
Section3. System Access and File Systme
Things to remember in Linux (39)
- root
- case-sensitive
- avoid spacing in files and directory (use hipens or dashes)
- Linux kernel Linux OS(operating system)
- Linux : mostly CLI(command line interface), not GUI(Graphical user interface)
- very flexible
Linux file system (40)
- File system Closet in your home
- commands = /usr/bin
- Attached Devices = /dev
- Applications = /etc or /var
- Linux filesystems store information in a hierachy of directories and files
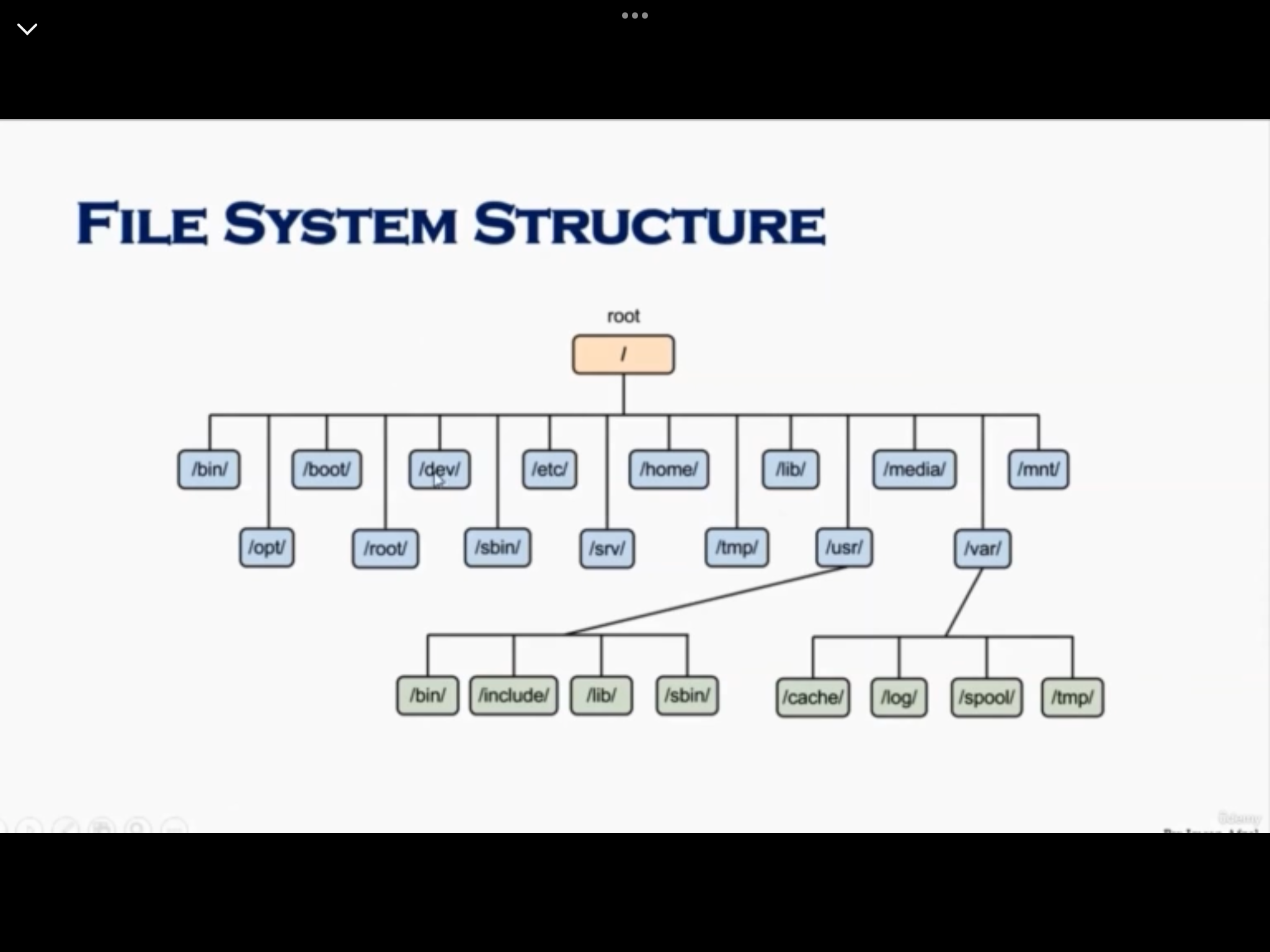
File system structure and its description (41)
File system navigation commands (42)
-
cd (change directory)
- .. : one step back (upper directory)
-
pwd (print working directory)
-
ls (list)
- -l : with all info
- -ltr : in modified time order
What is root? (43)
-
root account
-
root as / : the very first directory, refered as root directory
-
root home directory : /root
Absolute and Relative Paths (44)
- absolute path
- start with "/"
$ cd /var/log/samba- relative path
- not start with "/"
- relative to my current position
$ cd /var
$ cd log
$ cd sambaDirectory Listing Attributes (45)
- ls -a : gives all attributes!
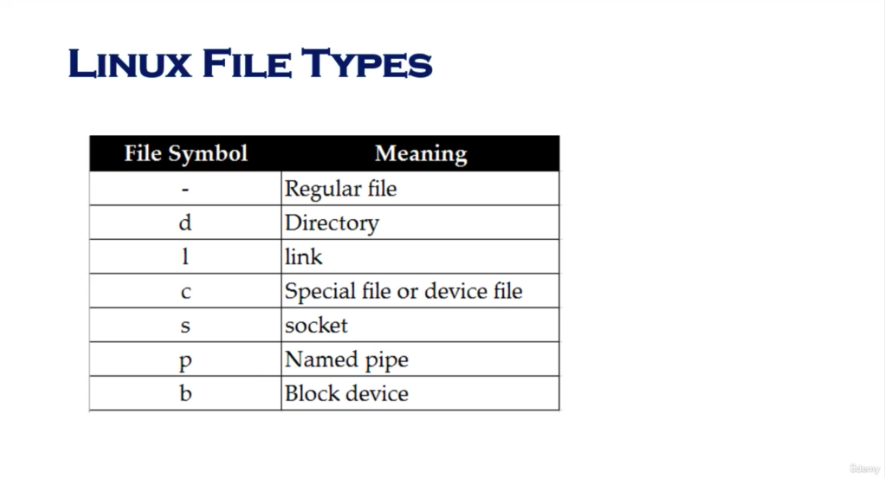
- Type : begins with
- d : directory
- l : link
- '-' : regular files
- Number of Links
- Owner
- Group
- Size
- Month
- Day
- Time
- Name
- Type : begins with
Creating Files and Directories (46)
- Creating files
- touch : create file (of course, empty file)
$ touch {name1} {name2} ...: create empty file name1, name2, ...
- cp : copying an existing file and creating a new file
$ cp {name1} {name2}: copy file {name1} as {name2}
- vi : an editor, explained later
$ vi {name}: bring you to file editor, shift + :wq! (write and quit)
- Creating directories
$ mkdir {name1} {name2}: make empty directory name1, name2,...
: cf. if you do not have permission, it can be denied
Copying Directories (47)
- Copying directories
- in Linux, cp with the "-R" option for recursive
$ cp -R {name1} {name2}: copy folder {name1} to {name2}
Linux file types (48)
Fining files and directories (49)
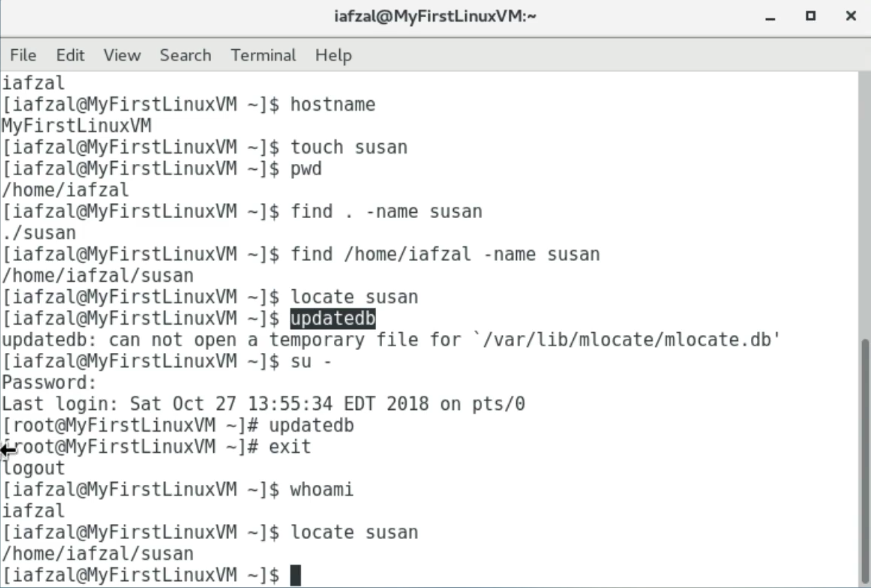
- Two main commands are used to find files/directories
- find
- locate
- find
- starting directory
- . : relative path, from current directory
- / : absolute path
- starting directory
$ find {starting directory} -name "{finding name}"- locate
$ locate {}
- What if "Permission denied"?
- get root 권한 by
su -
- get root 권한 by
Difference between find and locate (50)
locateuse a prebuilt database,- which should be regularly updated
finditerates over a filesystem to locate fileslocateis much faster thanfind, but can be inaccurate if the database is not updated- To update locate database, run
updatedb
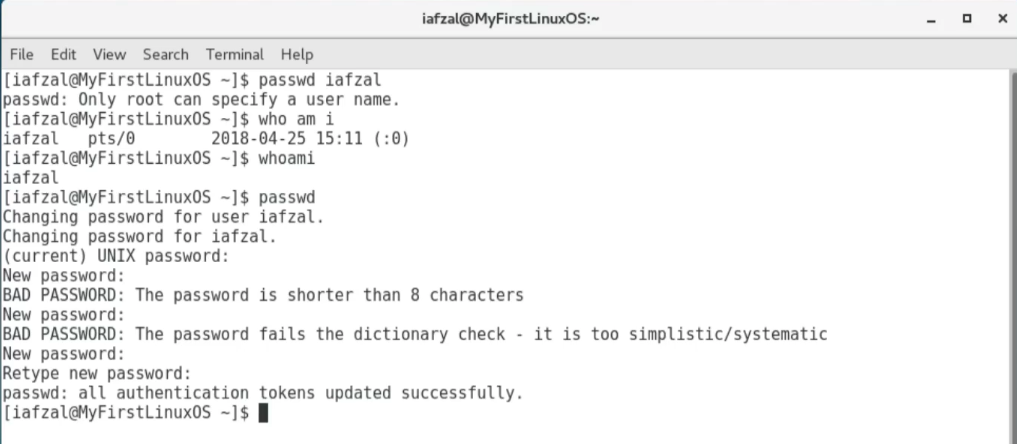
Changing password (51)
- should change my initial password as soon as I login
$ passwd {userid}

