문제


입출력예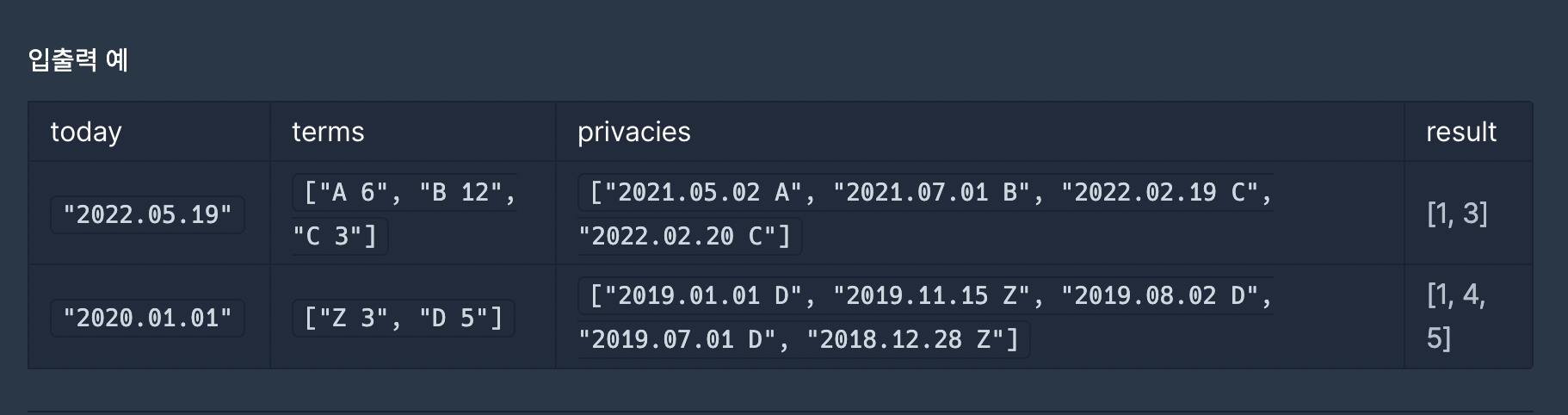
풀이
public static void main(String[] args) {
String today = "2020.12.01";
String[] terms = new String[]{"Z 3", "D 12"};
String[] privacies = new String[]{"2019.12.01 D", "2019.11.15 Z", "2019.08.02 D", "2019.07.01 D", "2018.12.28 Z"};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution(today, terms, privacies)));
}
public static Integer[] solution(String todayString, String[] terms, String[] privacies){
Policies policies = new Policies(terms);
Day today = new Day(todayString);
List<Privacy> privacyList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String privacy : privacies) {
Privacy privacy1 = new Privacy(privacy);
privacyList.add(privacy1);
}
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 1; i <= privacyList.size(); i++){
if(privacyList.get(i-1).isExpired(policies, today)) result.add(i);
}
return result.toArray(Integer[]::new);
}
public static class Privacy {
Day savedDay;
String policy;
public Privacy(String privacyString){
String[] s = privacyString.split(" ");
savedDay = new Day(s[0]);
policy = s[1];
}
public boolean isExpired(Policies policies, Day today){
int term = policies.getTerm(policy); // 사생활 정보의 유효기간
Day expiringDay = savedDay.addMonth(term);
System.out.println("expiringDay : " + expiringDay);
return today.isLaterThan(expiringDay) || today.equals(expiringDay);
}
}
public static class Policies {
Map<String, Integer> policies = new HashMap<>();
public Policies(String[] arr){
for(String policy : arr){
String[] s= policy.split(" ");
policies.put(s[0], Integer.parseInt(s[1]));
}
}
public int getTerm(String policy){
return policies.get(policy);
}
}
public static class Day{
int year;
int month;
int day;
public Day(String dayString){
String[] data = dayString.split("\\.");
year = Integer.parseInt(data[0]);
month = Integer.parseInt(data[1]);
day = Integer.parseInt(data[2]);
}
public Day addMonth(int month){
this.month += month;
System.out.println("added month : "+ this.month);
if(this.month > 12){
if(this.month % 12 == 0){
year += (this.month / 12)-1;
this.month = 12;
}else {
year += (this.month / 12);
this.month %= 12;
}
}
return this;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return year + "." + month + "." + day;
}
public boolean isLaterThan(Day otherDay) {
if(this.year > otherDay.year) return true;
else if(this.year == otherDay.year && this.month > otherDay.month) return true;
else if(this.year == otherDay.year && this.month == otherDay.month && this.day > otherDay.day) return true;
else return false;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object otherDay){
Day other = (Day) otherDay;
return this.year == other.year && this.month == other.month && this.day == other.day;
}
}
계산이 복잡한 부분이 없고 객체지향적으로 풀면 딱이다 싶었던 문제인데,
한 달 28일 고정인 점을 이용해서 단순 곱 연산을 이용해 푼 사람도 있었음.... 그렇게도 풀 수 있겠구나 깨달음
12월달을 나누는 부분에서 몫이 0이 되는 경우에 대한 처리를 해야 되는데 빼먹는 바람에 디버깅이 너무 길어져버렸다. 다음부터는 나머지가 0인 경우를 항상 염두에 두고 풀어야겠다.
