문제 - 최소 힙 (Silver 2) / 최대 힙 (Silver 2) / 절댓값 힙 (Silver1)
minHeap
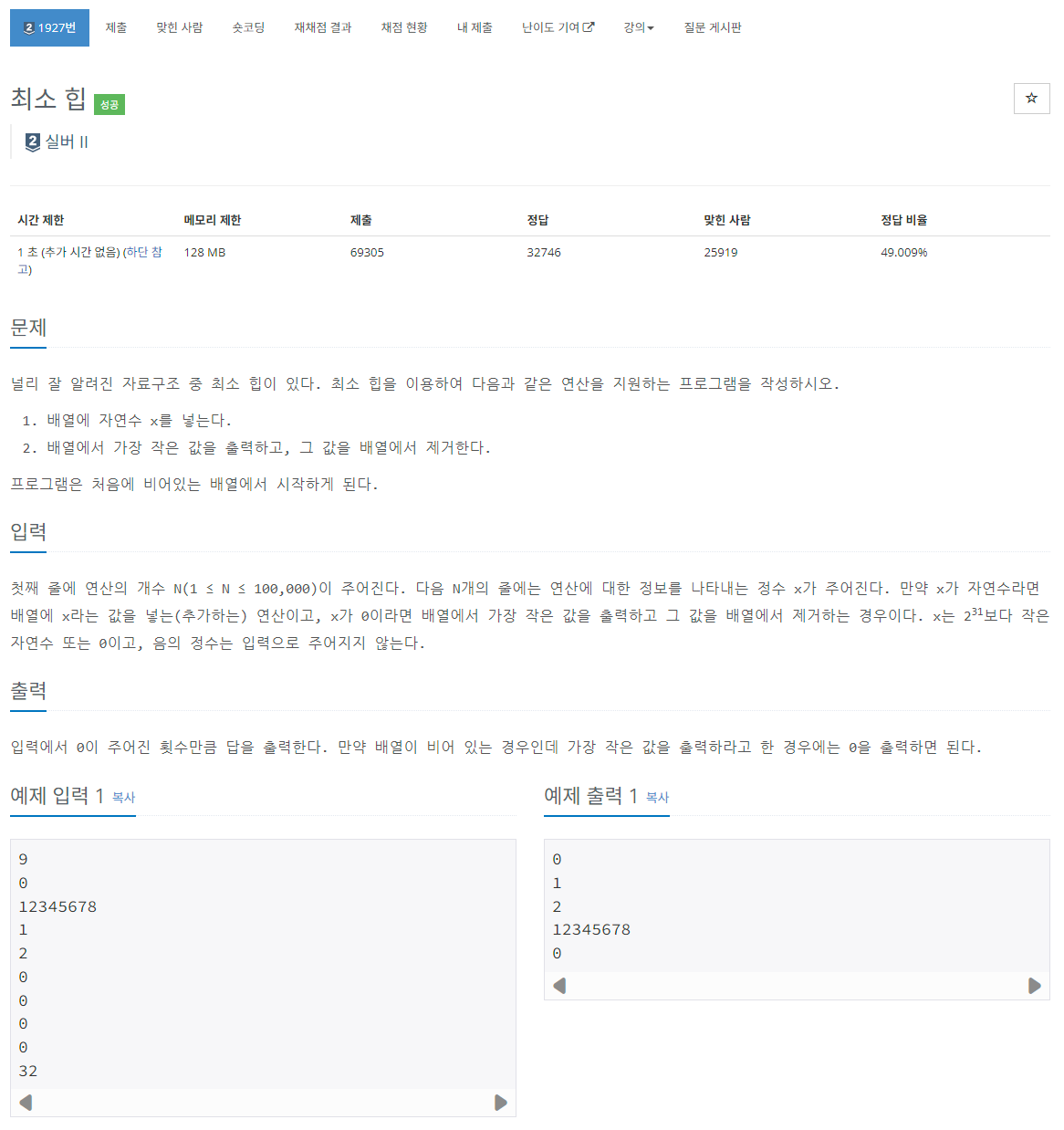
[백준 1927] https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1927
maxHeap
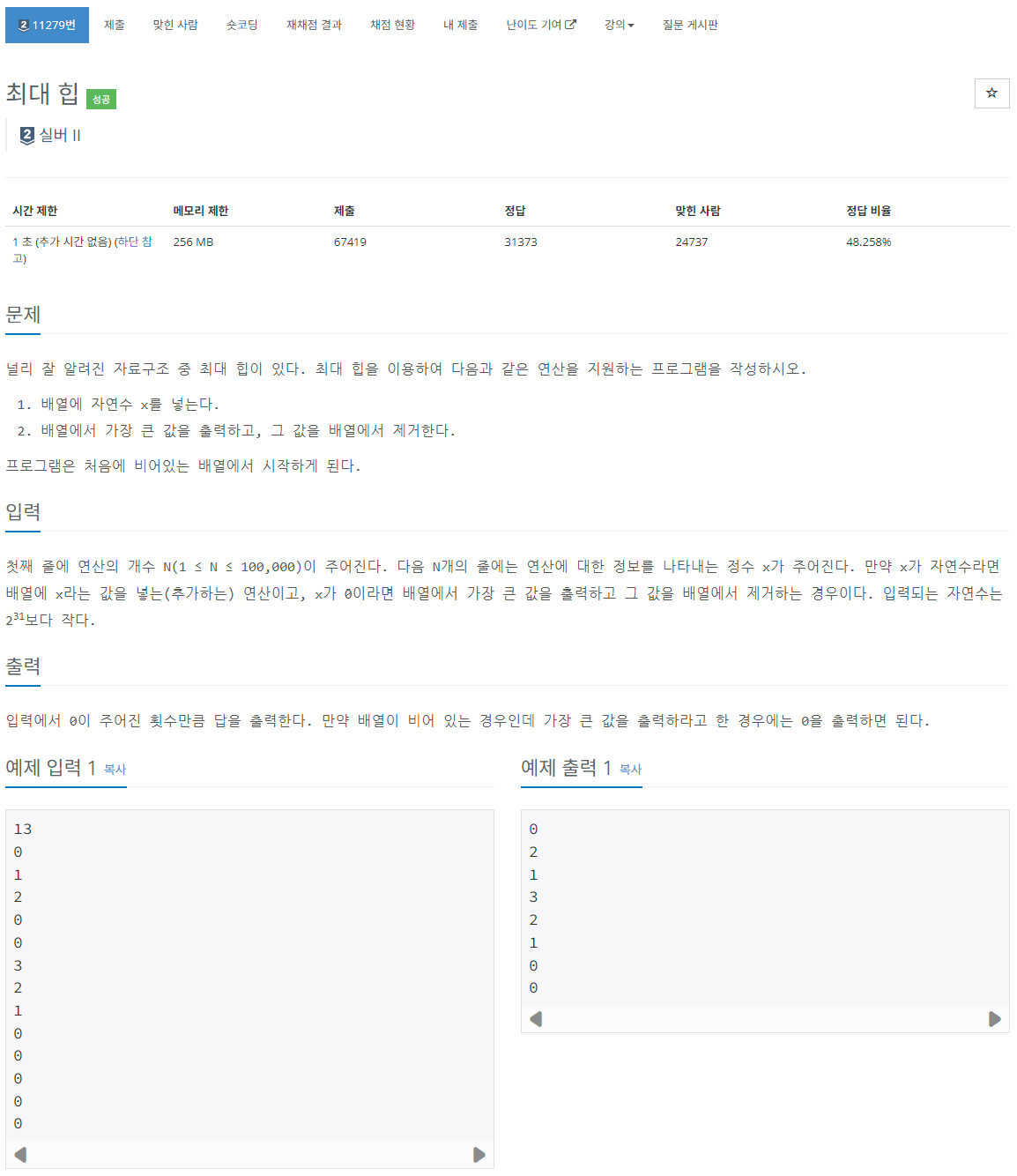
[백준 11279] https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11279
absHeap
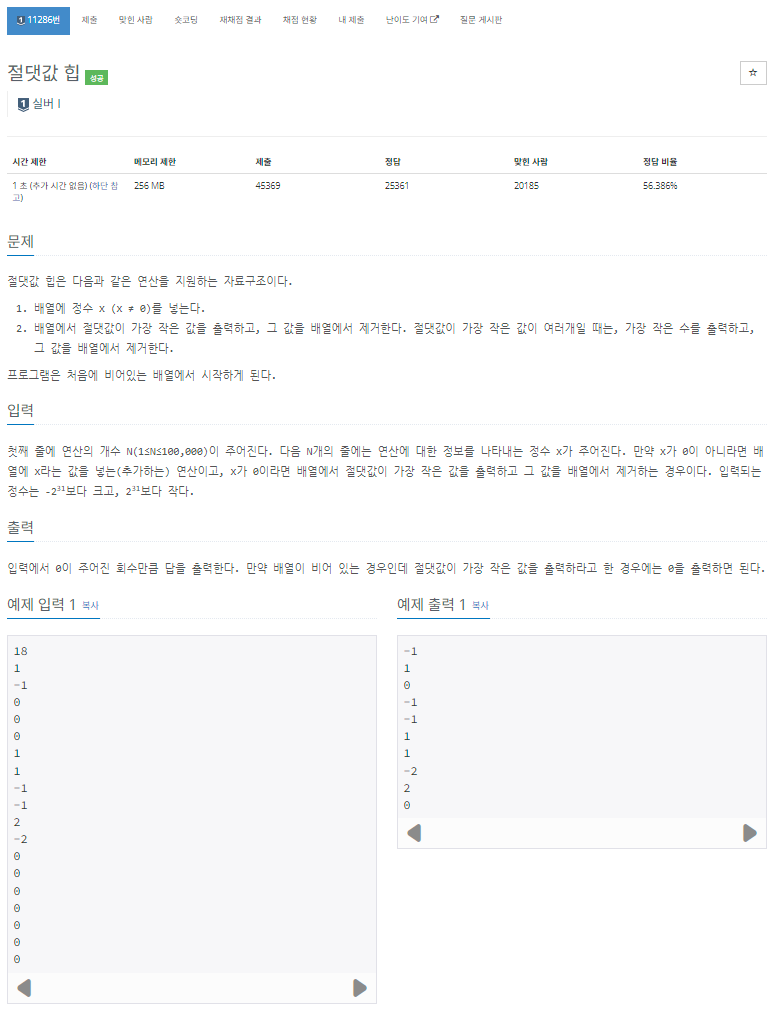