Wildcards(*,?,^[]) (52)

- Examples
$ touch abcd{1..9}-xyz: create 9 files!$ rm a*: remove all the files starting with "a"$ rm *xyz: remove all the files ending with "xyz"$ ls -l ?bcd*$ ls -l *[cd]*

Soft and hard links (53)
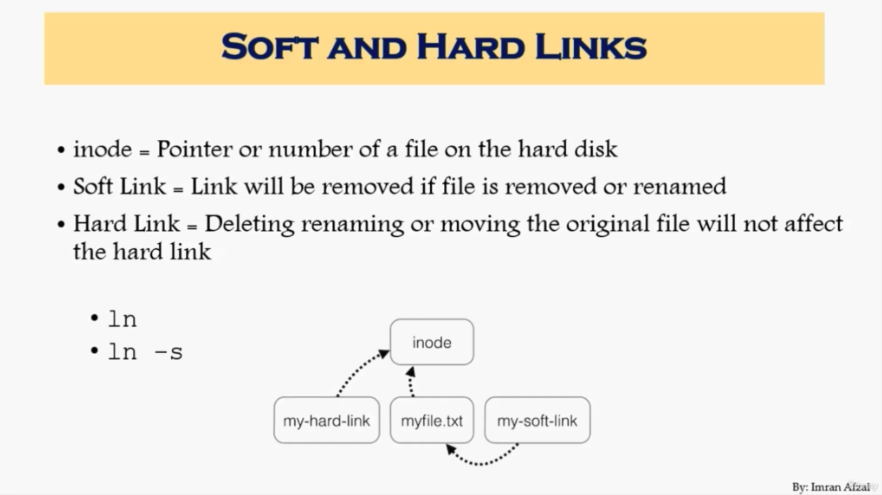
- inode
- Soft Link :
$ ln -s - Hard Link :
$ ln - Link Shortcut
- How softlink works?
$ touch hulk
$ cd /tmp
$ ls -s /home/iafzal/hulk

- How hardlink works?
$ touch hulk
$ echo "hulk is superhero" > hulk
$ cat hulk
$ cd /tmp
$ ln /home/iafzal/hulk
: there is no pointing in hardlink!

| hard link | soft link |
|---|---|
| 한 파일의 복사본을 만드는 것 cf. cp랑은 다른 개념! -cp는 원본과 복사본 파일의 inode가 다르다 -따라서, 복사본/원본의 수정여부가 서로에게 영향을 미치지 않음 | 바로가기 아이콘을 만드는 것 |
| 원본-하드링크 파일은 같은 inode를 가짐 | 원본-소프트링크 파일은 다른 inode를 가짐 |
| 어디에서 수정을 하던지, 함께 수정이 이루어짐 | 어디에서 수정을 하던지, 함께 수정이 이루어짐 |
| 원본을 지워도 하드링크 파일을 실행가능/내용보존 | 원본을 지우면 연결이 끊겨, 링크 파일 실행 불가능 |
| Type : "-" | Type : "l" |
출처 : 파일 링크 : ln - 하드 링크(Hard Link), 소프트 링크(Soft Link)
Section4. Linux Fundamentals
Linux Command Syntax (57)
- command have options and arguments
$ command option(s) argumnet(s)- options
- modify the way that a command works
- usually consist of hypen or dash followed by a single letter
- some commands accept multiple options which can be grouped together after a single hypen
- arguments
- most commands are used together with (one or more) argumnets
- some commands have default option (if none is supplied)
- argmuments may be required/optional
ls: list files and directorys-l: list-t: order by time-r: reverse orderls -l {file or directory name}: list only the argument
rm: remove-f: forcefully-r: recursivelyrm -rf {file or directory name}
mkdir: make directorymkdir {file or directory name}
man {command}: manual for command- to go to bottom, keep padding Space key
- to kill, press Esc + q
Files and Directory Permissions (chmod) (58)

