개념 정리
위상정렬: 방향그래프에 존재하는 노드들의 선행순서를 위배하지 않고, 모든 노드를 나열하는 것

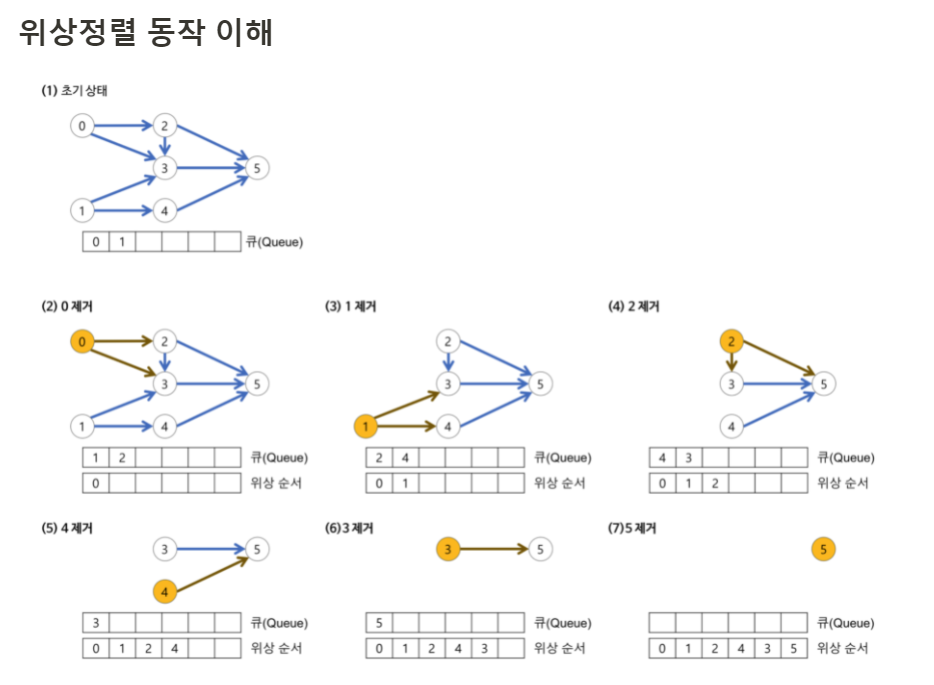
내 풀이
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class baekjoon_2252 {
static int N, M;
static List<Integer>[] graph;
static int[] students;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] inputs = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = Integer.parseInt(inputs[0]);
M = Integer.parseInt(inputs[1]);
students = new int[N+1];
graph = new ArrayList[N+1];
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
inputs = br.readLine().split(" ");
int A = Integer.parseInt(inputs[0]);
int B = Integer.parseInt(inputs[1]);
graph[A].add(B);
students[B] += 1;
}
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (students[i] == 0) {
q.add(i);
}
}
List<Integer> results = new ArrayList<>();
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int node = q.poll();
results.add(node);
for (int i = 0; i < graph[node].size(); i++) {
int next = graph[node].get(i);
students[next] -= 1;
if (students[next] == 0) {
q.add(next);
}
}
}
results.stream().forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + " "));
}
}