문제
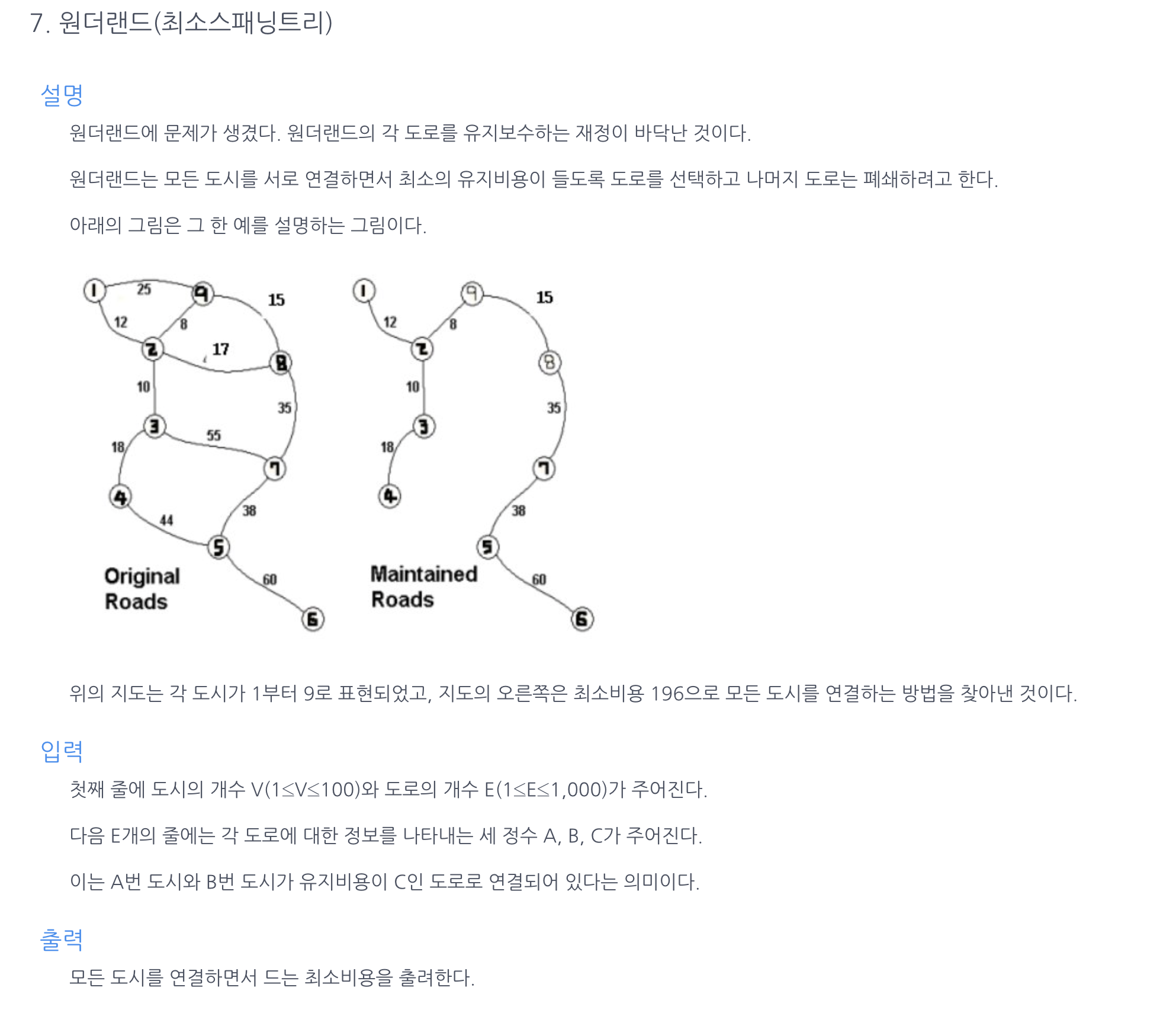
설명
최소 스패닝 트리를 찾는 문제이다.
