🐣 Spring DI
-
Spring DI: 다른 프레임워크와 차별화된 의존관계 주입 기능
✔️ 객체 간의 의존성을 객체 내부에서 직접 호출(new연산자)하는 대신 외부 객체(스프링 컨테이너)를 생성하여 넣어주는 방식 -
의존성 주입(Dependency Injection, DI): 외부에서 두 객체 간의 관계를 결정해주는 디자인 패턴
✔️ 인터페이스를 사이에 두어서 클래스 레벨에서는 의존관계가 고정되지 않도록 하고, 런타임 시에 관계를 동적으로 주입하여 유연성을 확보하고 결합도를 낮춤
// 이 경우 School객체가 Student객체에 의존성이 있다고 표현
public class School {
private Student student
}
개념
- DI가 필요한 이유: 결합도↓, 유연성↑
➊ 두 클래스가 강하게 결합되어 있음(상속은 제약이 많고 확장성이 떨어짐)
➋ 객체들 간의 관계가 아니라 클래스 간의 관계가 맺어짐(관심사 분리X)
📑 변경에 유리한 코드
➊ 다형성, factorty method
✅ 변경포인트 2군데
SportsCar car = new SportsCar();
➡️ Truck car = new Truck();
✅ 변경포인트 1군데, 사용코드 변경
Car car = new SportsCar();
➡️ Car car = new Truck();
✅ 메서드 변경만으로 변경 가능
Car car = new getCar();
static Car getCar(){ return new SportsCar(); }
➡️ static Car getCar(){ return new Truck(); }
➋ Map과 외부파일: 프로그램 변경X, Map(Object, Object), Propeties(String, String)
Config.txt
car = com.fastcampus.ch3.diCopy1.SportsCar
Engine = com.fastcampus.ch3.diCopy1.Engine
- 출력결과
car = com.fastcampus.ch3.diCopy1.SportsCar@3567135c
engine = com.fastcampus.ch3.diCopy1.Engine@327471b5
class Car{}
class SportsCar extends Car{}
class Truck extends Car {}
class Engine {}
public class Main1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Car car = (Car)getObject("car");
Engine engine = (Engine)getObject("Engine");
System.out.println("car = " + car);
System.out.println("engine = " + engine);
}
static Object getObject(String key) throws Exception {
Properties p = new Properties();
p.load(new FileReader("config.txt"));
Class clazz = Class.forName(p.getProperty(key));
return (Object) clazz.newInstance();
}
+) 객체지향(OOP)에서 필요한 분리
➊ 변하는 것, 변하지 않는 것
➋ 관심사
➌ 중복 코드(AOP)
🛒 객체 컨테이너(ApplicationContext)
- 출력결과
car = com.fastcampus.ch3.diCopy2.Truck@327471b5
engine = com.fastcampus.ch3.diCopy2.Engine@4157f54e
class AppContext{
Map map; // 객체 저장소
AppContext(){
try {
Properties p = new Properties();
p.load(new FileReader("config.txt"));
// Properties에 저장된 내용을 Map에 저장
map = new HashMap(p);
// 반복문으로 클래스 이름을 얻어서 객체를 생성해서 다시 map에 저장
for(Object key : map.keySet()){
Class clazz = Class.forName((String)map.get(key));
map.put(key, clazz.newInstance());
}
} catch ( Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Object getBean(String key){
return map.get(key);
}
}
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
AppContext ac = new AppContext();
Car car = (Car) ac.getBean("car");
Engine engine = (Engine) ac.getBean("engine");
System.out.println("car = " + car);
System.out.println("engine = " + engine);
}
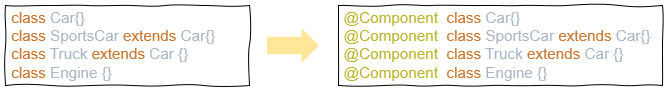
}🏷️ 자동 객체 등록 - Component Scanning
- 출력결과
car = com.fastcampus.ch3.diCopy3.Car@52f759d7
engine = com.fastcampus.ch3.diCopy3.Engine@7cbd213e