[백준 11286] https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11286
텍스트
우선 두 문제를 하나의 포스트에 함께 정리한 이유는 두 문제의 코드가 단 한줄의 차이이기 때문이다.
이 두 문제는 Queue에 원소가 오름차순으로 들어가냐 내림차순으로 들어가냐의 차이이기 때문에 Priority_Queue를 선언할 때만 차이가 난다.
풀이 전략
- 우선순위 큐를 사용해서 입력 값에 따라 숫자를 push/pop 한다.
- 우선순위 큐는 기본값이 queue에 들어간 숫자들이 제일 큰 수가 top에 있도록 정렬되기 때문에 최소힙 문제는
greater<int>를 사용해서 제일 작은 수가 top에 있도록 정렬하고, 최대힙 문제는 그대로 사용한다.- 절댓값 힙은 특이하게 절댓값이 작은 순서대로 출력하는거기 때문에 따로 cmp 구조체를 만들어서 수들을 비교하는 코드를 우선순위 큐에
greater<int>넣는다.
참고
[Priority Queue 오름차순 정렬]
https://zoosso.tistory.com/993[MaxHeap / MinHeap 이해하기에 좋은 글]
https://code-lab1.tistory.com/12#google_vignette
[Priority_Queue]
기존 Queue와 달리 Priority_Queue는 Queue에 있는 모든 원소 중에서 가장 큰 값이 Top을 유지하도록 설계되어 있다.(설명을 위해 Priority_Queue를 줄여서 PQ라고 하겠다.)
