트리(Tree)
- 뿌리와 가지로 구성되어 거꾸로 세워놓은 나무처럼 보이는 계층형 비선형 자료 구조(계층적 혹은 망 구조)
- 선형구조는 자료를 저장하고 꺼내는 것에 초점이 맞춰져 있고,
비선형구조는 표현에 초점이 맞춰져 있음
- 이진 트리, 이진 탐색 트리, 균형 트리(AVL 트리, red-black 트리), 이진 힙(최대힙, 최소힙) 등
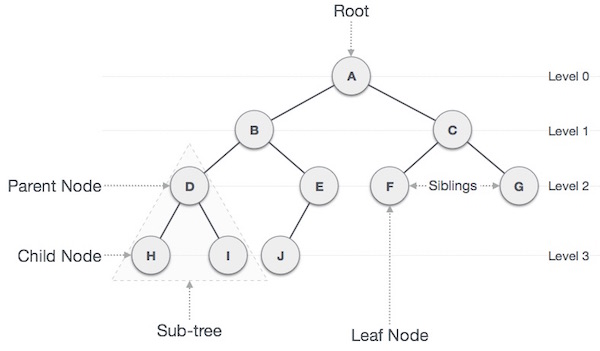
Node: 트리에서 데이터를 저장하는 기본 요소
Root Node: 트리 맨 위에 있는 노드
Level: 최상위 노드를 Level 0으로 하였을 때, 하위 Branch로 연결된 노드의 깊이를 나타냄
Parent Node: 어떤 노드의 상위 레벨에 연결된 노드
Child Node: 어떤 노드의 하위 레벨에 연결된 노드
Leaf Node(Terminal Node): Child Node가 하나도 없는 노드
Sibling: 동일한 Parent Node를 가진 노드
Depth: 트리에서 Node가 가질 수 있는 최대 Level
이진 트리(Binary Tree)
o Level 0
o o o Level 1
o o o Level 2 # 이진 트리(X)
o Level 0
o o Level 1
o o o Level 2 # 이진 트리(O)
완전 이진 트리(Complete Binary Tree)
- 노드를 삽입할 때 최하단 왼쪽 노드부터 차례대로 삽입해야 함
o Level 0
o o Level 1
o o Level 2 # -> 이진 트리 O 완전 이진 트리 X
o Level 0 # 루트 노드
o o Level 1
o o o Level 2 # -> 이진 트리 O 완전 이진 트리 O
# 트리의 높이는? 2 - 0 = 2
# 완전 이진 트리의 높이
level 0 의 노드 수 -> 2^0개
level 1 의 노드 수 -> 2^1개
level 2 의 노드 수 -> 2^2개
..
level k 의 노드 수 -> 2^k개
# 높이가 h인 완전 이진 트리의 전체 노드 수
1 + 2^1 + 2^2 + 2^3 + ... 2^h = 2^(h+1) - 1
# 최대 노드의 개수가 N일 때, 높이 h?
2^(h+1) -1 = N
2^(h+1) = N + 1
h + 1 = log_2(N+1)
h = log_2(N+1)-1 (최대 높이)
-> 최대 높이라도 O(log(N))의 시간복잡도
트리를 구현할 때는 편의성을 위해 0번째 인덱스는 사용되지 않습니다!
그래서 None 값을 배열에 넣고 시작합니다! [None]
8 Level 0 -> [None, 8] 첫번째 레벨의 8을 넣고,
6 3 Level 1 -> [None, 8, 6, 3] 다음 레벨인 6, 3을 넣고
4 2 5 Level 2 -> [None, 8, 6, 3, 4, 2, 5] 다음 레벨인 4, 2, 5를 넣으면 됩니다!
[None, 8, 6, 3, 4, 2, 5]
1 2 3 4 5 6 [6] [4]
1. 현재 인덱스 * 2 -> 왼쪽 자식의 인덱스 2 * 2 = 4
2. 현재 인덱스 * 2+1 -> 오른쪽 자식 인덱스 2 * 2 + 1 = 5 [2]
3. 현재 인덱스 // 2 -> 부모의 인덱스 2 // 2 = 1
[8]
예를 들어서 1번째 인덱스인 8의 왼쪽 자식은 6, 오른쪽 자식은 3 입니다.
