, emer_phone_num)
-> degree(차수)는 6이다.
relational database
-
relational data model에 기반하여 구조화된 database
-
relational database는 여러 개의 relations로 구성된다.
relational database schema
- relation schemas set + integrity constraints set
📌relation의 특징들
relation은 중복된 tuple을 가질 수 없다.
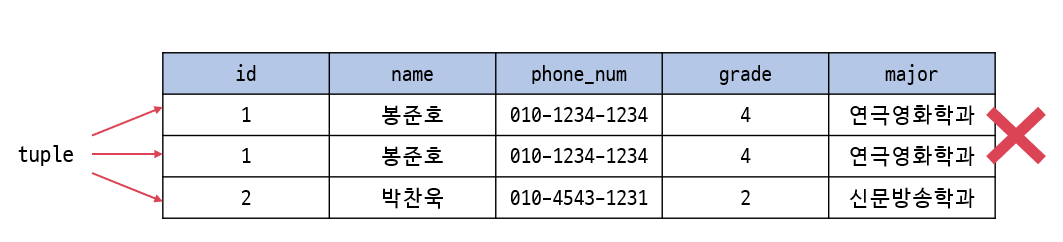
relation의 tuple을 식별하기 위해 attribute의 부분 집합을 key로 설정한다.
relation에서 tuple의 순서는 중요하지 않다.
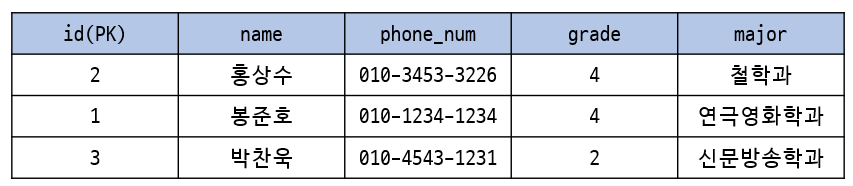
- tuple의 순서가 바뀌어도 테이블의 의미나 데이터에 변화가 생기지 않는다.
하나의 relation에서 attribute의 이름은 중복되면 안된다.
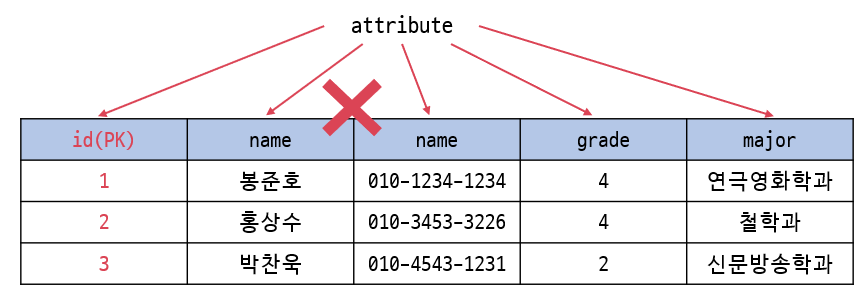
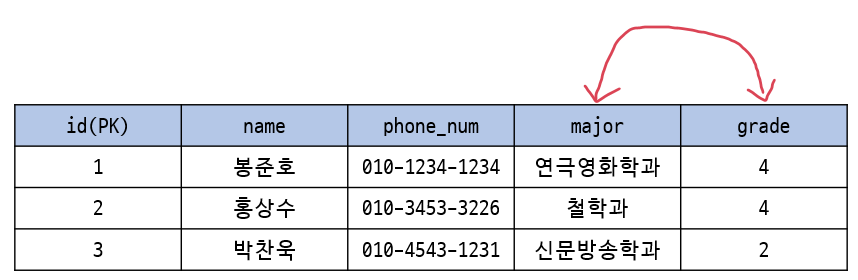
하나의 tuple에서 attribute의 순서는 중요하지 않다.