- 기본 메소드
push(): PQ에 원소를 추가pop(): PQ의 top에 있는 원소를 제거top(): PQ의 top에 있는 원소를 반환 (PQ에서는 제일 큰 수)empty(): PQ가 비어있으면 true, 아니면 false를 반환size(): PQ에 들어있는 원소의 개수를 반환*기존의 Priority_Queue 선언
priority_queue<int> PQ;*작은 숫자가 top에 오게 하는 방법 (오름차순 정렬)
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> PQ;Priority Queue를 선언할 때 오름차순 정렬으로 선언하는 방법도 있지만, 원소를 넣을 때 음수로 변환해서 넣으면 음수는 절댓값 숫자가 작을수록 더 큰 수이기 때문에 절댓값이 작은 숫자가 Top으로 오게 된다.
소스 코드
maxHeap은 C와 C++버전 두 개가 있다.
미리 설명하자면, Priority_Queue를 C언어로 구현하기 위해서는 Tree를 사용해야 한다.

왜냐하면 Priority_Queue는 Top에 제일 큰 원소가 오기 때문에 Tree를 구현해서 부모와 자식을 비교한 뒤 자식 노드에 있는 원소가 부모 노드에 있는 원소보다 크면 부모와 자식을 Swap해서 우선순위를 높여야 하기 때문이다.

그렇기 때문에 C언어로 구현하면 C++로 구현할 때 보다 훠~~~얼씬 코드가 길고 복잡한 것은 어떻게 보면 당연한 일이다.
minHeap
[C++]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int N;
cin>>N;
vector<int> A(N);
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> PQ;
// 오름차순 정렬 우선순위 큐 선언
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
cin>>A[i];
if(A[i]==0){ // 입력값이 0이면
if(!PQ.empty()){
cout<<PQ.top()<<'\n';
PQ.pop();
}
// PQ가 비어있지 않으면 top의 값을 출력하고 그 값을 pop함
else{
cout<<"0"<<'\n';
}
// PQ가 비어있으면 0 출력
}else{
PQ.push(A[i]);
} // 입력값이 0이 아니면 PQ에 입력값을 push함
}
return 0;
}[C]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int compare(const void *a, const void *b){
return (*(int*)a)-(*(int*)b);
} // 작은 수가 위로오게 하기 위함
typedef struct PriorityQueue *PQ;
struct PriorityQueue{
int capacity;
int size;
int* Element;
};
PQ createQueue(int MaxSize){
PQ pq=(PQ)malloc(sizeof(struct PriorityQueue));
if(pq==NULL){
return NULL;
}
pq->capacity=MaxSize;
pq->size=0;
pq->Element=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(MaxSize+1));
if(pq->Element==NULL){
free(pq);
return NULL;
}
return pq;
}
PQ destroyQueue(PQ pq){
free(pq->Element);
free(pq);
}
int isEmpty(PQ pq){
return pq->size==0;
}
int isFull(PQ pq){
return pq->size==pq->capacity;
}
void Push(PQ pq, int data){
if(isFull(pq)){
return;
}
pq->Element[++pq->size]=data;
int child=pq->size;
int parent=child/2;
while(parent>0 && compare(&pq->Element[child],&pq->Element[parent])<0){
int temp=pq->Element[parent];
pq->Element[parent]=pq->Element[child];
pq->Element[child]=temp;
child=parent;
parent=child/2;
}
}
int Pop(PQ pq){
if(isEmpty(pq)){
return 0;
}
int Top=pq->Element[1];
pq->Element[1]=pq->Element[pq->size--];
int parent=1;
while(1){
int leftchild=2*parent;
int rightchild=2*parent+1;
int smallest=parent;
if(leftchild<=pq->size && compare(&pq->Element[leftchild],&pq->Element[smallest])<0){
smallest=leftchild;
}
if(rightchild<=pq->size && compare(&pq->Element[rightchild],&pq->Element[smallest])<0){
smallest=rightchild;
}
if(smallest!=parent) {
int temp=pq->Element[parent];
pq->Element[parent]=pq->Element[smallest];
pq->Element[smallest]=temp;
parent=smallest;
}else{
break;
}
}
return Top;
}
int main(void){
int N;
scanf("%d",&N);
PQ pq=createQueue(N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
int num;
scanf("%d",&num);
if(num==0){
if(!isEmpty(pq)){
printf("%d\n",Pop(pq));
}else{
printf("0\n");
}
}else{
Push(pq,num);
}
}
destroyQueue(pq);
return 0;
}maxHeap
[C++]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int N;
cin>>N;
vector<int> A(N);
priority_queue<int> PQ;
// minHeap 문제와 이 한줄만 차이가 난다.