그래프는 노드(또는 정점)와 이들 노드를 연결하는 간선(또는 링크)로 이루어져 있는데,
최소 스패닝 트리(MST, Minimum Spanning Tree)는 그래프 내의 모든 정점을 정확히 한 번씩만 방문하면서 전체 가중치(간선의 가중치 합)가 최소가 되는 트리를 말한다. 다시 말해, MST는 그래프의 모든 정점을 연결하는 부분 그래프 중에서 간선의 가중치 합이 가장 적은 트리이다.
MST를 구하는 알고리즘으로는 크루스칼과 프림이 있다.
풀이(크루스칼)
package inflearn.nine.원더랜드_최소스패닝트리_크루스칼;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
cityNum = sc.nextInt();
roads = sc.nextInt();
cities = new int[cityNum+1];
for(int i = 0; i< cityNum+1; i++) cities[i] = i;
edges = new int[roads][3];
for(int i = 0; i<roads; i++){
edges[i][0] = sc.nextInt();
edges[i][1] = sc.nextInt();
edges[i][2] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(solution());
}
static int cityNum;
static int roads;
static int[] cities;
static int[][] edges;
/**
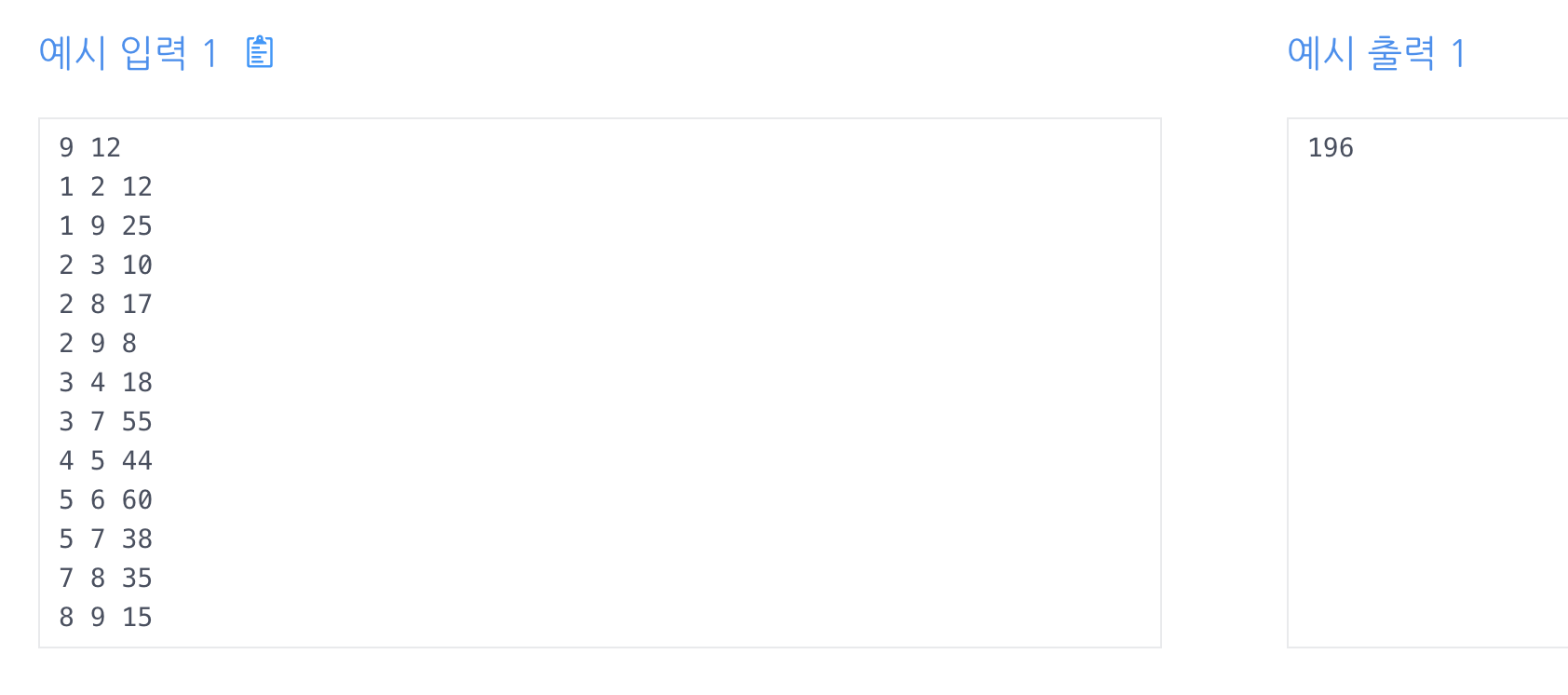
9 12
1 2 12
1 9 25
2 3 10
2 8 17
2 9 8
3 4 18
3 7 55
4 5 44
5 6 60
5 7 38
7 8 35
8 9 15
*/
public static int solution(){
int result = 0;
Arrays.sort(edges, (o1, o2)->{
return o1[2] - o2[2];
});
for(int[] edge : edges){
if(find(edge[0]) != find(edge[1])){
result += edge[2];
union(edge[0], edge[1]);
}
}
return result;
}
public static void union(int city1, int city2){
cities[find(city1)] = find((city2));
}
public static int find(int city){
if(city == cities[city]) return city;
else return cities[city] = find(cities[city]);
}
}
풀이 설명
- 크루스칼 알고리즘에서는 union & find 가 사용된다.