그러면 1 * 2 = 2번째 인덱스! 6!
그러면 1 * 2 + 1 = 3번째 인덱스! 3! 입니다!
부모를 찾아보면, 3 // 2 = 1번째 인덱스 8 이므로 부모를 찾을 수 있습니다.
이를 다시 생각해보면
[None, 8, 6, 3, 4, 2, 5] 는
8 밑에 6, 3 이 있고, 6, 3 밑에 4, 2, 5가 있는 완전 이진 트리구나! 생각할 수 있습니다.
힙(Heap)
- 데이터에서 최대값과 최소값을 빠르게 찾기 위해 고안된 완전 이진 트리(Complete Binary Tree)
- 항상 큰 값이 상위 레벨에 있고 작은 값이 하위 레벨에 있도록 하는 자료구조. 부모 노드의 값이 자식 노드의 값보다 항상 커야 함(max heap)
Maxheap에 원소 추가
- 원소를 맨 마지막에 넣는다.
- 그리고 부모 노드와 비교한다. 만약 더 크다면 자리를 바꾼다.
- 부모 노드보다 작거나 가장 위에 도달하지 않을 때까지 2. 과정을 반복
class MaxHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.items = [None]
def insert(self, value):
self.items.append(value)
cur_index = len(self.items) - 1
while cur_index > 1:
parent_index = cur_index // 2
if self.items[cur_index] > self.items[parent_index]:
self.items[cur_index], self.items[parent_index] = self.items[parent_index], self.items[cur_index]
cur_index = parent_index
else:
return
max_heap = MaxHeap()
max_heap.insert(3)
max_heap.insert(4)
max_heap.insert(2)
max_heap.insert(9)
print(max_heap.items)
MaxHeap의 원소 삭제
- 최대값, 루트 노드만 삭제할 수 있음
- O(log(N)) 만큼의 시간 복잡도
- 루트 노드와 맨 끝에 있는 원소를 교체
- 맨 뒤에 있는 원소를 (원래 루트 노드)를 삭제
- 변경된 노드와 자식 노드들을 비교. 두 자식 중 더 큰 자식과 비교해서 자신보다 자식이 더 크다면 자리를 바꿈
- 자식 노드 둘 보다 부모 노드가 크거나 가장 바닥에 도달하지 않을 때까지 3. 과정을 반복
- 2에서 제거한 원래 루트 노드를 반환
class MaxHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.items = [None]
def insert(self, value):
self.items.append(value)
cur_index = len(self.items) - 1
while cur_index > 1:
parent_index = cur_index // 2
if self.items[parent_index] < self.items[cur_index]:
self.items[parent_index], self.items[cur_index] = self.items[cur_index], self.items[parent_index]
cur_index = parent_index
else:
break
def delete(self):
self.items[1], self.items[-1] = self.items[-1], self.items[1]
prev_max = self.items.pop()
cur_index = 1
while cur_index <= len(self.items) - 1:
left_child_index = cur_index * 2
right_child_index = cur_index * 2 + 1
max_index = cur_index
if left_child_index <= len(self.items) - 1 and self.items[left_child_index] > self.items[max_index]:
max_index = left_child_index
if right_child_index <= len(self.items) - 1 and self.items[right_child_index] > self.items[max_index]:
max_index = right_child_index
if max_index == cur_index:
break
self.items[cur_index], self.items[max_index] = self.items[max_index], self.items[cur_index]
cur_index = max_index
return prev_max
max_heap = MaxHeap()
max_heap.insert(8)
max_heap.insert(6)
max_heap.insert(7)
max_heap.insert(2)
max_heap.insert(5)
max_heap.insert(4)
print(max_heap.items)
print(max_heap.delete())
print(max_heap.items)