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
cin>>A[i];
if(A[i]==0){
if(!PQ.empty()){
cout<<PQ.top()<<'\n';
PQ.pop();
}else{
cout<<"0"<<'\n';
}
}else{
PQ.push(A[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}[C]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Priority_Queue *PQ;
struct Priority_Queue {
int capacity; // 최대 Size
int size; // 원소 개수
int *Element; // 원소를 저장할 배열
};
PQ CreatePQ(int MaxSize) {
PQ pq = (PQ)malloc(sizeof(struct Priority_Queue));
if (pq == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
pq->size = 0;
pq->capacity = MaxSize;
pq->Element = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (MaxSize + 1));
if (pq->Element == NULL) {
free(pq);
return NULL;
}
return pq;
}
int isEmpty(PQ pq) {
return pq->size == 0;
}
int isFull(PQ pq) {
return pq->size == pq->capacity;
}
void Push(PQ pq, int value) {
if (isFull(pq)) {
return;
}
pq->Element[++pq->size] = value;
int child = pq->size;
int parent = child / 2;
while (parent > 0 && pq->Element[parent] < pq->Element[child]) {
int temp = pq->Element[parent];
pq->Element[parent] = pq->Element[child];
pq->Element[child] = temp;
child = parent;
parent = child / 2;
} // 부모보다 자식이 더 크면 Swap한 뒤, 위로 올라감
}
int Pop(PQ pq) {
if (isEmpty(pq)) {
return 0;
}
int top = pq->Element[1]; // 1번 위치가 Root 노드이기 때문
pq->Element[1] = pq->Element[pq->size--];
// Pop을 하면 Top의 원소가 제거되기 때문
int parent = 1;
while (1) {
int leftchild = 2 * parent;
int rightchild = 2 * parent + 1;
int largest = parent;
if (leftchild <= pq->size && pq->Element[leftchild] > pq->Element[largest]) {
largest = leftchild;
} // 왼쪽 자식이 부모보다 크면 왼쪽자식을 largest로 업데이트
