시작하기 전에
블록체인 구조에 대한 내용은 네이버 블로그에 간단하게 작성해두었습니다.
원래 이전에 Javascript로 진행하다가 예외처리를 좀 더 확실하게 하고자, Typescript로 다시 진행합니다.
이전 포스팅을 보시던 분들께는 죄송합니다ㅠ
Typescript도 크게 다른 부분이 없으니 다시 복습한다는 생각으로 다시 해보시면 좋을 것 같습니다.
1장. 블록체인 구조 및 서버 만들기
1. 목표
- 블록 구조를 만들어보고
Jest를 이용해서 제대로 만들어지는지 검증해본다. - http 서버와 p2p 서버를 구축해본다.
2. 개발 환경
⚙ Dev Tools
Ubuntu-20.04VScode
📚 Languages & Libraries
TypeScriptJestNode-js
3. 소스 코드
4. 구현 과정
1) 블록 구조
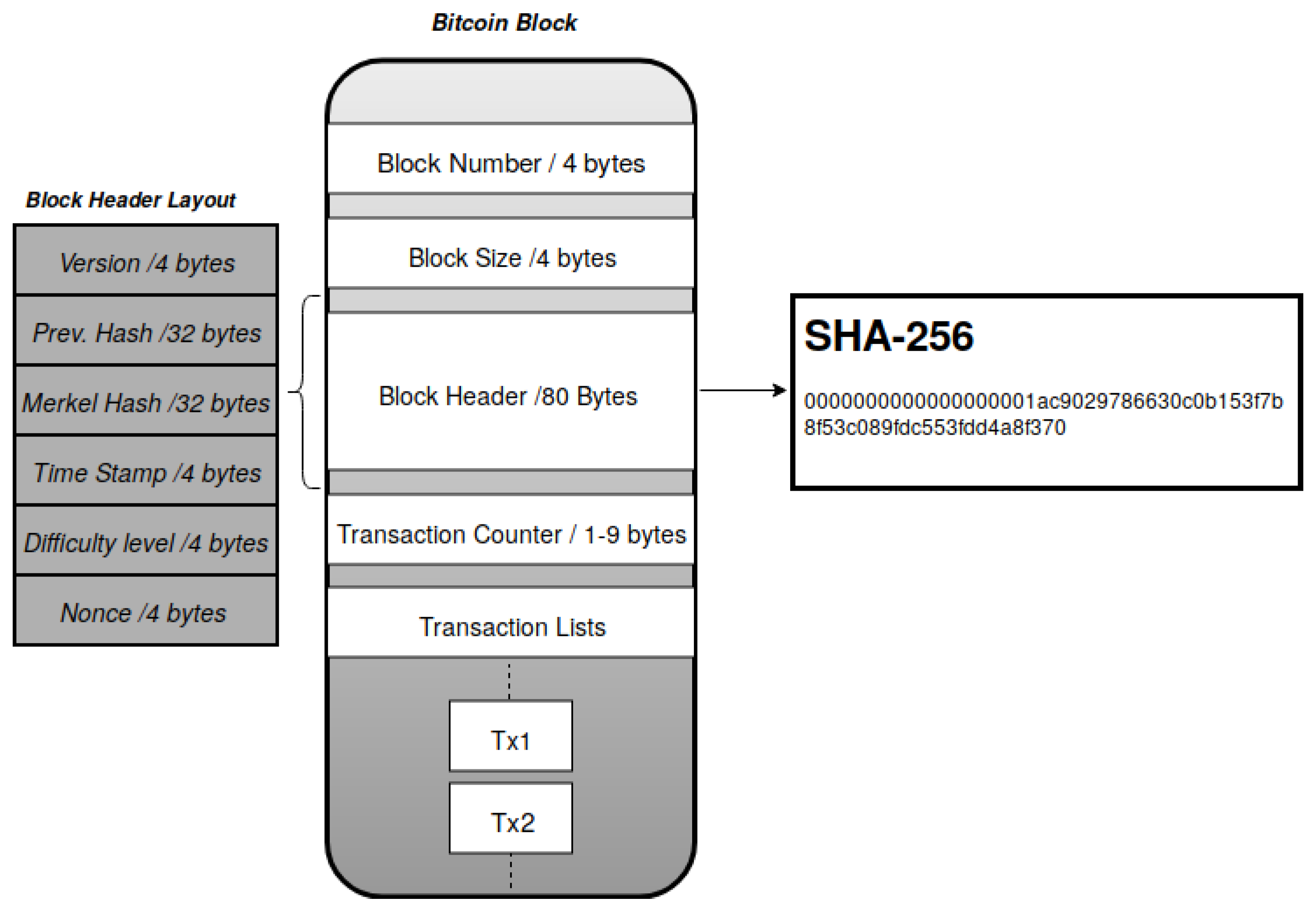
비트코인의 Block 구조를 토대로 class를 만들어보자.