chmod: change modechmod g-w {file name}: remove write permissions from group in {file name}chmod a-r {file name}: remove read permissions from all in {file name}chmod u-w {file name}: remove write permissions from user in {file name}
rm {file name}:cat {file name}: read filechmod u+rw {file name}chmod a-x {folder name}/
File Permissions Using Numeric Mode (59)
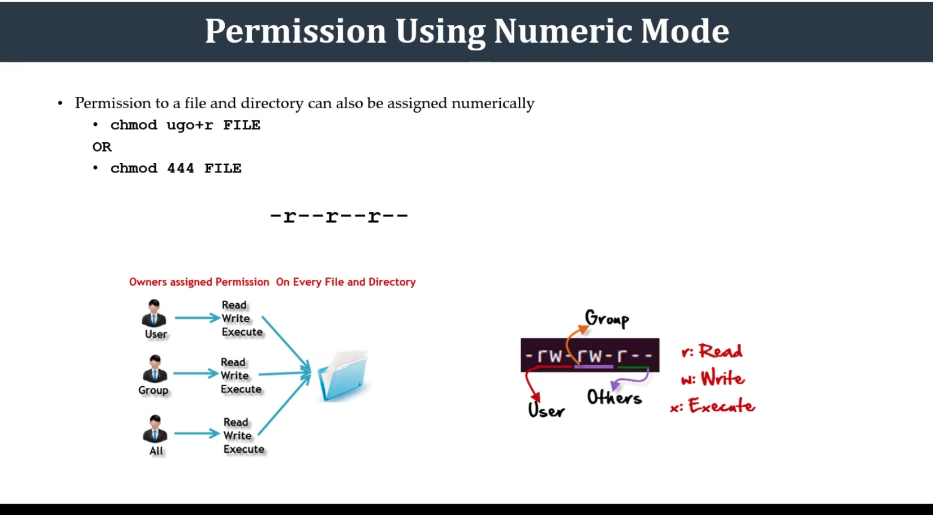
- Numbers assigned to permissions types

- User types : User, Group, Others
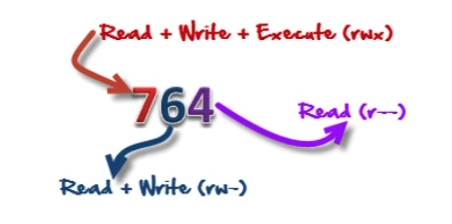
chmodchmod 777 {file name}
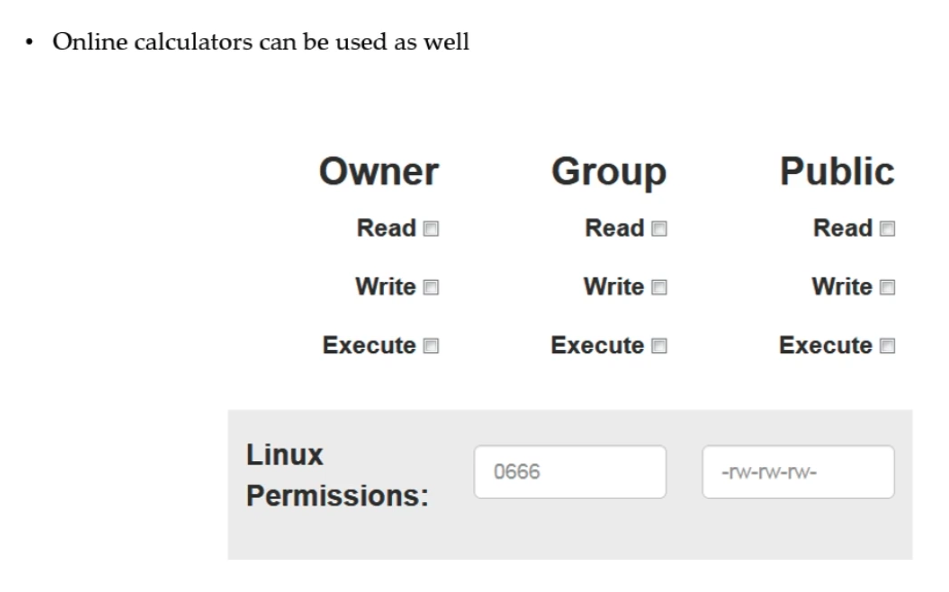
- Online calculator
File ownership (60)
- 2 types of owner
- user : who create the file/directory
- group : group which the user belongs to
- Command to change file ownership
chown: changes the ownership of a filechgrp: changes the group ownership of a file- option
-R: recursive option
- cf. login as root
su -: log in as rootexit: exit root
Access Control list (61)
- What is ACL?
- an additional & more flexible permission mechanism for file systems
- to assist with UNIX file permissions
- allow you to give permissions for any user or group to any disc resource
- Use of ACL

- Commands for ACL
setfacl: set file ACLsetfacl -m u:{user name}:rwx /path/to/file: change user's permissionssetfacl -m g:{group name}:rwx /path/to/file: change group's permissionssetfacl -Rm "entry" /path/to/dir: to allow all files or directories to ingerit ACL entries from the directory it is withinsetfacl -x u:{user name} /path/to/file: to remove a specific entry (for a specific user)setfacl -b /path/to/file: to remove a specific entry (for all users)- note

getfacl: get (current) file ACL
Help commands (62)
- There are 3 types of help commands
$ whatis {command}$ {command} --help$ man {command}
cf. MAC deos not support $ {command} --help any more!

TAB Completion and Up Arrow (63)

Adding text to files(Redirects) (64)

- 3 ways
$ echo "{text}" > {fileName}: override text!$ echo "{text}" >> {fileName}: keep lines and add line
- read files
$ cat {fileName}
Input and Output Redirects (65)
-
3 redirects in Linux

