Promise.all
Promise.all
promise.all 메서드는 모든 promise 가 실행될 때까지 기다린다. promise 와 promise.all 을 사용해서 파일을 업로드 한다고 했을 때 어떤 차이가 있는지 살펴보자.
promise
const onClickPromise = async () => {
console.time("Promise 시작!!!"); // 걸리는 시간 측정하기
const result1 = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("https://dog1.jpg");
}, 3000);
});
console.log(result1);
const result2 = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("https://dog2.jpg");
}, 1000);
});
console.log(result2);
const result3 = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("https://dog3.jpg");
}, 2000);
});
console.log(result3);
console.timeEnd("Promise 시작!!!"); // 이름이 똑같아야 측정가능
};promise.all
const onClickPromiseAll = async () => {
const result = await Promise.all([
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("https://dog1.jpg");
}, 3000);
}),
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("https://dog2.jpg");
}, 1000);
}),
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("https://dog3.jpg");
}, 2000);
}),
]);
};console.time() 과 console.timeEnd 를 사용해서 처음부터 끝까지 실행했을 때의 시간을 비교해보면 Promise.all 을 사용했을 때 시간이 절반 가까이 단축된 걸 확인할 수 있다.
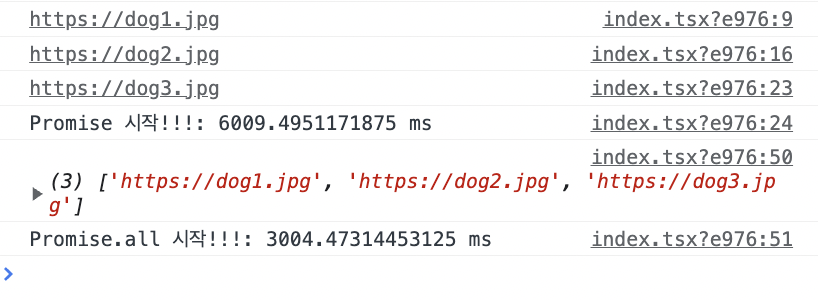
Promise.all 리팩토링
map을 이용해 더 간결하게 코드를 작성해줄 수 있다.
const result = await Promise.all(
["https://dog1.jpg", "https://dog2.jpg", "https://dog3.jpg"].map(
(el) =>
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(el);
}, 3000);
})
)
);