
📗 WebMvcConfigurer
📄 WebMvcConfigurer란?
WebMvcConfigurer는 Spring에서 제공하는 interface로 MVC 설정에 필요한 것들을 기본적으로 설정해둔 곳이다. 해당 부분은 Spring에서 미리 정의해두어서 그대로 사용해도 되지만 해당 부분을 오버라이딩 하여 수정해서도 사용이 가능하다.
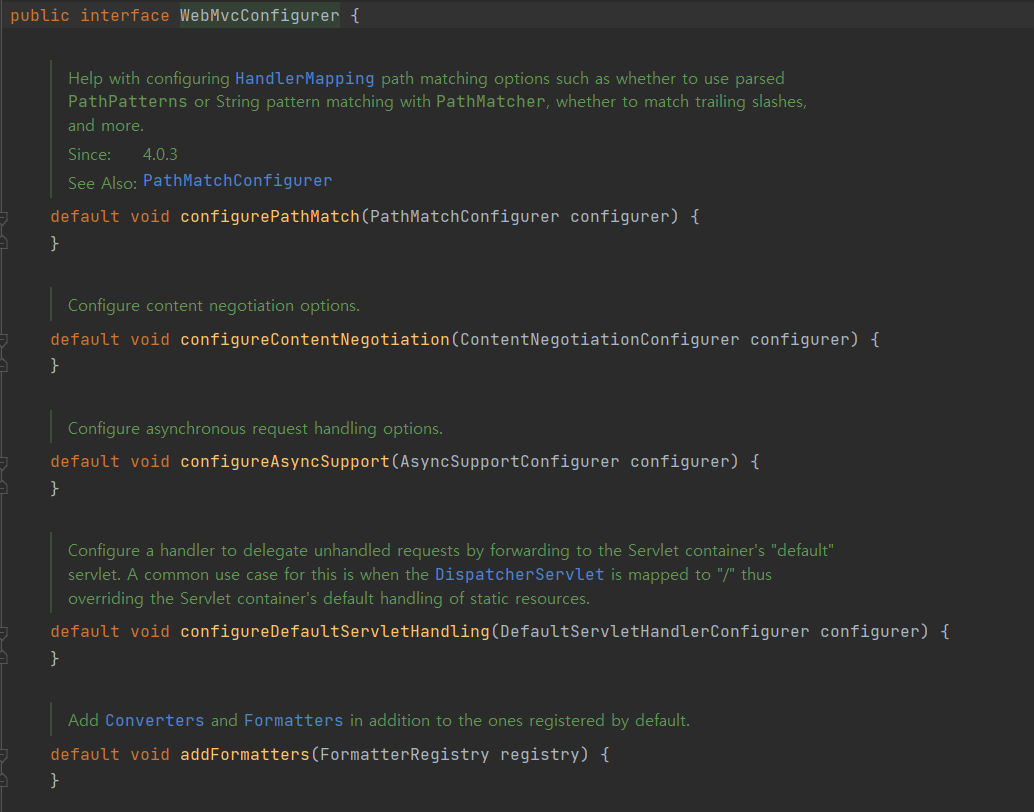
실제 소스를 뜯어 보면
package org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
import org.springframework.format.Formatter;
import org.springframework.format.FormatterRegistry;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.validation.MessageCodesResolver;
import org.springframework.validation.Validator;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter;
/**
* Defines callback methods to customize the Java-based configuration for
* Spring MVC enabled via {@code @EnableWebMvc}.
*
* <p>{@code @EnableWebMvc}-annotated configuration classes may implement
* this interface to be called back and given a chance to customize the
* default configuration.
*
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @author Keith Donald
* @author David Syer
* @since 3.1
*/
public interface WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* Help with configuring {@link HandlerMapping} path matching options such as
* whether to use parsed {@code PathPatterns} or String pattern matching
* with {@code PathMatcher}, whether to match trailing slashes, and more.