-
Output

-
Input

-
Error

Standard Output to a File (tee) (66)
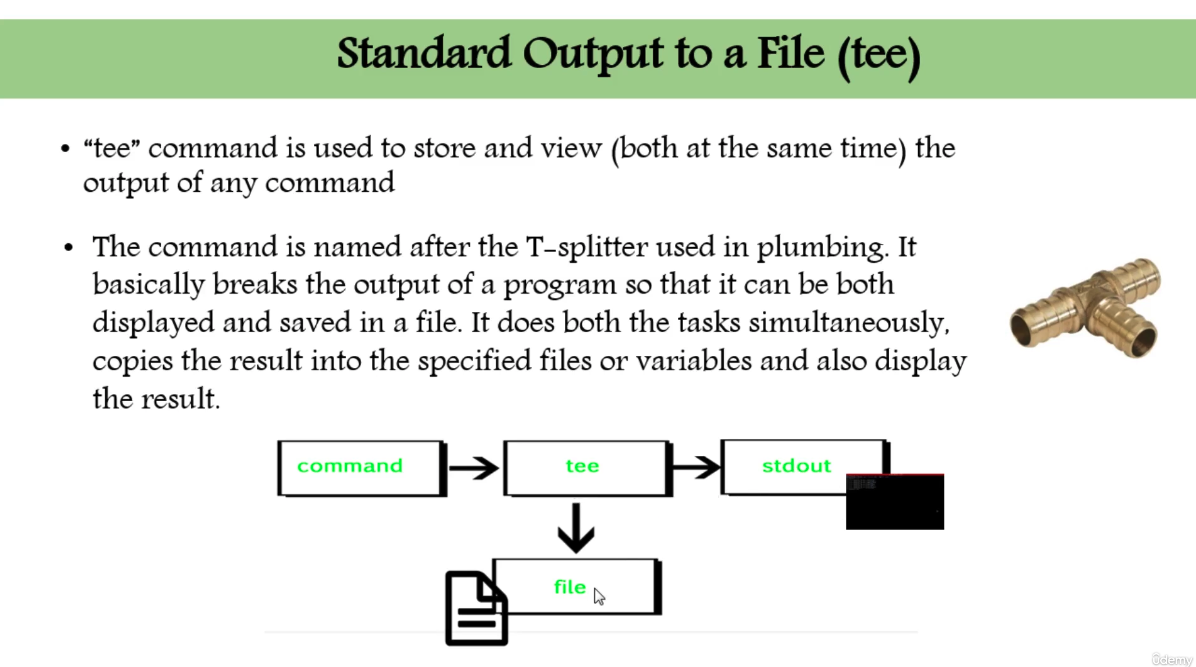
- command
tee$ echo "{your text}" | tee {filename}- This overrides the extisting text!
- How to add/append text to a file?
$ echo "{your text}" | tee -a {filename}
- How to count # of words in a file?
$ wc -c {filename}
Pipes (|) (67)
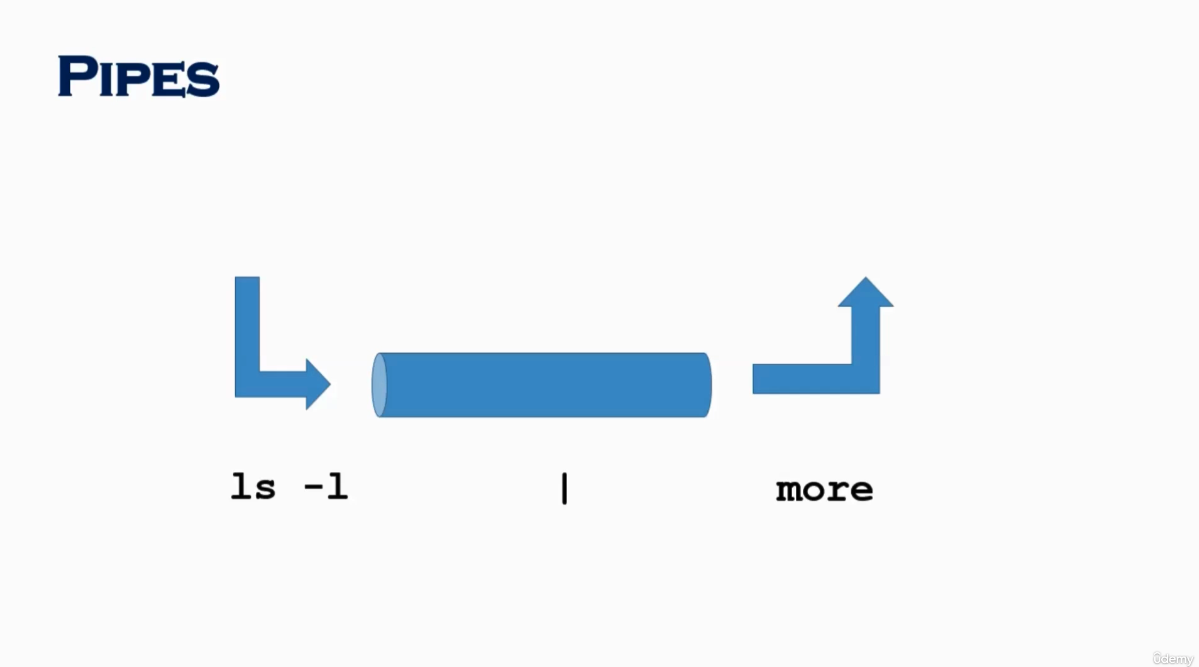
- e.g.
$ ls -ltr | more$ ls -l |
File Maintenance Commands (68)
-
$ cp: copy -
$ rm: remove -
$ mv: move or rename -
$ mkdir: make directory -
$ rmdiror$ rm -r: remove directory -
$ chgrp: change group -
$ chown: chagne ownership (at the user level) -
How to use?
$ cp {file1} {file2}: copy file1 to file2$ cp {file1} {directory}: copy file1 in directory (with the same file name)$ mv {file1} {file2}: change file name from file1 to file2$ mv {file1} {directory}: change location of file$ rm {filename}: remove file$ rm -Rf: forcefully remove the sub-directories and its contents as well$ chown {ownership} {file1}: change ownership of file1 to ownership (ownership - user, root)
File Display Commands (69)
- How can you view INSIDE of a file?
$ cat: views the entire content (regardless of 1 page, 2 page, ...)$ more: go over 1 page at a time$ less: go over 1 line at a time, in the reverse order- press
j: 1 line below - press
k: 1 line above (go back up)
- press
$ head: views top of the file$ head -{#lines} {filename}
$ tail: views bottom of the file$ tail -{#lines} {filename}
Filters - Text Processing Commands (70)
cutawkgrepandegrepsortuniq: uniquewc: word counts
cut - Text Processors Commands (71)

awk - Text Processors Commands (72)

grep/egrep - Text Processors Commands (73)

sort/uniq - Text Processors Commands (74)

wc - Text Processors Commands (75)

Compare files (diff and cmp) (76)

- diff :
$ diff {file1} {file2} - cmp :
$ diff {file1} {file2}
Compress and uncompress (tar, gzip, gunzip) (77)
tar: actually do not compress (nearly)tar cvf {file_name}.tar {directory}: taring files in {directory} to {file_name}.tar filetar xvf {file_name}.tar: untaring file {file_name}.tar
gzip: compress filesgzip {file_name}: compress {file_name}
gzip -dORgunzip: compress / uncompress filesgzip -d {file_name}: uncompress {file_name}
Truncate file size (truncate) (78)

truncate -s {size} {filen_name}
Combining and splitting files (79)

split -l {# of lines} {file_name} {splitted_file_name}
Section5. System Administration
"sed" Command (86)

[Replace strings]
$ sed 's/{from_word}/{to_word}/g' {file_name}s: subtituteg: globally (multiple cases, at the same time)- only print changed in terminal, not actually change the file!
$ sed -i 's/{from_word}/{to_word}/g' {file_name}
- add option
-i: insert
[Remove strings]
$ sed 's/{from_word}//g' {file_name}$ sed -i 's/{from_word}//g' {file_name}
[Remove all the lines containing strings]
$ sed '/{word}/d' {file_name}$ sed -i '/{word}/d' {file_name}
[Remove empty lines]
$ sed '/^$/d' {file_name}^: starts with$: ends with
[Remove 1st lines]
$ sed '1d' {file_name}
[Replace tab to space]
$ sed 's/\t/ /g' {file_name}$ sed -i 's/\t/ /g' {file_name}
[Print some lines only]
$ sed -n {starting_num},{ending_num}p {file_name}
[Print file except some lines]
$ sed {starting_num},{ending_num}d {file_name}
[Add empty line between lines]
$ sed G {file_name}
[Replace strings except 8th lines]
$ sed '8!s/{from_word}/{to_word}/g' {file_name}
User Account Management (87)
- First, become root! :
$ su -- What if it does not work?
$ sudo -s: login sudo$ passwd root: change password for root
- 그래도 안되네...
- What if it does not work?
[Add user]
$ useradd {user_name}$ id {user_name}$ cd /homeand$ ls -ltr
[Add groups]
$ groupadd {group_name}
[Change group of user]
-
$ usermod -G {group_name} {user_name} -
$ chgrp -R {group_name} {user_name} -
$ cat /etc/passwd -
$ cat /etc/group -
$ cat /etc/shadow

