
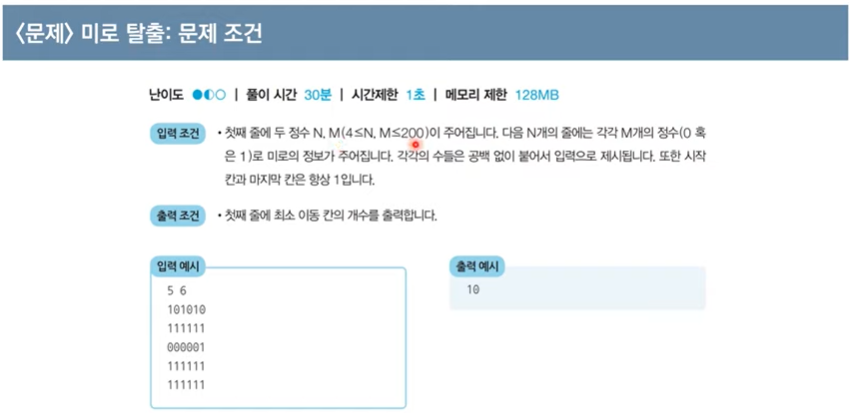
-
문제 풀이 전반을 보면서 느낀 것은 BFS의 경우는 큐로 자료구로를 사용해야하기 때문에 방향벡터를 사용하고 DFS 같은 경우는 재귀호출방식이여서 따로 방향 벡터를 설정 하지 않는 것 같다.
-
물론 확실하지는 않지만 감을 어느정도 잡힌다.
import java.util.*;
class Node {
private int x;
private int y;
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return this.x;
}
public int getY() {
return this.y;
}
}
public class Main {
public static int n, m;
public static int[][] graph = new int[201][201];
// 이동할 네 가지 방향 정의 (상, 하, 좌, 우)
public static int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
public static int dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
public static int bfs(int x, int y) {
// 큐(Queue) 구현을 위해 queue 라이브러리 사용
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new Node(x, y));
// 큐가 빌 때까지 반복하기
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Node node = q.poll();
x = node.getX();
y = node.getY();
// 현재 위치에서 4가지 방향으로의 위치 확인
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
// 미로 찾기 공간을 벗어난 경우 무시
if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) continue;
// 벽인 경우 무시
if (graph[nx][ny] == 0) continue;
// 해당 노드를 처음 방문하는 경우에만 최단 거리 기록
if (graph[nx][ny] == 1) {
graph[nx][ny] = graph[x][y] + 1;
q.offer(new Node(nx, ny));
}
}
}
// 가장 오른쪽 아래까지의 최단 거리 반환
return graph[n - 1][m - 1];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// N, M을 공백을 기준으로 구분하여 입력 받기
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine(); // 버퍼 지우기
// 2차원 리스트의 맵 정보 입력 받기
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String str = sc.nextLine();
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
graph[i][j] = str.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
// BFS를 수행한 결과 출력
System.out.println(bfs(0, 0));
}
}import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main2 {
public static int N, M;
public static int[][] graph = new int[201][201];
public static int[] dx = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
public static int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
String str = st.nextToken();
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) graph[i][j] = str.charAt(j) - '0';
}
System.out.println(bfs(0, 0));
}
public static int bfs(int x, int y) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new Node(x, y));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
x = node.getX();
y = node.getY();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= M) continue;
if (graph[nx][ny] == 0) continue;
if (graph[nx][ny] == 1) {
graph[nx][ny] = graph[x][y] + 1;
queue.offer(new Node(nx, ny));
}
}
}
return graph[N - 1][M - 1];
}
}
class Node {
private int x;
private int y
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return this.x;
}
public int getY() {
return this.y;
}
}참조
https://velog.io/@taehyeon96/3.-%EC%9D%B4%EC%BD%94%ED%85%8C-DFS-BFS-%EB%AF%B8%EB%A1%9C-%ED%83%88%EC%B6%9C-BFS-%ED%95%B5%EC%8B%AC
.
https://velog.io/@taehyeon96/3.-%EC%9D%B4%EC%BD%94%ED%85%8C-DFS-BFS-%EB%AF%B8%EB%A1%9C-%ED%83%88%EC%B6%9C-BFS-%ED%95%B5%EC%8B%AC