- 모든 간선에 대해 cost 기준 내림차순으로 정렬한다.
- 모든 간선을 순회한다.
- 간선에 해당하는 두 개의 도시가 이미 union되어있는지 확인하고, 그렇지 않다면 해당 간선을 사용하여 두 city를 하나의 그룹으로 묶는다(union)
모든 노드를 cost가 적은 간선들만 이용하여 모두 잇는 것.
풀이(프림)
package inflearn.nine.원더랜드_최소스패닝트리_프림;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
cityNum = sc.nextInt();
roads = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i<roads; i++){
int city1 = sc.nextInt();
int city2 = sc.nextInt();
int cost = sc.nextInt();
List<Edge> list1 = map.getOrDefault(city1,new ArrayList<>());
list1.add(new Edge(city1,city2,cost));
List<Edge> list2 = map.getOrDefault(city2,new ArrayList<>());
list2.add(new Edge(city2,city1,cost));
map.put(city1,list1);
map.put(city2,list2);
}
visited = new boolean[cityNum+1];
System.out.println(solution());
}
/**
9 12
1 2 12
1 9 25
2 3 10
2 8 17
2 9 8
3 4 18
3 7 55
4 5 44
5 6 60
5 7 38
7 8 35
8 9 15
*/
static int cityNum;
static int roads;
static Map<Integer,List<Edge>> map = new HashMap<>();
static boolean[] visited;
public static int solution(){
int result = 0;
PriorityQueue<Edge> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
queue.addAll(map.get(1));
visited[1] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Edge edge = queue.poll();
if(!visited[edge.city2]){
result += edge.cost;
visited[edge.city2] = true;
queue.addAll(map.getOrDefault(edge.city2, new ArrayList<>()));
}
}
return result;
}
public static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int city1;
int city2;
int cost;
public int compareTo(Edge other){
return this.cost - other.cost;
}
public Edge(int c1, int c2, int cost){
city1 = c1;
city2 = c2;
this.cost = cost;
}
}
}
풀이 설명
- 각 노드 별 간선을 저장한다.
- 임의의 노드를 선택하여 해당 노드에 해당하는 간선을 PriorityQueue에 저장한다.
- queue에서 poll하여 cost가 가장 작은 간선을 얻는다.
- 얻은 간선이 향하는 다른 city가 아직 방문되지 않았다면 해당 노드를 트리에 추가한다 (간선의 cost를 더한다.)
- 새로 추가된 노드의 간선을 모두 PriorityQueue에 추가한다.
- 모든 노드에 대한 처리가 이뤄질 때까지 3~5의 과정을 반복한다.
크루스칼 vs 프림
풀이는 크루스칼 알고리즘이 개인적으로 더 직관적이고 쉽게 느껴진다.
하지만 크루스칼 알고리즘의 경우 cost에 따른 정렬이 필요하므로 간선이 많은 경우 프림 알고리즘을 사용하는 것이 더욱 효율적이다.
따라서 MST를 구해야 하는 상황에 대한 두 알고리즘을 모두 알고 있는 것이 좋다.
