AOP
: Aspect-Oriented Programming, 관점 지향 프로그래밍
✔️ 횡단관심사(cross-cutting concerns)
↪ 각 모듈에서 공통적으로 사용하는 부분(Logging ,Transaction, Security)
✔️ 관점을 기준으로 다양한 기능을 각각 모듈화하는 프로그래밍
✔️ 변경에 유리하도록 관심사에 따라 코드 분리
✔️ 부가기능(advice)를 동적(실행중)으로 추가해주는 기술
✔️ 메서드의 시작 또는 끝네 자동으로 코드(Advice) 추가
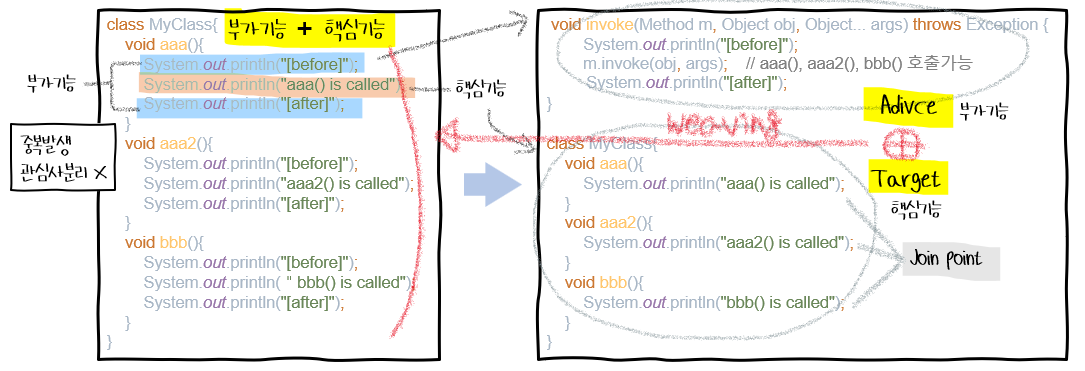
🏷️ 공통코드의 분리
여러 메서드에 공통 코드를 추가해야할 때 공통코드 분리
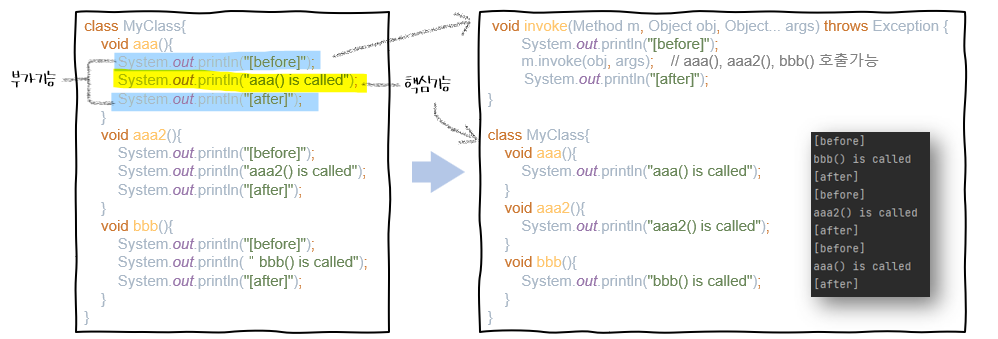
특정 메서드에서만 공통코드 실행
✅ MyAdvice 클래스에 패턴 추가:
ex) a로 시작하는 메서드 Pattern p = Pattern.compile("a.*")
[before]
aaa() is called
[after]
bbb() is called
[before]
aaa2() is called
[after]
public class AopMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
MyAdvice myAdvice = new MyAdvice();
Class myClass = Class.forName("com.fastcampus.ch3.aop.MyClass");
Object obj = myClass.newInstance();
for (Method m : myClass.getDeclaredMethods()){
myAdvice.invoke(m, obj, null);
}
}
}
class MyAdvice{
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("a.*"); // a로 시작하는 경우
boolean matches(Method m){
Matcher matcher = p.matcher(m.getName());
return matcher.matches();
}
void invoke(Method m, Object obj, Object... args) throws Exception {
if(matches(m)) // a로 시작하는 method만 실행
System.out.println("[before]");
m.invoke(obj, args); // aaa(), aaa2(), bbb() 호출가능
if(matches(m))
System.out.println("[after]");
}
}
class MyClass{
void aaa(){
System.out.println("aaa() is called");
}
void aaa2(){
System.out.println("aaa2() is called");
}
void bbb(){
System.out.println("bbb() is called");
}
}✅ @Tranactional 어노테이션 활용
[before]
aaa() is called
[after]
aaa2() is called
bbb() is called
class MyAdvice{
void invoke(Method m, Object obj, Object... args) throws Exception {