1-1) BlockHeader class
class BlockHeader { public version: string; public index: number; public prevHash: string; public merkleRoot: string; public timestamp: number; public difficulty: number; public nonce: number; constructor( version: string, index: number, prevHash: string, merkleRoot: string, timestamp: number, difficulty: number, nonce: number ) { this.version = version; this.index = index; this.prevHash = prevHash; this.merkleRoot = merkleRoot; this.timestamp = timestamp; this.difficulty = difficulty; this.nonce = nonce; } }
1-2) Block class
/** * @brief Block class * @header * - type: BlockHeader(Object) * - description: contains detail of block's info (version, index, prevHash ...) * @hash * - type: string * - description: calculated SHA256 hash value using this BlockHeader * @data * - type: array * - description: contains block's data such as Transactions */ class Block { public header: BlockHeader; public hash: string | null; public data: any[]; constructor(header: BlockHeader, hash: string | null, data: any[]) { this.header = header; if (hash === null) { this.hash = "0".repeat(64); } else { } this.hash = hash; this.data = data; } }
2) 블록 함수들
함수를 export할 때 편리하도록 사용되는 함수들을 Block class 안에서 했고,
여기서는 전체 코드 중에서 일부분만 간략하게 설명하겠습니다.
2-1) 블록의 hash 값 계산
static calHashOfBlock = (blockHeader: BlockHeader): string | null => { if (typeof blockHeader === "object") { const blockString: string = blockHeader.version + blockHeader.index + blockHeader.prevHash + blockHeader.merkleRoot + blockHeader.timestamp + blockHeader.difficulty + blockHeader.nonce; const hash = cryptojs.SHA256(blockString).toString(); return hash; } console.log("calHashOfBlock : Invalid BlockHeader"); // ! returns null when blockHeader's type is invalid return null; };
이와 같이 블록의 hash 값은 prevHash, merkleRoot 등과 같이, 이전 블록의 hash와 현재 블록의 데이터를 이용해서 얻을 수 있다.
이 때문에 블록의 header 또는 트랜잭션 데이터를 바꾼다면, 이와 연결된 모든 블록과의 연결이 끊어진다.
2-2) 채굴 난이도 조정
static getAdjustDifficulty = ( lastBlock: Block, newBlockTimeStamp: number ): number => { let difficulty = lastBlock.header.difficulty; const newBlockCreationInterval = newBlockTimeStamp - lastBlock.header.timestamp; const diffifcultyAdjustmentTimeInterval = config.DIFFICULTY_ADJUSTMENT_INTERVAL_BLOCK * config.DIFFICULTY_ADJUSTMENT_INTERVAL_SECOND; if ( lastBlock.header.index % config.DIFFICULTY_ADJUSTMENT_INTERVAL_BLOCK === 0 && lastBlock.header.index !== 0 ) { if (newBlockCreationInterval * 2 < diffifcultyAdjustmentTimeInterval) { return --difficulty; } else if ( newBlockCreationInterval / 2 > diffifcultyAdjustmentTimeInterval ) { return ++difficulty; } } return difficulty; };
DIFFICULTY_ADJUSTMENT_INTERVAL_BLOCK와 DIFFICULTY_ADJUSTMENT_INTERVAL_SECOND을 통해 주기적으로 채굴 난이도를 조절해준다.
여기서는 각각 10개, 10초로 설정했기 때문에 100초에 한 번 난이도를 조정한다.
그리고 실제 채굴에 걸린 시간이 예상한 채굴 시간(50초~200초)를 벗어나면 난이도를 조정했다.
2-3) 새로운 블록 생성
static getNewBlock = (lastBlock: Block, data: any[]): Block | null => { const version: string = lastBlock.header.version; const index: number = lastBlock.header.index + 1; const prevHash: string | null = lastBlock.hash; const merkleRoot: string = data.length === 0 ? "0".repeat(64) : merkle("sha256").sync([JSON.stringify(data)]).root(); let timestamp: number = Math.round(Date.now() / 1000); // seconds let difficulty: number = this.getAdjustDifficulty(lastBlock, timestamp); let nonce: number = 0; // ! exception handling : lastBlock hash could be null if (prevHash === null) { return null; } let blockHeader: BlockHeader; let hash: string | null; //* Find block hash which starts with ("0" * difficulty) do { timestamp = Math.round(Date.now() / 1000); blockHeader = new BlockHeader( version, index, prevHash, merkleRoot, timestamp, difficulty, nonce ); hash = this.calHashOfBlock(blockHeader); // ! exception handling : calculated hash could be null if (hash === null) { return null; } nonce++; } while (!hash.startsWith("0".repeat(difficulty))); const newBlock = new Block(blockHeader, hash, data); return newBlock; };
새로운 블록 채굴하려면 간단한 퀴즈를 하나 풀어야 한다.
그 퀴즈는 difficulty의 값만큼 0으로 시작하는 hash를 찾는 것이다.
예를 들어 difficulty = 3 이라면 000으로 시작하는hash를 찾아야만 새로운 블록이 생성되게 된다.
version이나 index 등 블록의 요소들은 고정되어 있는 값이기 때문에, nonce라는 값을 변화시켜 새로운 hash를 계산하게 된다.
merkleRoot 는 merkle 모듈을 사용했다.