* @since 4.0.3
* @see PathMatchConfigurer
*/
default void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
}
/**
* Configure content negotiation options.
*/
default void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {
}
/**
* Configure asynchronous request handling options.
*/
default void configureAsyncSupport(AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer) {
}
/**
* Configure a handler to delegate unhandled requests by forwarding to the
* Servlet container's "default" servlet. A common use case for this is when
* the {@link DispatcherServlet} is mapped to "/" thus overriding the
* Servlet container's default handling of static resources.
*/
default void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
}
/**
* Add {@link Converter Converters} and {@link Formatter Formatters} in addition to the ones
* registered by default.
*/
default void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Add Spring MVC lifecycle interceptors for pre- and post-processing of
* controller method invocations and resource handler requests.
* Interceptors can be registered to apply to all requests or be limited
* to a subset of URL patterns.
*/
default void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Add handlers to serve static resources such as images, js, and, css
* files from specific locations under web application root, the classpath,
* and others.
* @see ResourceHandlerRegistry
*/
default void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Configure "global" cross-origin request processing. The configured CORS
* mappings apply to annotated controllers, functional endpoints, and static
* resources.
* <p>Annotated controllers can further declare more fine-grained config via
* {@link org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin @CrossOrigin}.
* In such cases "global" CORS configuration declared here is
* {@link org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration#combine(CorsConfiguration) combined}
* with local CORS configuration defined on a controller method.
* @since 4.2
* @see CorsRegistry
* @see CorsConfiguration#combine(CorsConfiguration)
*/
default void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Configure simple automated controllers pre-configured with the response
* status code and/or a view to render the response body. This is useful in
* cases where there is no need for custom controller logic -- e.g. render a
* home page, perform simple site URL redirects, return a 404 status with
* HTML content, a 204 with no content, and more.
* @see ViewControllerRegistry
*/
default void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Configure view resolvers to translate String-based view names returned from
* controllers into concrete {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.View}
* implementations to perform rendering with.
* @since 4.1
*/
default void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
}
/**
* Add resolvers to support custom controller method argument types.
* <p>This does not override the built-in support for resolving handler
* method arguments. To customize the built-in support for argument
* resolution, configure {@link RequestMappingHandlerAdapter} directly.
* @param resolvers initially an empty list
*/
default void addArgumentResolvers(List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers) {
}
/**
* Add handlers to support custom controller method return value types.
* <p>Using this option does not override the built-in support for handling
* return values. To customize the built-in support for handling return
* values, configure RequestMappingHandlerAdapter directly.
* @param handlers initially an empty list
*/
default void addReturnValueHandlers(List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> handlers) {
}
/**
* Configure the {@link HttpMessageConverter HttpMessageConverter}s for
* reading from the request body and for writing to the response body.
* <p>By default, all built-in converters are configured as long as the
* corresponding 3rd party libraries such Jackson JSON, JAXB2, and others
* are present on the classpath.
* <p><strong>Note</strong> use of this method turns off default converter
* registration. Alternatively, use
* {@link #extendMessageConverters(java.util.List)} to modify that default
* list of converters.
* @param converters initially an empty list of converters
*/
default void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
}
/**
* Extend or modify the list of converters after it has been, either
* {@link #configureMessageConverters(List) configured} or initialized with
* a default list.
* <p>Note that the order of converter registration is important. Especially
* in cases where clients accept {@link org.springframework.http.MediaType#ALL}
* the converters configured earlier will be preferred.
* @param converters the list of configured converters to be extended
* @since 4.1.3
*/
default void extendMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
}
/**
* Configure exception resolvers.
* <p>The given list starts out empty. If it is left empty, the framework
* configures a default set of resolvers, see
* {@link WebMvcConfigurationSupport#addDefaultHandlerExceptionResolvers(List, org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManager)}.
* Or if any exception resolvers are added to the list, then the application
* effectively takes over and must provide, fully initialized, exception
* resolvers.
