문제
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city when viewed from a distance. Given the locations and heights of all the buildings, return the skyline formed by these buildings collectively.
The geometric information of each building is given in the array buildings where buildings[i] = [lefti, righti, heighti]:
lefti is the x coordinate of the left edge of the ith building.
righti is the x coordinate of the right edge of the ith building.
heighti is the height of the ith building.
You may assume all buildings are perfect rectangles grounded on an absolutely flat surface at height 0.
The skyline should be represented as a list of "key points" sorted by their x-coordinate in the form [[x1,y1],[x2,y2],...]. Each key point is the left endpoint of some horizontal segment in the skyline except the last point in the list, which always has a y-coordinate 0 and is used to mark the skyline's termination where the rightmost building ends. Any ground between the leftmost and rightmost buildings should be part of the skyline's contour.
Note: There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline. For instance, [...,[2 3],[4 5],[7 5],[11 5],[12 7],...] is not acceptable; the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such: [...,[2 3],[4 5],[12 7],...]- 도시의 빌딩의 위치가 배열로 주어진다.
- 배열의 원소는 각각 아래와 같다
1번째 원소 : 빌딩의 x축 시작지점
2번째 원소 : 빌딩의 x축 끝지점
3번째 원소 : 빌딩의 높이
- 배열의 원소는 각각 아래와 같다
- 빌딩이 겹쳐질수 있다고 가정한다.
- 빌딩은 x축 시작지점에 정렬되어 있다.
- 빌딩의 높이가 변화되는 지점에 대해, 변화 후의 좌표만 모아서 리턴하시오.
Ex.
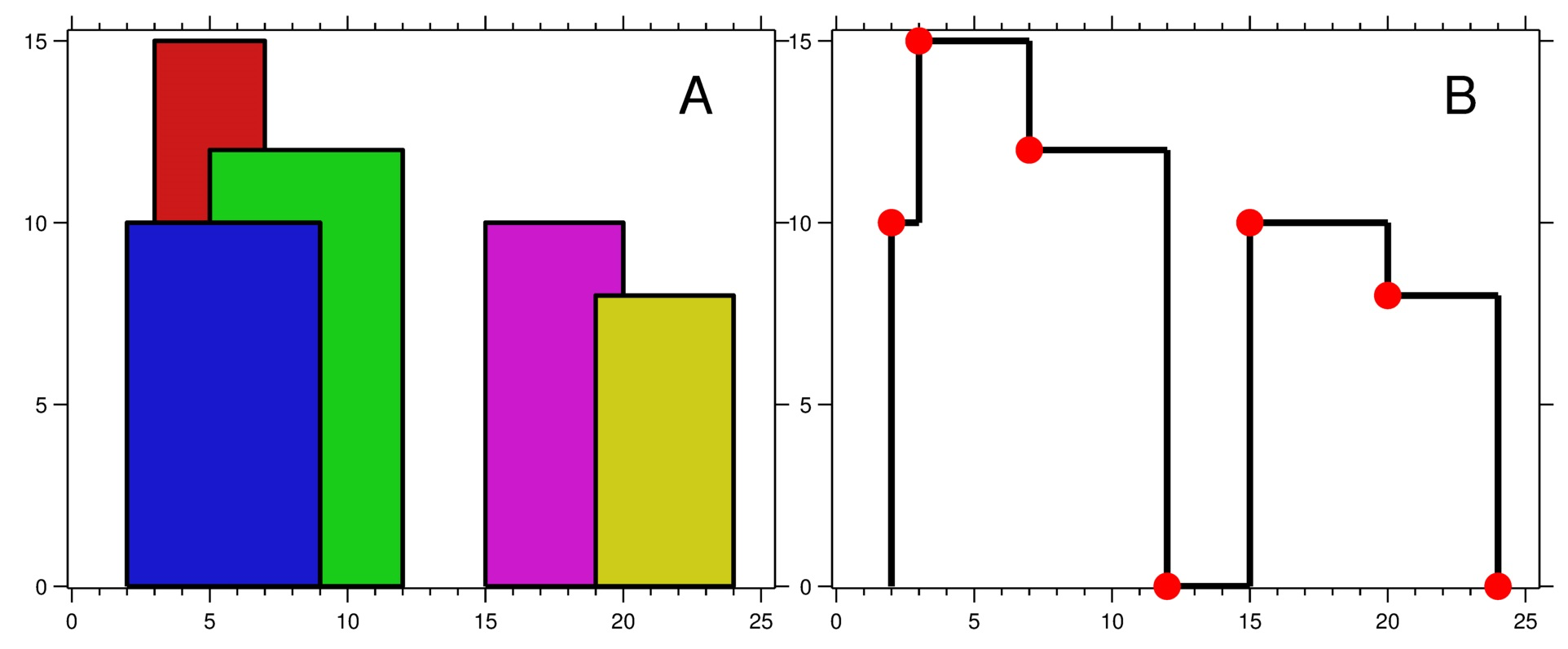
- 빌딩의 높이가 변화되면, 변화된 이후의 점의 좌표만 모은다. x축으로 정렬해서 리턴할것
예시
- 위 예시 리턴값은 [[2,10],[3,15],[7,12],[12,0],[15,10],[20,8],[24,0]]
제한
- 빌딩은 x축 시작점으로 오름차순 정렬 되어 있다.