[Add user with all options]
$ useradd -g {group_name} -s {shell_path} -c "{Description}" -m -d {home_directory} {user_name}
Enable Password Aging (88)
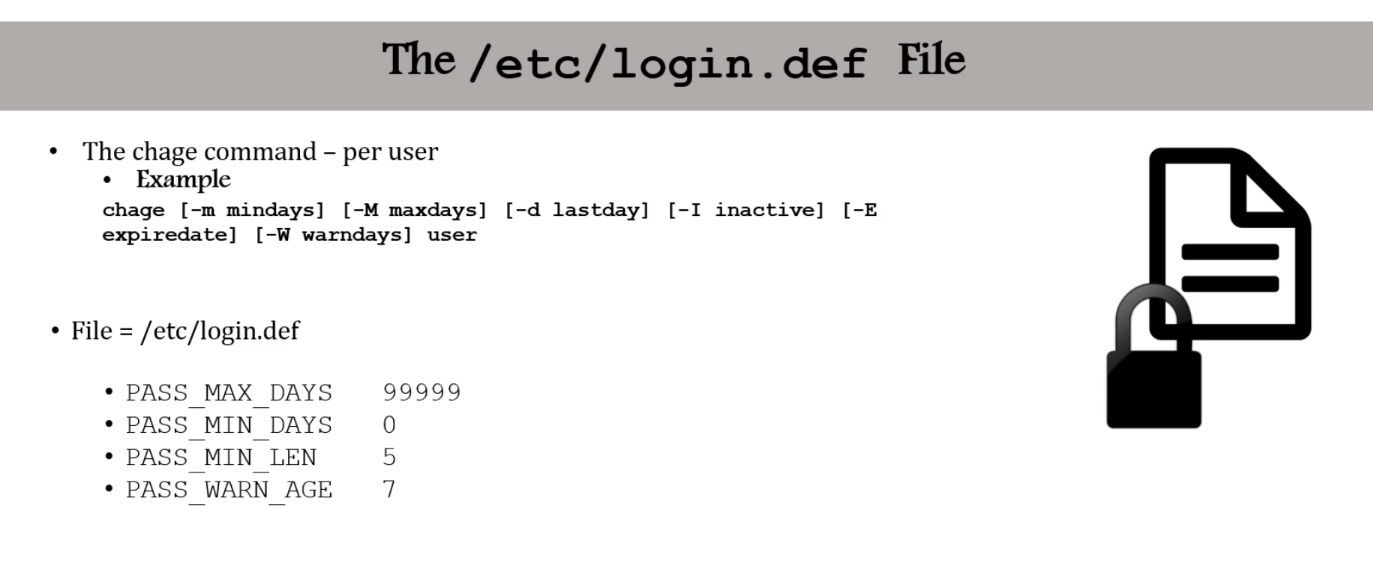
$ chage: change age, used to set parameters around password (cf.usermod)

Switch Users and Sudo Access (89)

$ whoami$ su - {user_name}$ exit$ su -: change user to root
[sudo commands]
$ dmidecode$ fdisk -l$ usermod -aG wheel {user_name}
Linux directory service - Account Authentification (92)
- What if you have to create a user account of 10000 different servers?
- Then, you have to have a domain or a directory account on a server
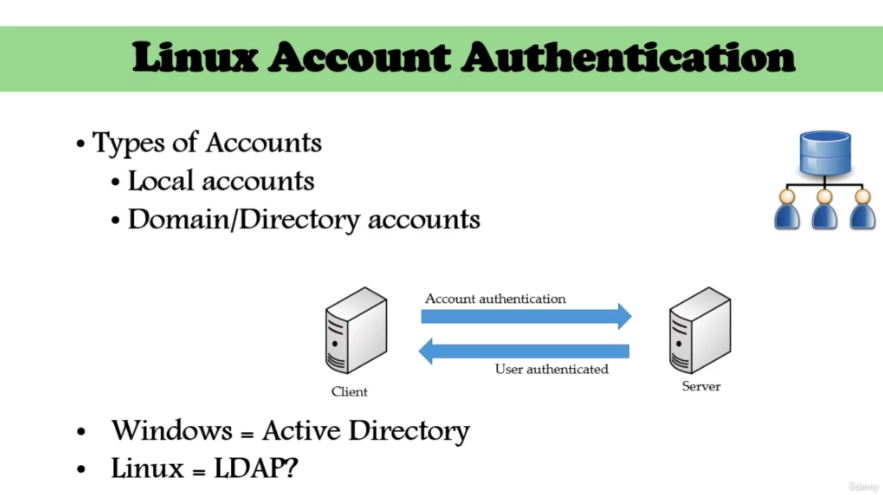
- Then, you have to have a domain or a directory account on a server
- LDAP
- Not only for Linux! (Window, Mac, ...)
- a protocol used for authentification against directory
Processes, Jobs and Scheduling (95)