* <p>Alternatively you can use
* {@link #extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List)} which allows you to extend
* or modify the list of exception resolvers configured by default.
* @param resolvers initially an empty list
* @see #extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List)
* @see WebMvcConfigurationSupport#addDefaultHandlerExceptionResolvers(List, org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManager)
*/
default void configureHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) {
}
/**
* Extending or modify the list of exception resolvers configured by default.
* This can be useful for inserting a custom exception resolver without
* interfering with default ones.
* @param resolvers the list of configured resolvers to extend
* @since 4.3
* @see WebMvcConfigurationSupport#addDefaultHandlerExceptionResolvers(List, org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManager)
*/
default void extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) {
}
/**
* Provide a custom {@link Validator} instead of the one created by default.
* The default implementation, assuming JSR-303 is on the classpath, is:
* {@link org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.OptionalValidatorFactoryBean}.
* Leave the return value as {@code null} to keep the default.
*/
@Nullable
default Validator getValidator() {
return null;
}
/**
* Provide a custom {@link MessageCodesResolver} for building message codes
* from data binding and validation error codes. Leave the return value as
* {@code null} to keep the default.
*/
@Nullable
default MessageCodesResolver getMessageCodesResolver() {
return null;
}
}다음과 같이 정의되어 있고 메서드를 하나씩 뜯어보자.
✅ configurePathMatch
사용자의 요청에 대한 컨트롤러를 매핑해주는 역할을 한다.
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.addPathPrefix("/v1", HandlerTypePredicate.forAnnotation(RestController.class, Controller.class));
}
} 다음과 같이 addPathPrefix() 메서드를 사용하여 RestController와 Controller의 Annotation에 PathPrefix를 두면
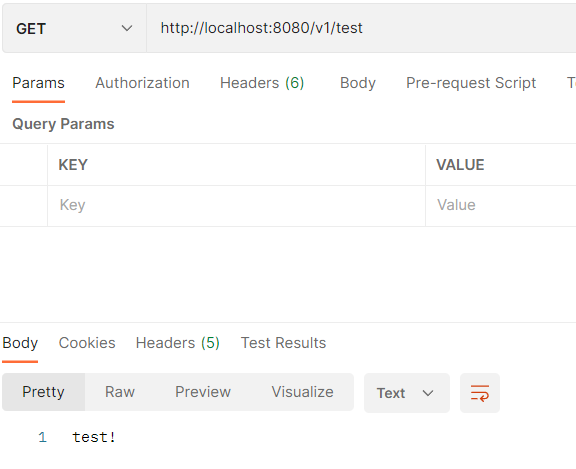
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public ResponseEntity<?> test(){
return ResponseEntity.ok("test!");
}
} 다음과 같이 @RestController 어노테이션이 붙은 Controller에 v1 url이 추가되어진다.
✅ 내가 생각한 사용 방법
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Component
public @interface V1 {
}다음과 같이 마커용 어노테이션을 생성하고
@V1
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public ResponseEntity<?> test(){
return ResponseEntity.ok("test!");
}
}이렇게 V1이라는 어노테이션을 달아준 Controller에 prefix를 줄 수 있다면 url 자체적으로 @Request("/v1") 이라는 버저닝을 따로 하지 않고 어노테이션에 따라서 해당 prefix를 조절할 수 있게 될 수 있어 편할거 같았다.
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
configurer
.setUseTrailingSlashMatch(true) // true : `/v1/test` == `/v1/test/`
.addPathPrefix("/v1", HandlerTypePredicate.forAnnotation(V1.class))
.setPathMatcher(new AntPathMatcher()) // @RequestMapping과 사용자 요청에 대한 url 매칭
.setUrlPathHelper(new UrlPathHelper()) // @PathVariable 값을 처리하는데 사용
;
}
}설정 부분도 다음과 같이 사용할 수 있었다.
아래 setPathMatcher와 setUrlPathHelper 또한 설정의 변경이 필요하다면 설정을 변경해주면 된다.