풀이
class Solution:
def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
events = []
ans = []
for s, e, h in buildings:
events.append((s, -h))
events.append((e, h))
events.sort()
height = [0]
remove_list = defaultdict(int)
prev = 0
for i, h in events:
if h < 0:
heappush(height, h)
else:
remove_list[h] += 1
curr = -height[0]
while remove_list[curr] > 0:
remove_list[curr] -= 1
heappop(height)
curr = -height[0]
if curr != prev:
ans.append([i, curr])
prev = curr
return ans사용된 알고리즘
- 해당 Line Sweep 알고리즘을 사용한다, 설명글 링크
- 간략하게 말하자면, 빌딩이 세워지고 내려가는 과정 자체를 전부 하나의 Event로 처리하는것이다.
- 그래서 맨 앞부분의 코드는 다음과 같은데
events = []
ans = []
for s, e, h in buildings:
events.append((s, -h))
events.append((e, h))- 빌딩이 시작되는 부분과 끝나는 부분을 이런식으로 정리해놓았다.
- 다만 왜 -를 높이에 붙혔냐? 파이썬은 정렬시 오름차순으로 정렬되기 때문에, 나중에 정리할때 건물이 세워지는 부분부터 처리를 해야 되어서 그렇다.
이후
1 events.sort()
2
3 height = [0]
4 remove_list = defaultdict(int)
5 prev = 0
6
7 for i, h in events:
8 if h < 0:
9 heappush(height, h)
10 else:
11 remove_list[h] += 1
12
13 curr = -height[0]
14 while remove_list[curr] > 0:
15 remove_list[curr] -= 1
16 heappop(height)
17 curr = -height[0]
18
19 if curr != prev:
20 ans.append([i, curr])
21 prev = curr1번 줄 : 이벤트 정렬
3~5번 줄 : 사용할 힙과 prev
-
prev : 높이가 변경될 때에만 저장되기에, 높이의 변경 여부를 확인해야 함
8~9번 줄: 건물이 세워지면 MaxHeap에 건물의 높이를 넣는다 -
즉, 세워진 건물의 가장 큰 높이를 계속 추적한다.
9~10번 줄: 건물이 내려가면, 삭제할 건물 리스트에 올려둔다.
13~17번 줄: 현재 가장 높은 건물에 해당하는 높이에 대해서, 해당 높이가 이미 끝난 건물인지 확인하고, 끝났으면 pop한다. -
이때 heappop을 그대로 사용가능해 시간복잡도상 유리해진다.
-
만약 remove_list를 쓰지 않고 list의 remove를 쓴다면 코드는 간단해 지지만, O(N^2)의 시간복잡도가 되어 버린다.
19~21번 줄: 끝난 건물들을 다 정리하고 남은 가장 높은 건물의 높이가 이전 높이와 다르다면, 정답에 추가if -height[0] != prev: ans.append([i, -height[0]]) prev = -height[0] -
여기서 curr은 가장 높으면서 끝나지 않은 건물을 의미하기에, 사실 이렇게 heap을 사용해도 정답은 변하지 않는다.
curr을 쓰지 않은 버전
class Solution: def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: events = [] ans = [] for s, e, h in buildings: events.append((s, -h)) events.append((e, h)) events.sort() height = [0] remove_list = defaultdict(int) prev = 0 for i, h in events: if h < 0: heappush(height, h) else: remove_list[h] += 1 while remove_list[-height[0]] > 0: remove_list[-height[0]] -= 1 heappop(height) if -height[0] != prev: ans.append([i, -height[0]]) prev = -height[0] return ans
