Nature of Security
- A
peopleproblem
- 우선적으로 보안과 보안 문제, 공격 등 보안 문제는 모두 사람과 관련이 있다. Attackers, victims, defenders, 그리고 investigators 등 많은 사람이 security 문제에 엮여 있다.
- 사람은 그리고, 때때로 weakest link 역할을 하기도 한다.
- An endless
process
- 보안은 끝이 없다. 세로운 기술과 공격 기법이 계속 등장하고 발전(emerging)하므로, 관련 조직과 시스템 등이 맞닥뜨린 risk를 완화하기(mitigate) 위해 끊임없이 조치를 취해야 한다.
- 그래서
No silver bullet, 즉 비장의 무기란 없다.
- A chain of
trust
- system, people, policy등의 신뢰 관계가 보안의 핵심이며, 실제로 certificates, signatures, infrastructures 등으로 구현된다. 따라서 방어자는 서로 신뢰할 수 있는지를 계속 검증하며 보안을 유지해야 하고, threat model은 이를 공격하기 위해 설계될 것이다.
Security Services
Confidentiality(기밀성)
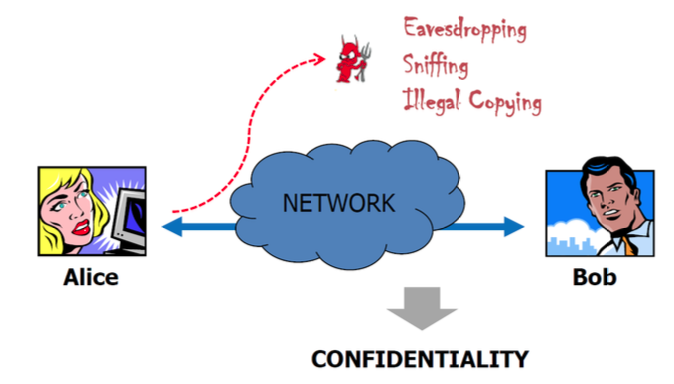
Protect data from unautorized disclosure.
다른 사람으로부터 내가 보낸, 받을 메시지나 데이터를 를 보호하는 것. Eavesdropping(도청), Sniffing, Illegal Copying 등을 방지하는 것에 해당한다.
Integrity(무결성)
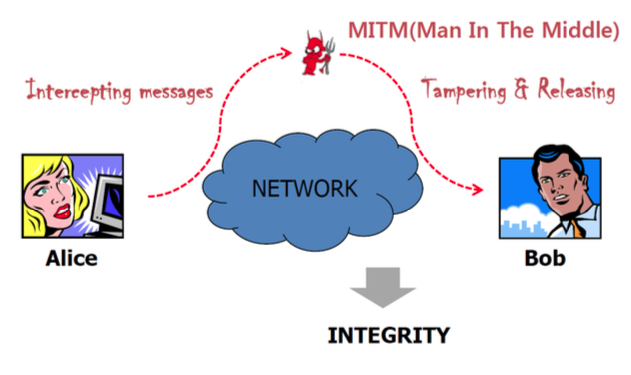
Preserving data from illegal modification.
내가 보낸, 받을 메시지나 데이터가 다른 사람으로 인해 변형되는 것을 막는 것.
Availability(가용성)
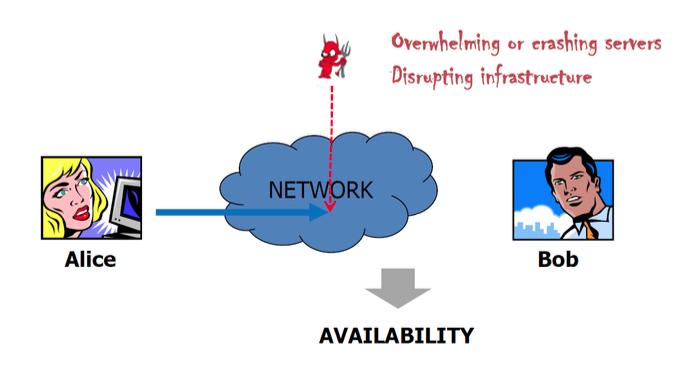
Maintaining a system by legitimate users.(e.g., Denial of Service)
그래서 내가 보낸 데이터가 정말 내가 보냈음을 증명할 수 있는 것.