Jest를 통해 확인했던 문제는 객체 형태의 데이터를 넣어주면 안의 내용이 달라도 똑같은 merkleRoot를 반환한다는 점이다.
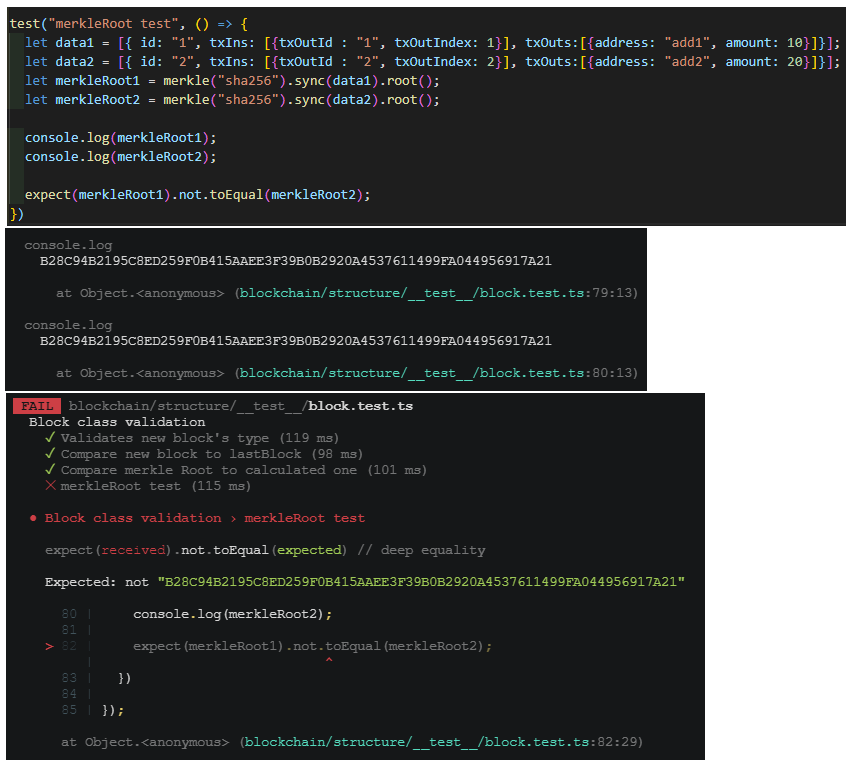
(아마도 merkle 모듈은 데이터를 shallow copy하여 사용하기 때문에 그런것 같다.)
이 문제를 해결하기 위해서 객체 형태의 데이터를 JSON 형식으로 바꾸어 넣어주었다.
=> [JSON.stringify(data)]
3) 서버 만들기
서버는 HTTP, P2P 총 두 개를 사용합니다.
HTTP Server는 클라이언트와 요청응답을 위해 사용하며,
P2P Server는 각 node 간 커뮤니케이션을 위해 사용됩니다.
여기서는 특정 요청보다는 간략하게 기본 서버 구성만 해두었습니다.
3-1) HTTP Server
import express from "express" import bodyParser from "body-parser"; import _ from "lodash"; // import middlewares import cors from "./middlewares/cors"; // import routers import {router as indexRouter} from "./routers/index" import {router as blocksRouter} from "./routers/blocks" const app = express(); const port = process.env.HTTP_PORT || 3001; app.set("port", port) app.use(cors); app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true })); app.use(bodyParser.json()); app.use("/", indexRouter); app.use("/blocks", blocksRouter); const server = app.listen(app.get("port"), () => { console.log(` ################################### 🕷 Server listening on port: ${port} 🕷 ###################################`); })
3-2) P2P Server
P2P는 Peer to Peer를 의미하며, Peer는 Node라고도 불린다.
const sockets: WebSocket[] = []; const initP2PServer = () => { const server: Server = new WebSocket.Server({ port }); server.on("connection", (ws: WebSocket) => { initConnection(ws); console.log(` ################################### 🕸 Server listening on port: ${port} 🕸 ###################################`); }); }
sockets: 현재 노드에 연결된 다른 노드를 저장하는 공간
const initConnection = (ws: WebSocket) => { // Add conncected ws into sockets list sockets.push(ws); initMessageHandler(ws); initErrorHandler(ws); // Query current blockchain to node write(ws, queryLastBlock()); // TODO : transaction pool query };
sockets.push(ws): 연결된 노드를sockets에 저장
queryLastBlock(): 연결된 노드의 마지막 블록을 요청하여
initMessageHandler(ws): 메세지 타입에 따라 어떤 동작을 할지 결정
initErrorHandler(ws): 에러 발생 시 연결 해제 및 에러 메세지 전달
5. 느낀점
Jest를 사용하는 것이 미숙하긴 하지만, 구현 과정에서 미리 에러를 찾을 수 있다는 장점이 있었다.
앞으로도 TDD기반으로 코딩하는 습관을 길러야겠다.
참고사이트 : naiveCoin
