배열 반복문
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
arr.forEach((e) => console.log(e));순차적으로 반복문을 돌면서 요소를 출력하는 코드입니다.
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const newArr = [];
arr.forEach((e) => newArr.push(e * 3));
console.log(newArr);arr의 요소를 * 3을 한 후에 newArr에 추가하는 코드입니다.
이 코드를 map을 사용해서 짧게 줄여보도록 하겠습니다.
map
순차적으로 요소를 돌며 return 값이 있는 문법입니다.
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const newArr = arr.map((e) => {
return e * 3;
});
console.log(newArr);includes
배열에 해당 요소가 존재하는지 확인이 가능합니다.
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
function isIncludes(number) {
return arr.includes(number);
}
console.log(isIncludes(3)); // trueindexOf
해당 값의 인덱스를 출력 존재하지 않으면 -1 출력
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
console.log(arr.indexOf(3)); // 2
console.log(arr.indexOf(5)); // -1findIndex
콜백 함수를 전달해서 true를 반환하는 첫번째 요소의 인덱스를 반환합니다.
const names = [{ name: "j" }, { name: "a" }, { name: "b" }, { name: "y" }];
console.log(names.findIndex((e) => e.name === "a")); // 1find
index를 가져오는 것이 아니라 요소를 반환합니다.
const names = [{ name: "j" }, { name: "a" }, { name: "b" }, { name: "y" }];
console.log(names.find((e) => e.name === "a")); // {name: "a"}filter
전달한 콜백함수가 true를 반환하는 모든 요소를 배열로 반환합니다.
const names = [
{ num: 1, name: "j" },
{ num: 2, name: "a" },
{ num: 3, name: "b" },
{ num: 4, name: "y" }
];
console.log(names.filter((e) => e.name === "j"));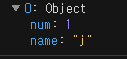
slice
배열을 자를 수 있습니다.
const names = [
{ num: 1, name: "j" },
{ num: 2, name: "a" },
{ num: 3, name: "b" },
{ num: 4, name: "y" }
];
console.log(names.slice(0, 2));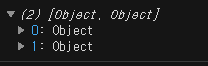
concat
배열을 붙일 수 있습니다.
const names1 = [
{ num: 1, name: "j" },
{ num: 2, name: "a" }
];
const names2 = [
{ num: 3, name: "b" },
{ num: 4, name: "y" }
];
const names3 = names1.concat(names2);
console.log(names3);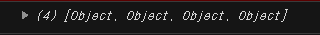
sort
배열을 사전순으로 정렬할 수 있습니다. (원본 배열을 정렬합니다.)
let arr = ["e", "d", "a", "b", "c"];
console.log(arr);
arr.sort();
console.log(arr);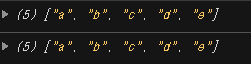
number 배열을 정렬해 보도록 하겠습니다.
let arr = [880, 20, 1, 10, 39, 0, 2, 20, 3, 30];
arr.sort();
console.log(arr);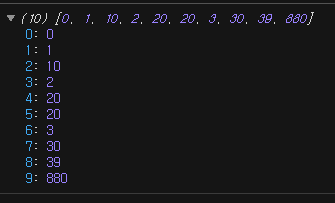
사전 순으로 정렬이 되기 때문에 이런 경우에는 직접 비교함수를 직접 만들어서 넣어야 합니다.
let arr = [880, 20, 1, 10, 39, 0, 2, 20, 3, 30];
const compare = (a, b) => {
if (a > b) {
// 2. a 가 b 보다 크다.
return 1;
} else if (a < b) {
// 3. a 가 b 보다 작다.
return -1;
}
// 1. 같다.
return 0;
};
arr.sort(compare);
console.log(arr);join
배열의 요소들을 string으로 합치는 역할을 합니다.
const arr = ["my", "name", "is", "jay"];
console.log(arr.join()); // my,name,is,jay
console.log(arr.join(" ")); // my name is jay 해당 게시글은 인프런 강의
"한입 크기로 잘라 먹는 리액트(React.js) : 기초부터 실전까지(이정환)"
를 정리한 내용입니다. 쉽게 잘 설명해주시니 여러분도 강의를 듣는 것을 추천드립니다.