if(m.getAnnotation(Transactional.class)!=null)
System.out.println("[before]");
m.invoke(obj, args); // aaa(), aaa2(), bbb() 호출가능
if(m.getAnnotation(Transactional.class)!=null)
System.out.println("[after]");
}📑 코드 자동 추가
✔️ Advice: 자동 추가할 코드
✔️ cf) 메서드의 맨 앞과 맨 끝은 고정인 반면 메서드 중간은 내용이 계속 바뀌기 때문에 중간에는 자동으로 추가할 수 없음
✅ Before Advice: 메서드 시작 부분에 자동코드 추가
✅ After Advice: 메서드 끝 부분에 자동코드 추가
✅ Around Advice: 메서드 시작과 끝 부분 모두에 자동코드 추가
🧰 AOP 관련 용어
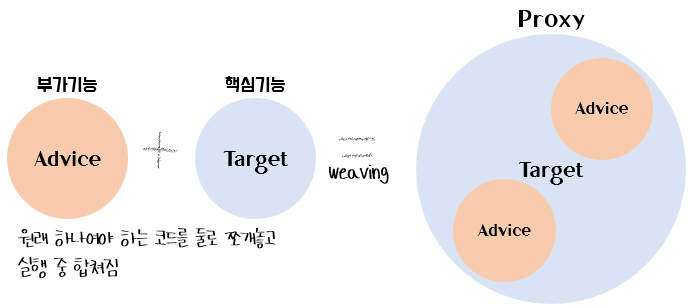
✅ target: advice에 추가될 객체
✅ advice: targret에 동적으로 추가될 부가기능(코드)
✅ join point: advice가 추가(join)될 대상(메서드)
✅ pointcut: join point 들을 정의한 패턴
↪ ex) execution(*com.fastcamput.*.*(..))
✅ proxy: target에 advice가 동적으로 추가되어 생성된 객체
✅ weaving: target에 advice를 추가해서 proxy를 생성하는 것
🪄Advice의 종류
✔️ XML과 애너테이션으로 Advice 설정 가능
✅ around advice | @Around | 메서드 시작과 끝 부분 모두에 추가되는 부가기능
✅ before advice | @Before | 메서드 시작에 추가
✅ after advice | @After | 메서드 끝에 추가
✅ after returning | @AfterReturning | 예외가 발생하지 않았을 때, 실행되는 부가기능(try문 끝)
✅ after throwing | @AfterThrowing | 예외가 발생했을 때, 실행되는 부가기능(catch문)
try{
......
[After Returning]
} catch(Exception e)
[After Throwing]
}
🏁 Pointcut expression
✔️ advice가 추가될 메서드를지정하기 위한 패턴
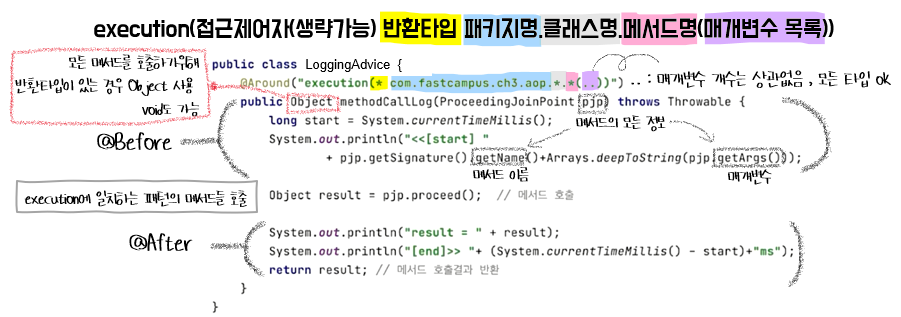
✔️ result를 return하는 이유: Advice가 여러 개 적용되는 경우 다음 Advice에게 호출 된 결과를 넘겨주기 위해
✅ Adivce 한 개만 적용되는 경우: 반환타입 void로 설정, return result 안해도 됨
✅ Advice 여러 개 적용되는 경우: return result
@Order(1), @Order(2)... 이런 식으로 advice가 어떤 순서로 진행될건지 설정할 수 있음
💻 실습
AOP 사용을 위해 라이브러리 추가
✔️ Maven dependency: spring-aop | aspectj weaver
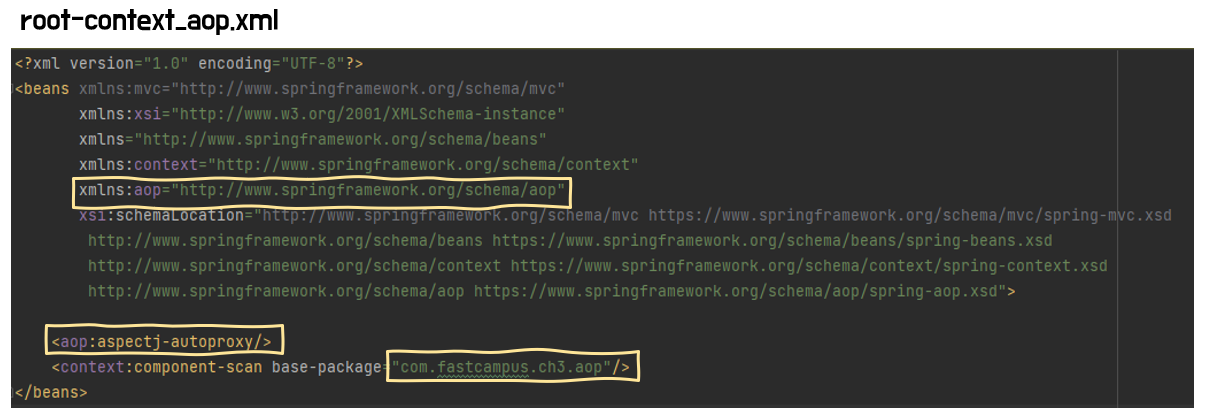
pom.xml