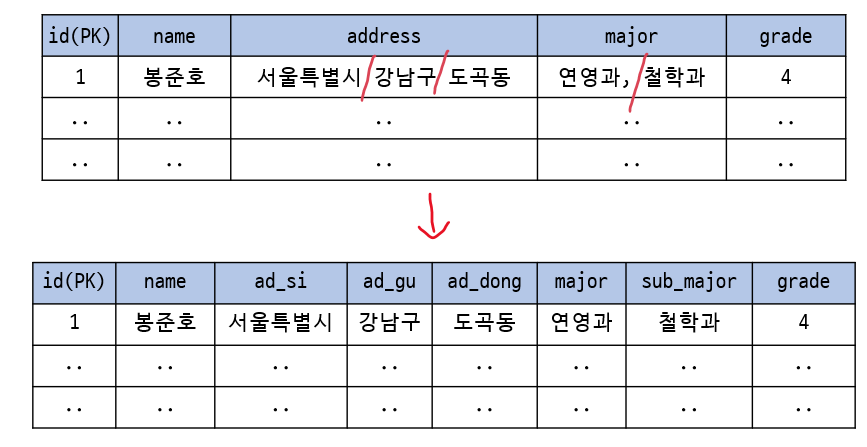
attribute는 atomic(더 이상 나누어질 수 없는) 해야 한다.
📌keys
super key
: relation에서 tuples를 unique하게 식별할 수 있는 attributes set
PLAYER(id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)의 super key는
1. {id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date}
2. {id, name}
3. {name, team_id, back_number} 등이 있다.
candidate key
: 어느 한 attribute라도 제거하면 unique하게 tuples를 식별할 수 없는 super key. minimal super key라고도 한다.
PLAYER(id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)의 candidate key는
1. {id}
2. {team_id, back_number}
-> {team_id, back_number} 에서 team_id를 제거하면 back_number(등번호)는 다른 팀의 선수와 중복이 될 수 있다.
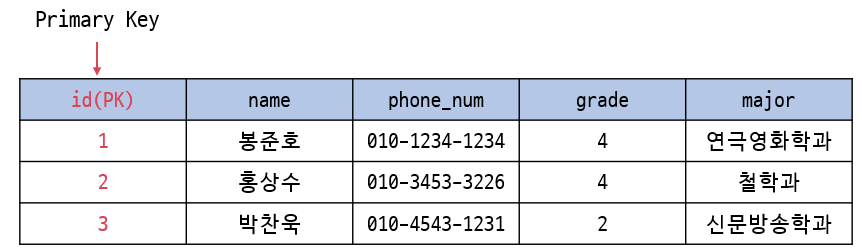
primary key
: relation에서 tuples를 unique하게 식별하기 위해 선택된 candidate key
PLAYER(id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)의 primary key는
1. {id}
2. {team_id, back_number}
-> 보통 primary key를 고를땐 attribute가 가장 적은 candidate key를 선택한다.
unique key(alternate key)
: primary key가 아닌 candidate keys. alternate key라고도 한다.
PLAYER(id(PK), name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)의 unique key는 {team_id, back_number} 이다.
foreign key
: 다른 relation의 PK를 참조하는 attributes set
PLAYER(id(PK), name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)
TEAM(id(PK), name, manager)
가 있을 때 foreign key는 PLAYER의 {team_id} 이다.
📌contraints
: relational database의 relation들이 언제나 항상 지켜줘야 하는 제약 사항
implicit constraints
: relational data model 자체가 가지는 constraints
- "relation은 중복되는 tuple을 가질 수 없다."
- "relation 내에서는 같은 이름의 attribute를 가질수 없다." 등이 있다.
explicit constraints
: 주로 DDL을 통해 schema에 직접 명시할 수 있는 constraints
- schema-based constraints라고도 한다.
여러 종류의 explicit constraints가 있다.
domain constraints
: attribute의 value는 해당 attribute의 domain에 속한 value여야 한다.
