
Comparator(compare(-, -)) -> 두 매개변수 객체를 비교하는 것
- 기본 정렬 기준 외에 다른 기주으로 정렬하고자 할 떄 사용
- 두 객체 비교
- 왼쪽 매개변수 < 오른쪽 매개변수 -> (-)음수
- 왼쪽 매개변수 = 오른쪽 매개변수 -> 0
- 왼쪽 매개변수 > 오른쪽 매개변수 -> (+)양수
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
class Student {
private String name;
private int korScore;
private int engScore;
private int mathScore;
public Student(String name, int korScore, int engScore, int mathScore) {
this.name = name;
this.korScore = korScore;
this.engScore = engScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
public int getKorScore() {
return korScore;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
class KorScoreSort implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getKorScore() - o2.getKorScore();
}
}
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> classRoom = new ArrayList<>();
KorScoreSort korScoreSort = new KorScoreSort();
classRoom.add(new Student("김철수", 80, 60, 90));
classRoom.add(new Student("나영희", 90, 80, 60));
classRoom.add(new Student("다람쥐", 30, 40, 20));
Collections.sort(classRoom, korScoreSort);
for (Student student : classRoom) {
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
}
}익명 객체 사용
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
class Student {
private String name;
private int korScore;
private int engScore;
private int mathScore;
public Student(String name, int korScore, int engScore, int mathScore) {
this.name = name;
this.korScore = korScore;
this.engScore = engScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
public int getKorScore() {
return korScore;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> classRoom = new ArrayList<>();
classRoom.add(new Student("김철수", 80, 60, 90));
classRoom.add(new Student("나영희", 90, 80, 60));
classRoom.add(new Student("다람쥐", 30, 40, 20));
//익명 클래스 사용
Collections.sort(classRoom, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getKorScore() - o2.getKorScore();
}
});
for (Student student : classRoom) {
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
}
}Comparable(compareTo(-)) -> 자기 자신과 매개변수 객체를 비교
- 기본 정렬 기준을 구현하는데 사용
- 두 객체 비교
- 자기 자신 < 비교하는 값 -> (+)양수
- 자기 자신 = 비교하는 값 -> 0
- 자기 자신 > 비교하는 값 -> (-)음수
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int korScore;
private int engScore;
private int mathScore;
public Student(String name, int korScore, int engScore, int mathScore) {
this.name = name;
this.korScore = korScore;
this.engScore = engScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
// if (this.engScore > o.engScore) {
// return 1;
// } else if (this.engScore == o.engScore) {
// return 0;
// } else{
// return -1;
// }
return this.engScore - o.engScore;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> classRoom = new ArrayList<>();
classRoom.add(new Student("김철수", 80, 60, 90));
classRoom.add(new Student("나영희", 90, 80, 60));
classRoom.add(new Student("다람쥐", 30, 40, 20));
Collections.sort(classRoom);
for (Student student : classRoom) {
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
}
}위에서 설명하듯이 자신과 상대방과의 차이를 비교하여 크면 양수, 같으면 0, 작으면 음수를 반환하도록 구현을 하였다. 이렇게 구현을하면 영어 점수가 높을 수록 뒤에가 오름차순으로 구현 할 수 있다.

내림차순으로 구하고 싶으면 결과값에 음수를 붙여 정렬을 반대로 만드는 것도 가능합니다.
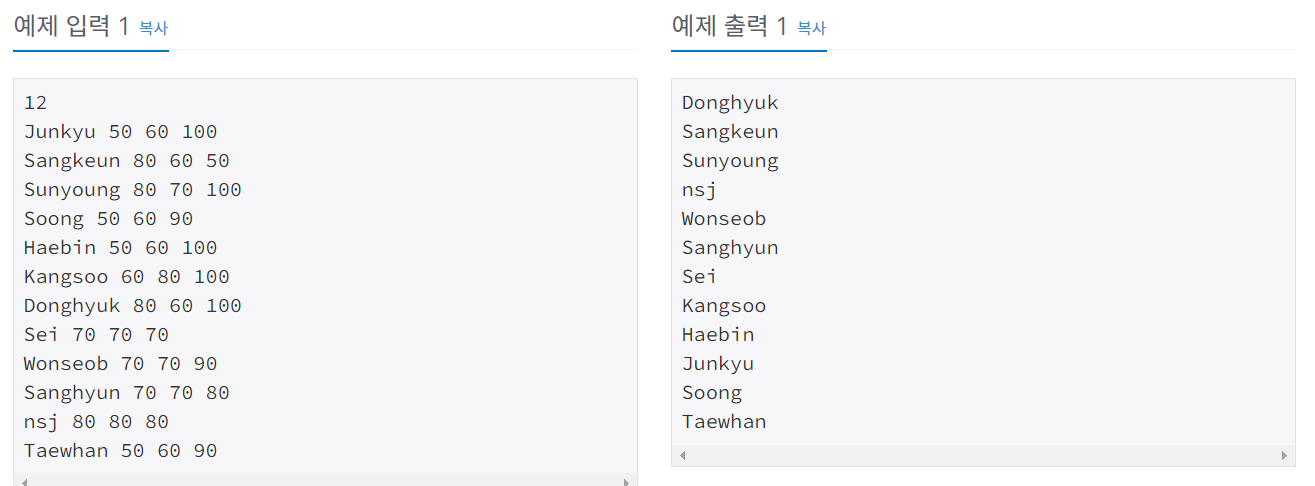
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
String name = st.nextToken();
int koreaScore = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int englishScore = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int mathScore = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
list.add(new Student(name, koreaScore, englishScore, mathScore));
}
Collections.sort(list);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
System.out.println(list.get(i).getName());
}
}
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private int koreaScore;
private int englishScore;
private int mathScore;
public Student(String name, int koreaScore, int englishScore, int mathScore) {
this.name = name;
this.koreaScore = koreaScore;
this.englishScore = englishScore;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
/*
* [ 정렬 기준 ]
* 1) 두 번째 원소를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬
* 2) 두 번째 원소가 같은 경우, 세 번째 원소를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬
* 3) 세 번째 원소가 같은 경우, 네 번째 원소를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬
* 4) 네 번째 원소가 같은 경우, 첫 번째 원소를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬
*/
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
// 정렬 기준은 내림차순
@Override
public int compareTo(Student other) {
if (this.koreaScore == other.koreaScore && this.englishScore == other.englishScore && this.mathScore == other.mathScore) {
return this.name.compareTo(other.name); // this.name, other.name 비교 오름차순
}
if (this.koreaScore == other.koreaScore && this.englishScore == other.englishScore) {
return Integer.compare(other.mathScore, this.mathScore); // 내림차순
}
if (this.koreaScore == other.koreaScore) {
return Integer.compare(this.englishScore, other.englishScore); // 오름차순
}
return Integer.compare(other.koreaScore, this.koreaScore); // 내림차순
}
}