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> <version>${org.springframework-version}</version> //version 주의 </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.20.1</version> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <!-- AspectJ --> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId> <version>${org.aspectj-version}</version> </dependency>
실습
MyMath.java
@Component
public class MyMath {
public int add(int a, int b){
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
public int add(int a, int b, int c){
int result = a + b + c;
return result;
}
public int subtract(int a, int b){
int result = a - b;
return result;
}
public int multiply(int a, int b){
int result = a * b;
return result;
}
}
LoggingAdvice.java
@Component
@Aspect
public class LoggingAdvice {
// pointcut: 부가기능이 적용될 메서드의 패턴
@Around("execution(* com.fastcampus.ch3.aop.MyMath.*(..))")
public Object methodCallLog(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("<<[start] " + pjp.getSignature().getName() +
Arrays.toString(pjp.getArgs()));
Object result = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("[end]>> " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
return result;
}
}AopMain2.java
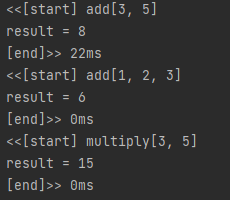
public class AopMain2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext ac = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(
"file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/spring/**/root-context_aop.xml");
MyMath mm = (MyMath) ac. getBean("myMath");
mm.add(3, 5);
mm.add(1, 2, 3);
mm.multiply(3, 5);
}
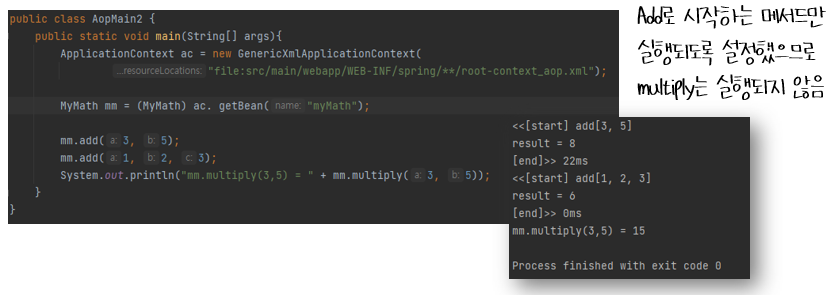
}if. add메서드만 실행하고 싶다면
LoggingAdvice.java | pointcut에서 메서드 add로 수정
@Around("execution(* com.fastcampus.ch3.aop.MyMath.add*(..))")
참고) 자바의 정석 | 남궁성과 끝까지 간다