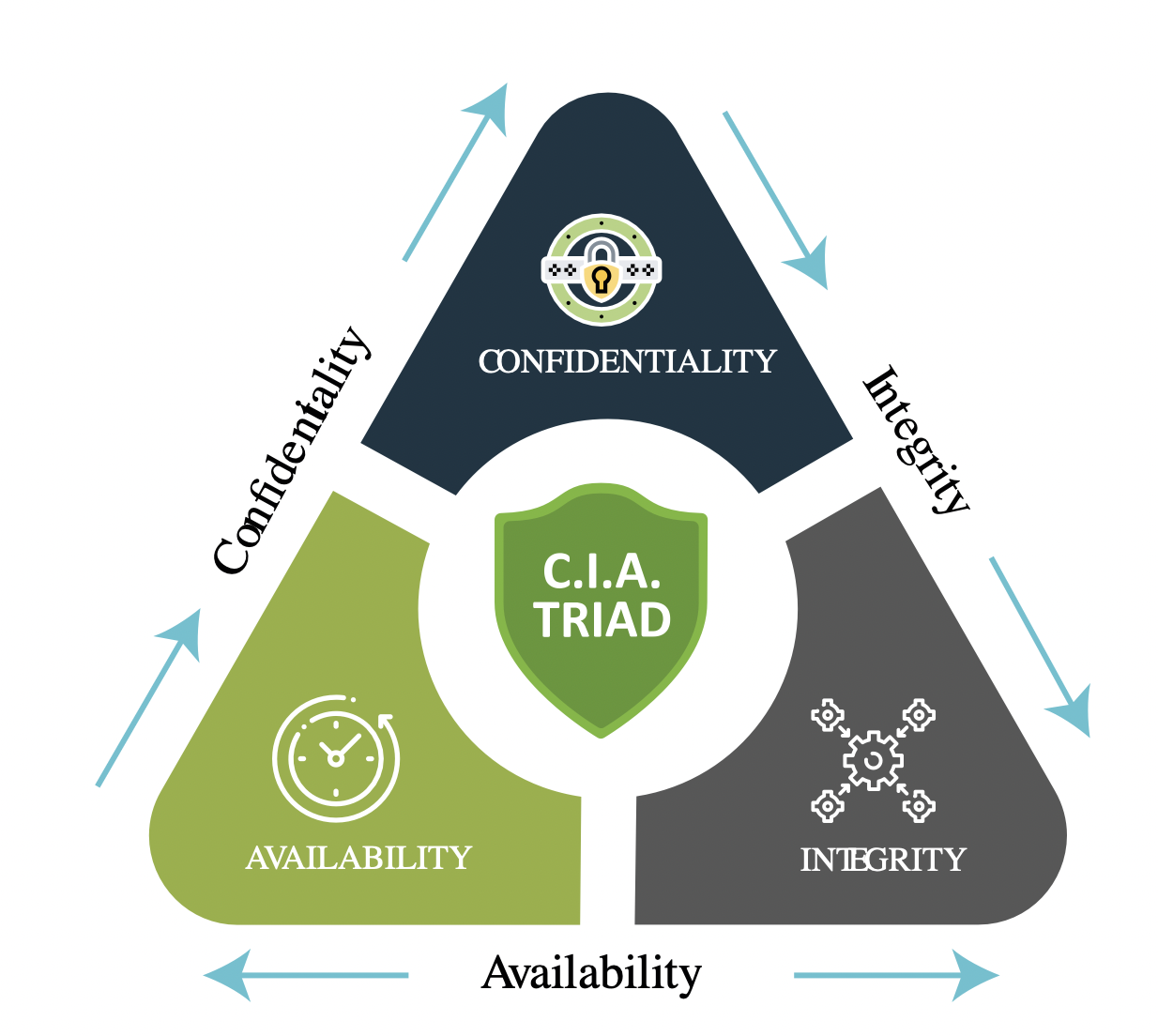
위 세 가지가 main security services가 되며, 이들을 CIA Triad라고 한다.
Authentication / Authorization(= Access Control)
Authentication(인증)은 사용자의 신원을 검증하는 행위다. 비밀번호나 생체 인식 등으로 현재 사용자가 누구인지 확인하는 것이 인증이다.
Three Schemes
- Knowledge-base 당신이 알고있는 것을 기반으로 인증하는 것
- passwords, security questions
- Downsides: Forgotten, Reusable, Guessed
- Possession-base: 당신이 가진 것으로 인증하는 것
- Phone, card, token, badge
- Downsides: Stolen, Lost, Duplicated(복제 가능)
- Biometrics-based: 당신이 누구인가(생체 인식)
- Fingerprint, Face, iris, voice
- Less acceptable, Costly, Somewhat spoof-able
Non-repudiation
Avoiding the dispute of an authorship or validation(non-deniability)
저작권 혹은 유효성에 대한 분쟁을 피하기 위해 작성자나 유효성을 부인할 수 없도록 하는 것. 예를 들어 내가 어제 분명 송금했는데 상대방이 받지 못했다고 부인할 수도 있다. 이러한 부분에 대한 Security.
Terms
- Threats: A potential cause of an incident that could harm an asset or service.
- Vulnerabilities: A weakness that makes a threat happening.