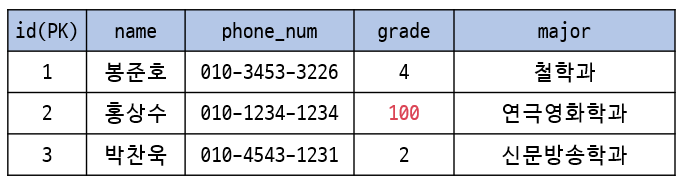
- 학년을 의미하는 grade에는 1~4까지의 숫자만 올 수 있고 100이라는 숫자는 올 수 없다.
key constraints
: 서로 다른 tuples는 같은 value의 key를 가질 수 없다.
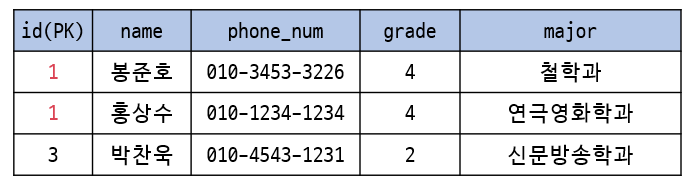
- 같은 value의 PK를 가질 수 없다.
NULL value constraints
: attribute가 NOT NULL로 명시됐다면 NULL 값을 가질 수 없다.
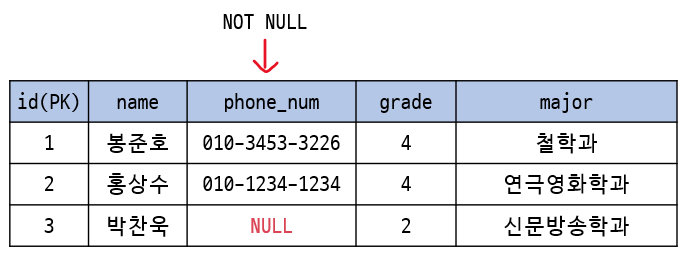
entity integrity constraints
: primary key는 value에 NULL을 가질 수 없다.
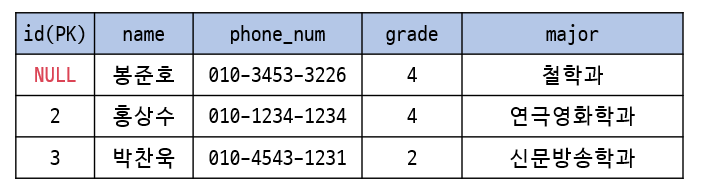
- PK는 tuples를 unique하게 식별하는 key이기 때문에 NULL 값이 들어가게 된다면 식별할 수 없게 된다. 따라서 PK에는 NULL 값을 가질 수 없다.
referential integrity constraints
: FK와 참조하는 테이블의 PK는 도메인이 같아야하고 PK에 없는 values를 FK가 가질 수 없다.
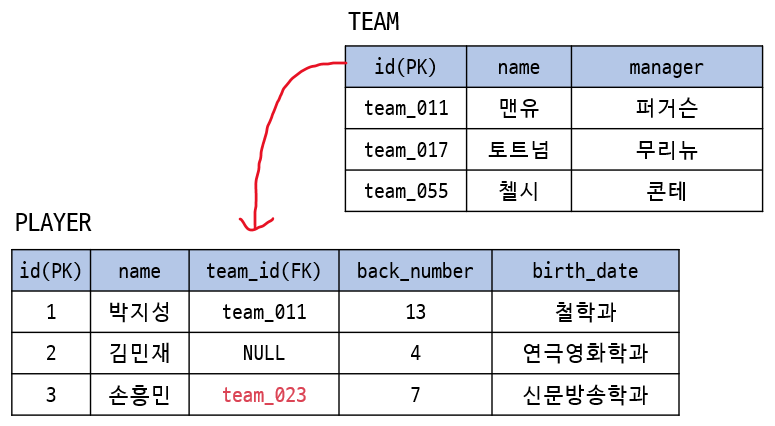
-
TEAM 테이블의 id(PK)를 참조한 PLAYER 테이블의 team_id(FK)가 있다고 했을 때 team_id에는 TEAM.id에 없는 값을 가질 수 없다.
-
단, NULL 값은 가질 수 있는데 김민재 선수가 현재 소속팀이 없는 경우가 있을 수 있기 때문이다.