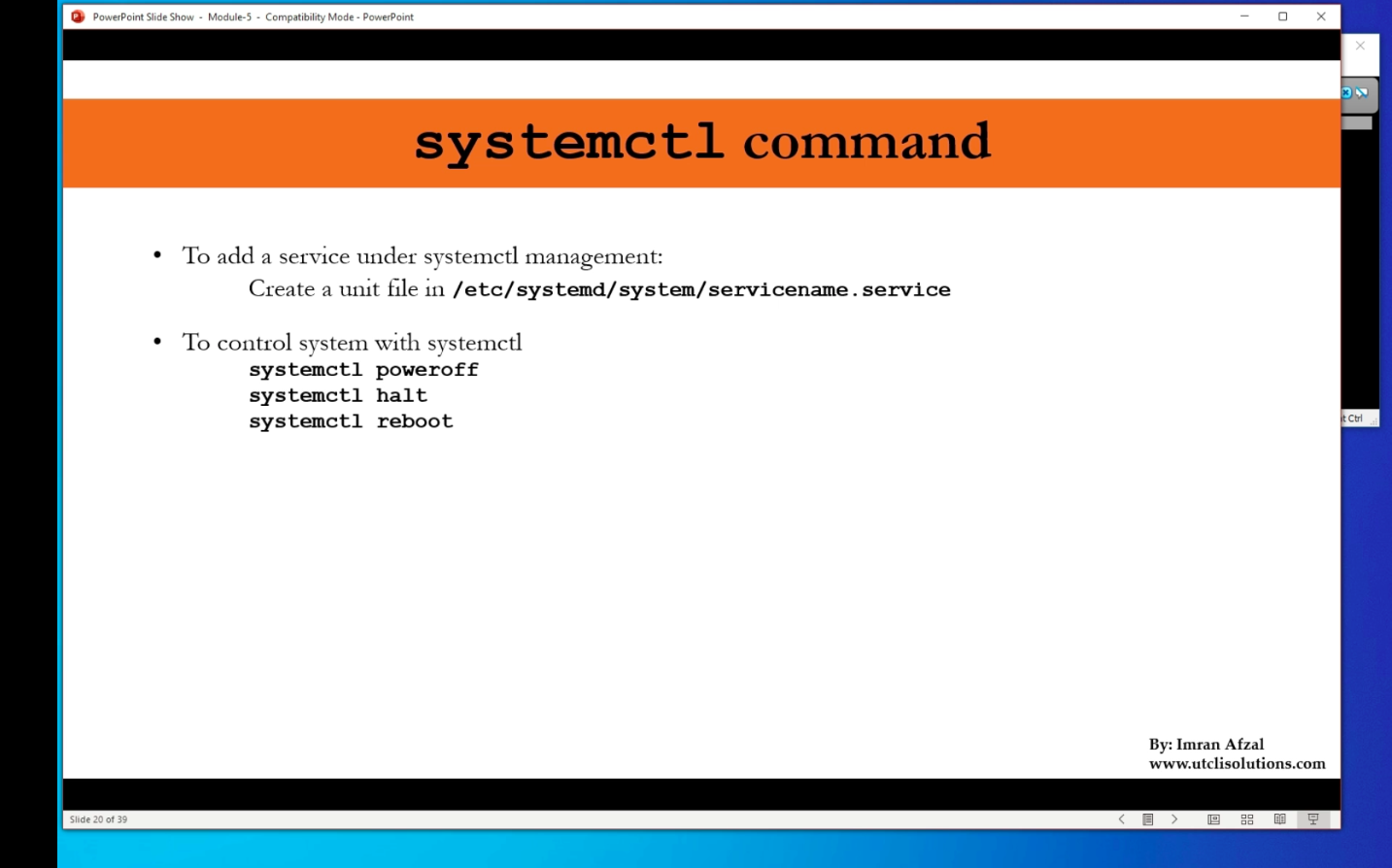
systemctl command (96)
- How to start an application in Linux?
- There is no GUI!
systemctl: system control
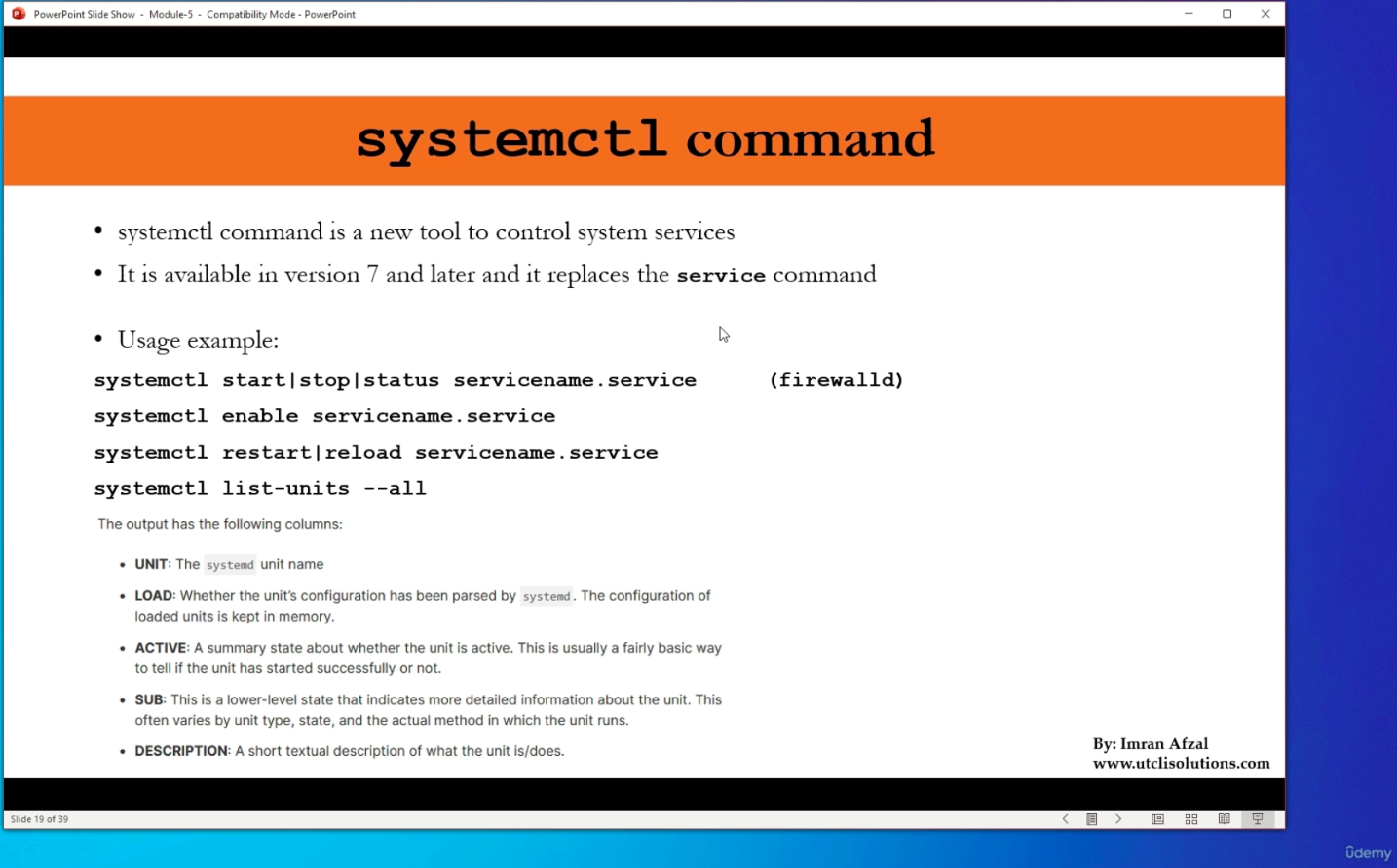
$ systemctl status firewalld.service$ systemctl stop firewalld.service$ systemctl status firewalld.service$ systemctl disable firewalld.service$ systemctl list-units- only active units
$ systemctl list-units -all
ps command (97)
ps: process status

top command (98)
top: show a real-time view of the running system- You don't need to be root user, to use
topcommand- But if you want to be kill a prcoess, you have to be root!