class AppContext{
Map map; // 객체 저장소
AppContext(){
map = new HashMap();
doComponentScan();
}
private void doComponentScan() {
try {
// 1. 패키지 내의 클래스 목록을 가져옴
// 2. 반복문으로 클래스를 하나씩 읽어와서 @Component이 붙어있는지 확인
// 3. @Component가 붙어있으면 객체를 생성해서 map에 저장
ClassLoader classLoader = AppContext.class.getClassLoader();
ClassPath classpath = ClassPath.from(classLoader);
Set<ClassPath.ClassInfo> set = classpath.getTopLevelClasses("com.fastcampus.ch3.diCopy3");
for(ClassPath.ClassInfo classInfo : set){
Class clazz = classInfo.load();
Component component = (Component) clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
if(component != null){
String id = StringUtils.uncapitalize(classInfo.getSimpleName());
map.put(id, clazz.newInstance());
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Object getBean(String key){
return map.get(key);
}
}+) Maven dependency: guava 추가
🔎 객체찾기 - by Name, by Type
AppContext ac = new AppContext();
Car car = (Car) ac.getBean("car"); // 이름(id)으로 찾기(key)
Car car2 = (Car) ac.getBean(Car.class); // 타입으로 찾기(value)
// 이름으로 찾기
Object getBean(String id){
return map.get(id);
}
// 타입으로 찾기
Object getBean(Class clazz){
for(Object obj : map.values()){
if(clazz.isInstance(obj)) //obj Instanceof clazz
return obj;
}
return null;
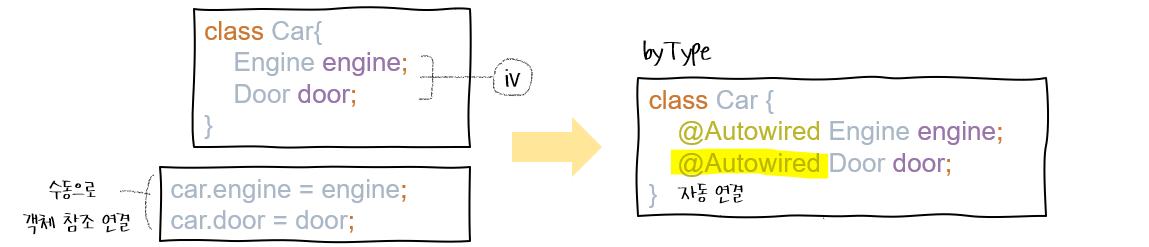
}🔖 객체 자동 연결
- 수동으로 객체 연결
car.engine = engine;
car.door = door;
@Autowired (byType)
: 필요한 의존 객체의 '타입'에 해당하는 빈을 찾아 DI(의존성 주입)을 도와주는 어노테이션
config.xml
<context:annotation-config/>
@Component class Car{
@Autowired Engine engine;
@Autowired Door door;
}
class AppContext{
Map map; // 객체 저장소
AppContext(){
map = new HashMap();
doComponentScan();
doAutowired();
}
private void doAutowired() {
// map에 저장된 객체의 iv중에 @Autowired가 붙어있으면
// map에서 iv의 타입에 맞는 객체를 찾아서 연결(객체의 주소를 iv저장)
try {
for(Object bean : map.values()){
for(Field fld : bean.getClass().getDeclaredFields()){
if(fld.getAnnotation(Autowired.class) != null) // byType
fld.set(bean, getBean(fld.getName())); // car.engine = obj;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void doComponentScan(){생략}
}@Resource (byName)
: 빈 이름을 이용하여 의존성 주입

+) @Resource 사용 시 라이브러리 추가
@Component
class Car{
@Resource Engine engine;
@Resource Door door;
}
class AppContext{
Map map; // 객체 저장소
AppContext(){
map = new HashMap();
doComponentScan();
doResource();
}
private void doResource() {
// map에 저장된 객체의 iv중에 @Resource가 붙어있으면
// map에서 iv의 이름에 맞는 객체를 찾아서 연결(객체의 주소를 iv저장)
try {
for(Object bean : map.values()){
for(Field fld : bean.getClass().getDeclaredFields()){
if(fld.getAnnotation(Resource.class) != null) // byName
fld.set(bean, getBean(fld.getType())); // car.engine = obj;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}참고) 자바의 정석 | 남궁성과 끝까지 간다