[Eclipse 연습]
[계산] class Rectangle6 { private int x, y, width, height; public Rectangle6(int x, int y, int width, int height) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.width = width; this.height = height; } public void show() { System.out.println("(" + x + "," + y + ")에서 크기가 " + width + "x" + height + "인 사각형"); } public int square() { return width * height; } public boolean contains(Rectangle6 r) { if (this.x < r.x && this.y < r.y) { // x = 가로시작점, y = 세로 시작점 / r.x = 비교할 가로 시작점, r.y = 비교할 세로 시작점 if ((this.width + this.x) > (r.x + r.width) && (this.height + this.y) > (r.y + r.height)) { return true; } } return false; } } public class Test23 { public static void main(String[] args) { Rectangle6 r = new Rectangle6(2, 2, 8, 7); Rectangle6 s = new Rectangle6(5, 5, 6, 6); Rectangle6 t = new Rectangle6(1, 1, 10, 10); r.show(); System.out.println("s의 면적은 " + s.square()); if (t.contains(r)) System.out.println("t는 r을 포함합니다."); if (t.contains(s)) System.out.println("t는 s를 포함합니다."); } }[결과값] (2,2)에서 크기가 8x7인 사각형 s의 면적은 36 t는 r을 포함합니다.
[접근 수준 지시자]
class : public, default만 붙는다.
접근 수준 지시자 : 클래스 앞 / 변수 앞 / 변수 앞 / 인스턴스 앞에 붙는다.
지역변수 앞에는 public이 붙지 않는다.
public으로 무조건 함수와 생성자를 지정한다.
(public Rectangle6(int x, int y, int width, int height) {})
private으로 무조건 데이터 멤버를 지정한다.
(>private int x,y;)……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
** 한 파일에 public 으로 선언된 클래스는 두 개 이상 오면 안됨**
하기 코드는 오류가 발생한다.
public을 진입점으로 줘서 public class부터 읽기 때문.
public class Rectangle{}
public class B{
public static void main(String[] args){}
}[캡슐화]
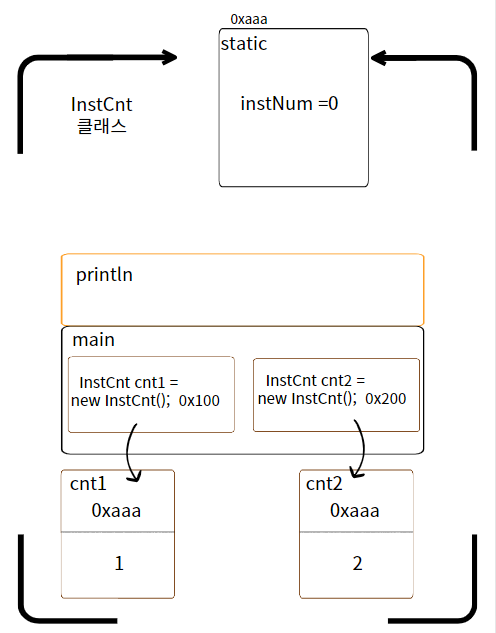
함수 앞에 static을 사용하면 메모리를 공유한다.(static int instNum=0)
static의 초기화 위치는 class에서 한다!(class InstCnt{static int instNum=100;)
static : 따로 객체생성 전에 먼저 한 번 메모리에 올린다.
[함수 읽는 방법]
[int num = 0;]
인스턴스 변수
지역변수
[static int num = 0;]
*static 변수 = 공유 변수 = 클래스 변수 = 정적변수[계산] class Instcnt { static int instNum = 0; // 클래스 변수(static 변수) // static을 없애면 결과는 인스턴스 생성: 1 (*3)으로 나온다. Instcnt() { instNum++; System.out.println("인스턴스 생성: " + instNum); } } public class ClassVar { public static void main(String[] args) { Instcnt cnt1 = new Instcnt(); // Instcnt cnt1을 만들면 먼저 Instcnt class에 static이 있는지 스캔(체크)한다. // 객체생성 전에 따로 먼저 4byte의 메모리 방을 잡는다. // cnt1(Instcnt)라는 방을 생성한다. // 메모리는 static int instNum을 제외하고 Instcnt()생성자만 생성한다. Instcnt cnt2 = new Instcnt(); Instcnt cnt3 = new Instcnt(); } }[결과값] 인스턴스 생성: 1 인스턴스 생성: 2 인스턴스 생성: 3
[계산] class AccessWay { static int num = 0; AccessWay() { incrCnt(); } void incrCnt() { num++; // 클래스 내부에서 이름을 통한 접근 } } public class ClassVarAccess { public static void main(String[] args) { AccessWay way = new AccessWay(); way.num++; // 외부에서 인스턴스의 이름을 통한 접근 AccessWay.num++; // 외부에서 클래스의 이름을 통한 접근 System.out.println("num = " + AccessWay.num); } }[결과값] num = 3
[계산] class InstCnt1 { static int instNum = 100; // 클래스 변수의 적절한 초기화 위치 InstCnt1() { instNum++; System.out.println("인스턴스 생성: " + instNum); } } //클래스 변수는 생성자 기반 초기화 하면 안된다! //이 경우 인스턴스 생성시마다 값이 리셋! public class OnlyClassNoInstance { public static void main(String[] args) { InstCnt1.instNum -= 15; // 인스턴스 생성 없이 instNum에 접근 System.out.println(InstCnt1.instNum); } }[결과값] 85