if (rightchild <= pq->size && pq->Element[rightchild] > pq->Element[largest]) {
largest = rightchild;
} // 오른쪽 자식이 부모보다 크면 오른쪽자식을 largest로 업데이트
if (largest != parent) {
int temp = pq->Element[parent];
pq->Element[parent] = pq->Element[largest];
pq->Element[largest] = temp;
parent = largest;
} // largest가 위에 있지 않으면 largest랑 부모를 swap
else {
break;
} // largest가 가장 위에 있으면 priority_queue가 성립하므로 무한루프 탈출
}
return top;
}
void freePQ(PQ pq) {
free(pq->Element);
free(pq);
}
int main(void) {
int N;
scanf("%d", &N);
PQ pq = CreatePQ(N);
int num;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
scanf("%d", &num);
if (num == 0) {
if (!isEmpty(pq)) {
printf("%d\n", Pop(pq));
} else {
printf("0\n");
}
} else {
Push(pq, num);
}
}
freePQ(pq);
return 0;
}
absHeap
[C++]
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
struct cmp{
bool operator()(int a, int b){
if(abs(a)==abs(b)){
if(a>b)
return a>b; // True
else{
return b<a; // False
}
}else{
return abs(a)>abs(b); // 절댓값이 작은 순서대로 배열하기 위함
}
}
};
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int N;
cin>>N;
vector<int> A(N);
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,cmp> pq;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
cin>>A[i];
if(A[i]==0){
if(pq.empty()){
cout<<"0"<<'\n';
}else{
cout<<pq.top()<<'\n';
pq.pop();
}
}else{
pq.push(A[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}결과
minHeap
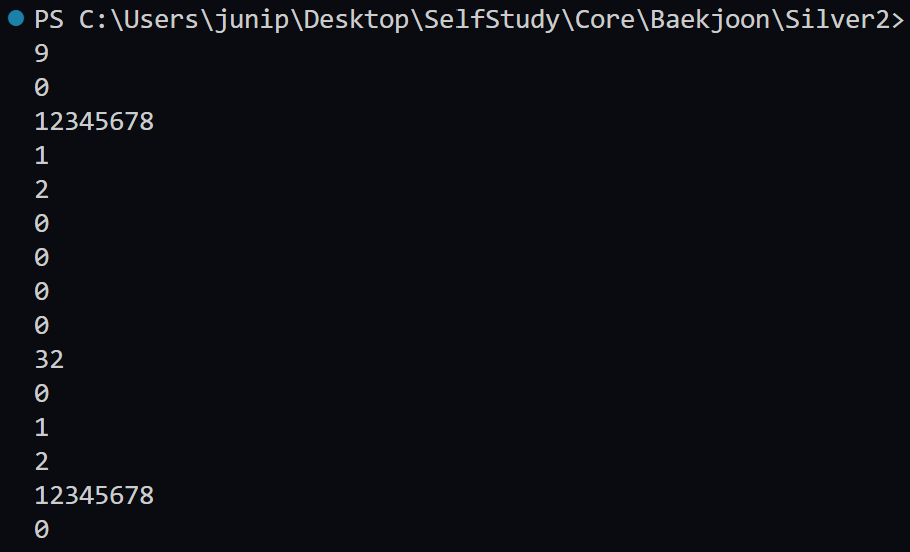

maxHeap
<C++ 제출>

<C 제출>
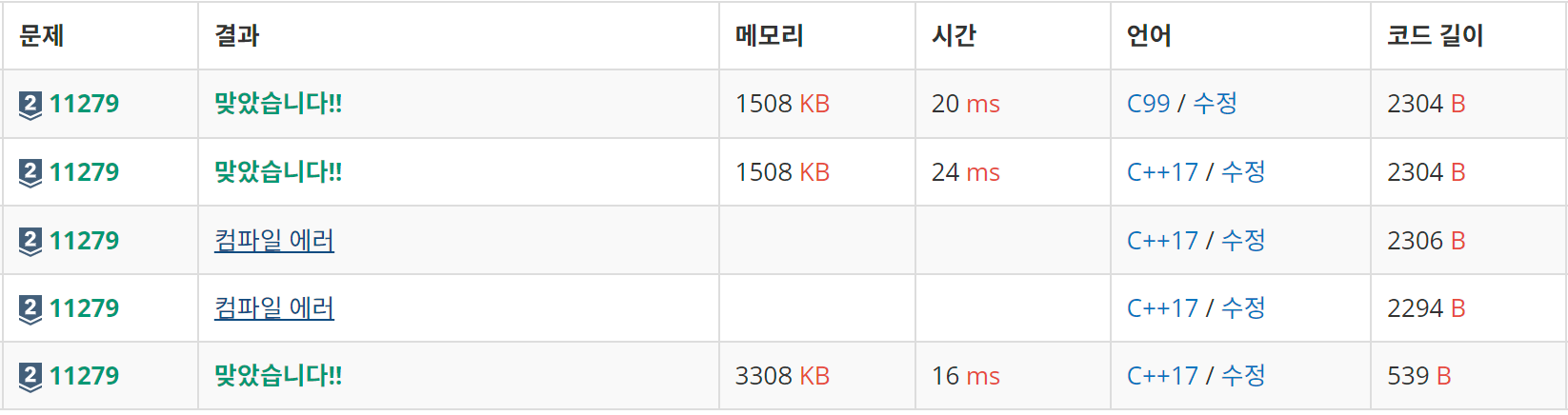
absHeap
maxHeap을 C로 제출할 때 두 번의 컴파일에러가 난 이유는 동적할당을 할 때, void*로 자동으로 들어가서 그런것 같다.
동적할당을 했기 때문에 코드 길이가 4배 차이남에도 메모리 크기는 1/2로 줄어든 것을 알 수 있다.
근데 왜 C++17이랑 C99랑 같은 코드인데도 4ms나 차이나는지는 의문이다..