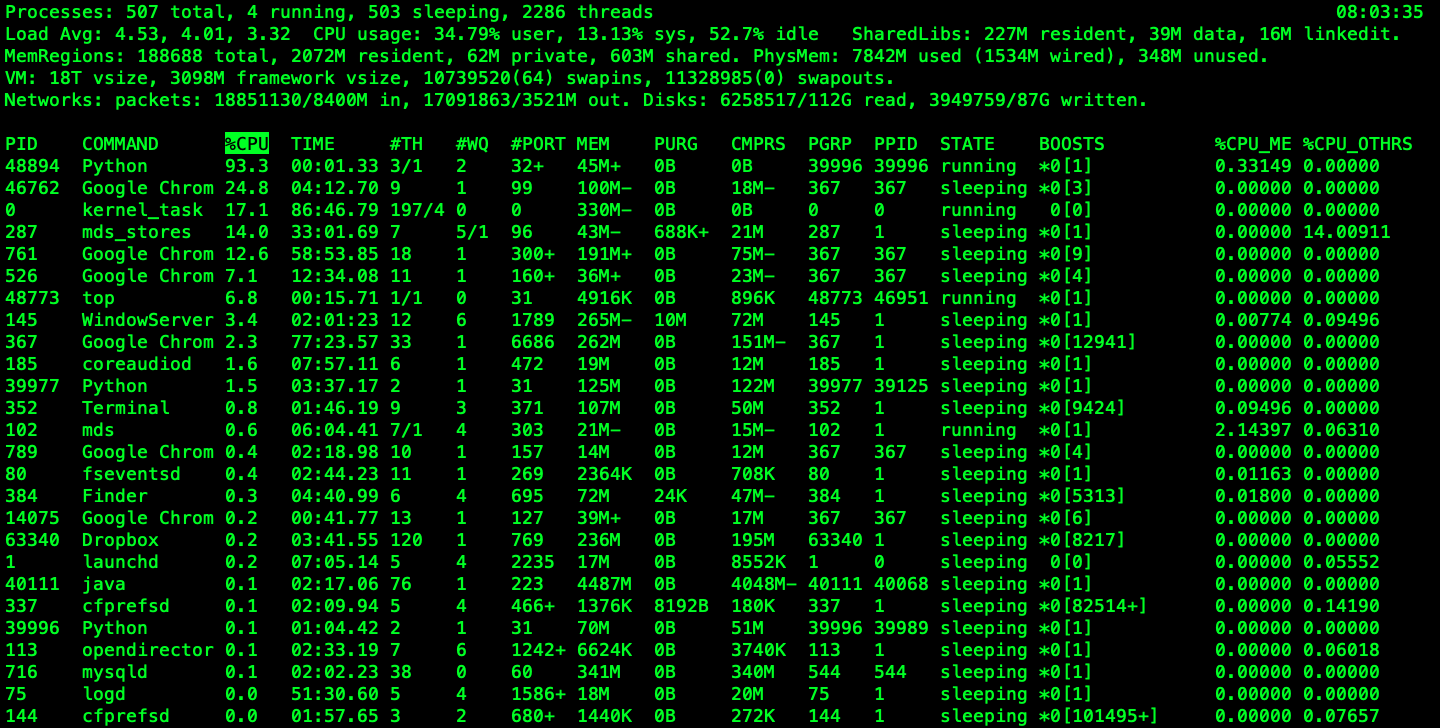
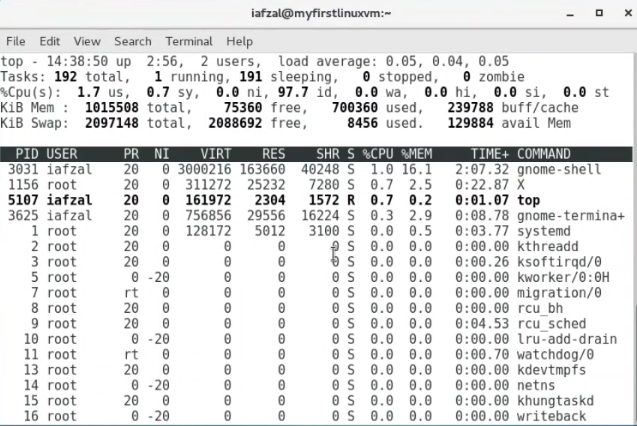
$ top -U {user name}$ sudo toppress shift + s writekillas a signal write the PID that you want to kill

kill command (99)

$ killall$ pkill

crontab command (100)

- cf.
crontabgives vi editing mode! crontab - e: edit crontabcrontab -l: list crontabcrontab -r: remove crontab
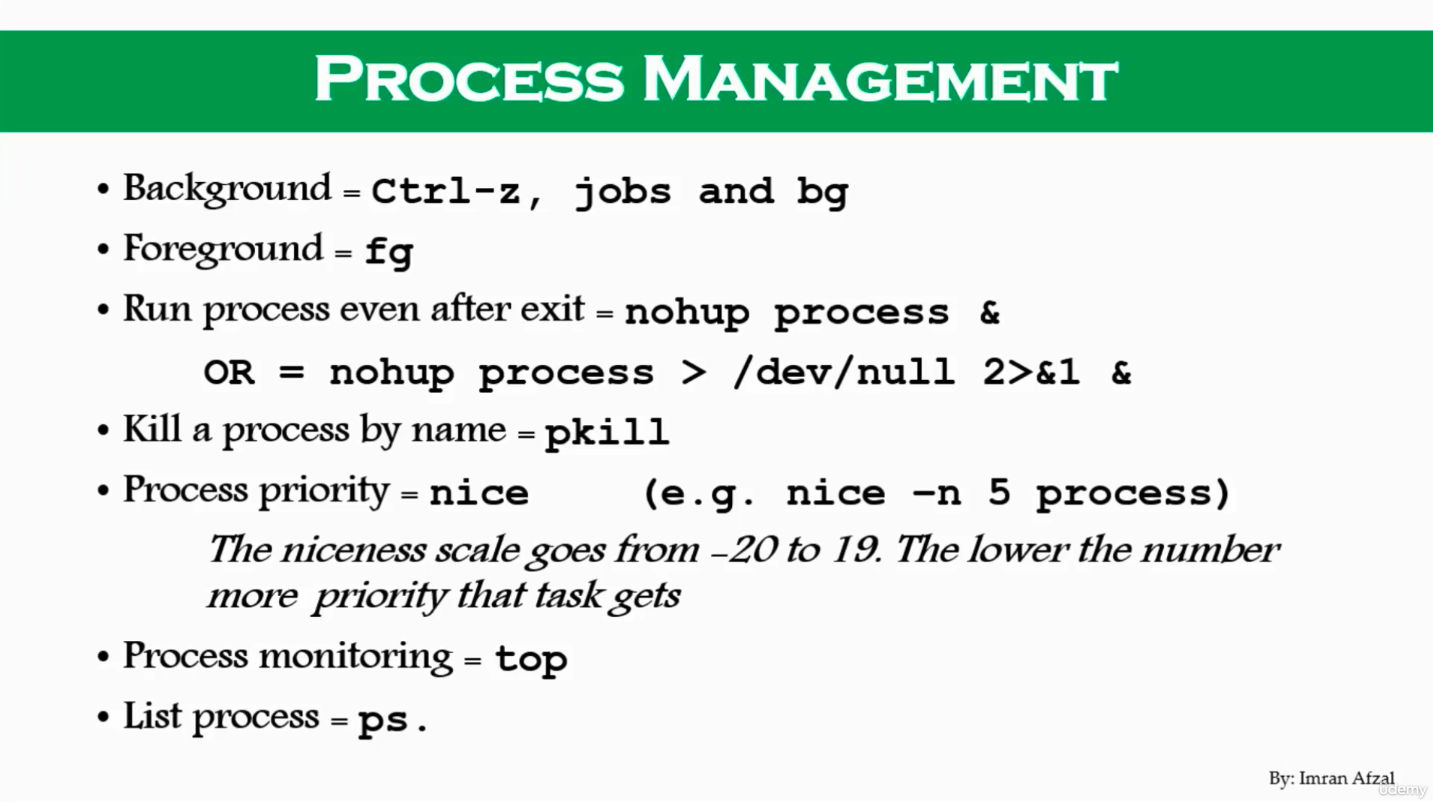
Process management (bg, fg, nice) (103)
- Check my IP address
$ ipconfig getifaddr en0: local IP$ curl ifconfig.me: public IP
- Put in background
- ctrl + z
$ bg
- Put in foreground
$ fg
- Run process even after eixt terminal
$ nohup {process command}$ nohup {process command} > /dev/null 2>&1 &
- Process priority
$ nice: e.g.$ nice -n 5 {process command}
System monitoring commands (df, dmesg, iostat, netstat, free, top) (104)

- All these commands will list all the system resources. These will tell you
- How the system is doing
- Hou is it behaving
- Whether it's running high or low
- These are system monitoring commands!
$ top- CPU, memory, which process is on, which user is running
- To quit, press q
$ df: disk partition information$ df -h: more human readable
$ sudo dmesg$ iostat: input output statistics$ iostat 1: iostat with refreshing every 1 second- To quit, press ctrl + c
$ netstat$ netstat -rnv$ netstat | more
$ top -l 1 -s 0 | grep PhysMem | sed 's/, /\n /g'- There is no
freecommand in Mac!
- There is no
$ sysctl -n machdep.cpu.brand_string- There is no result from
$ cat /proc/cpuinfoin Mac! - cf.
$ sysctl hw.ncpu: the number of CPUs
- There is no result from
$ sysctl hw.memsize
System log monitor (/var/log) (105)
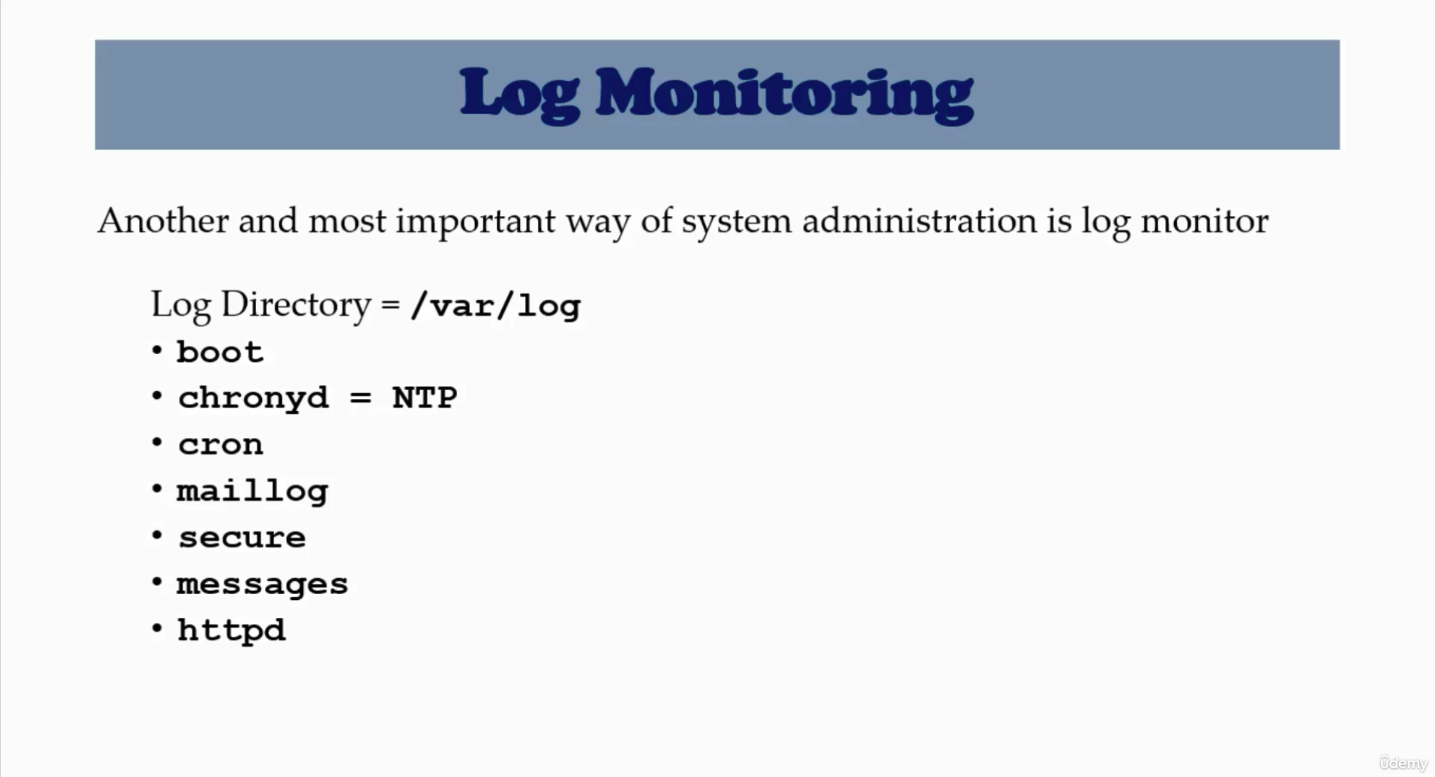
- Linux Mac in Log system ㅠ
boot- There is no
boot.login/var/log $ log show --predicate "processID == 0" --debug
- There is no
cron- There is no
crondirectory in/var/log $ whereis sysloggives/usr/bin/syslog$ whereis crongives/usr/sbin/cron
- There is no
secure
Terminal control keys (110)

Terminal commands (clear, exit, script) (111)

Environment variables (114)
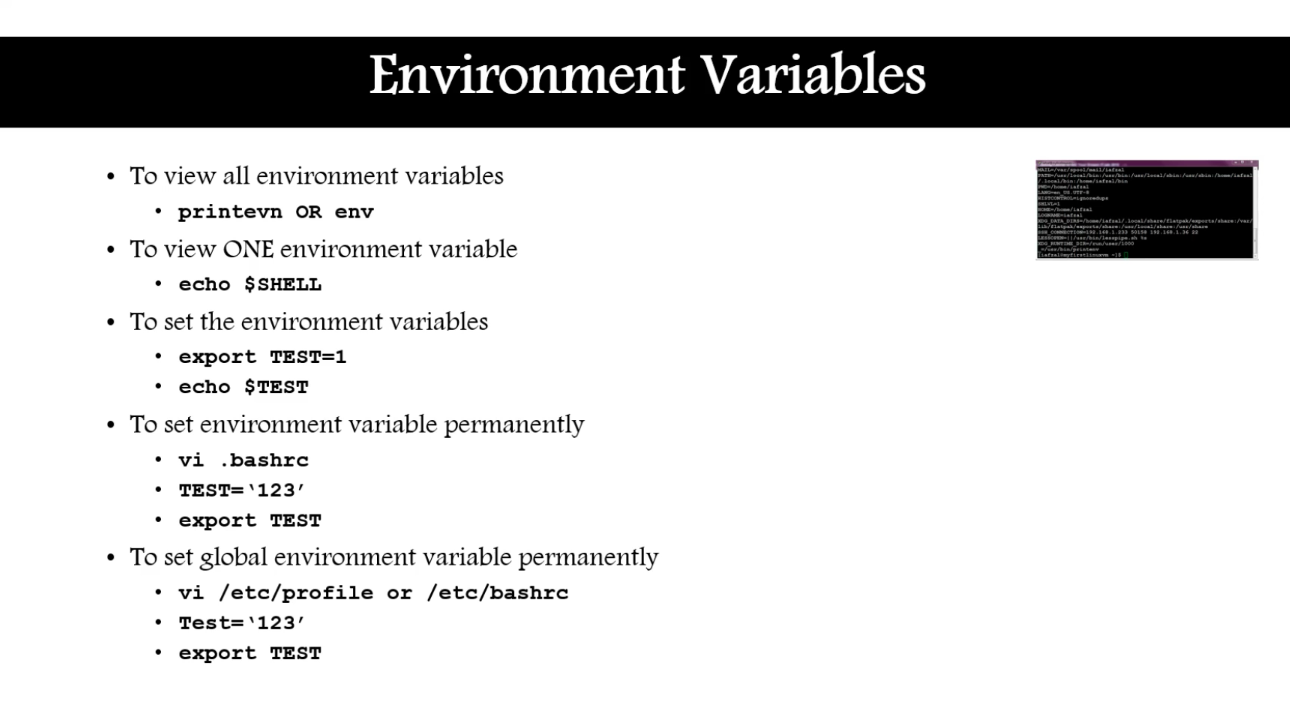
- 순서가
- 없는
- 목록
- 순서가
- 없는
- 없어용
