
220504
JavaScript 배열
indexOf();
요소의 인덱스를 찾고 싶을때const cafe = ['coffee', 'cake', 'tea', 'cookie']
cafe.indexOf('tea')
//expected output: 2
cafe.indexOf('coffe', 1)
//expected output: -1
cafe.indexOf('bread')
//expected output: -1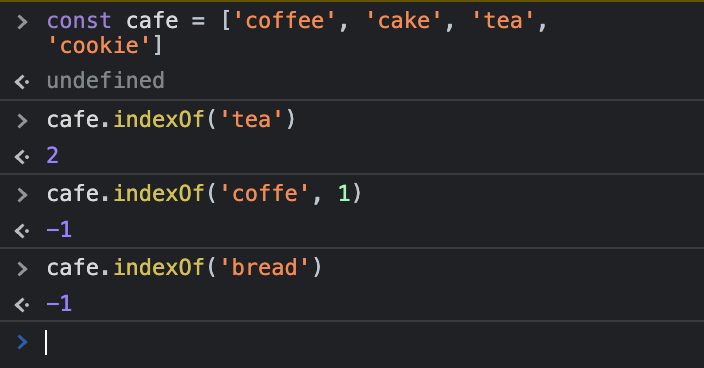
- 배열에 존재하지 않는 요소를 찾거나 해당 인덱스에서 지정된 요소가 탐색되지 않을 시 -1을 출력한다.
isArray();
인자가 배열인지 확인하고 싶을 때Array.isArray('coffee');
//expected output: false
Array.isArray(false);
//expected output: false
Array.isArray([1]);
//expected output: true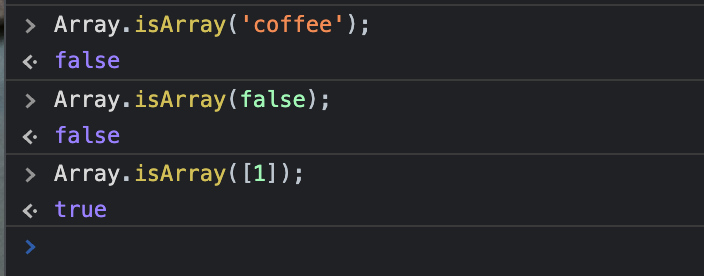
join();
요소들을 연결해 하나의 값으로 만들 때
join은 숫자만 입력하는 것이 좋다const cafe = ['coffee', 'cake', 'tea', 'cookie']
cafe.join('/')
//expected output: 'coffee/cake/tea/cookie'
cafe.join('')
//expected output: 'coffeecaketeacookie'
const example = ['coffee', null, undefined, 'cake']
example.join('')
//expected output: 'coffeecake'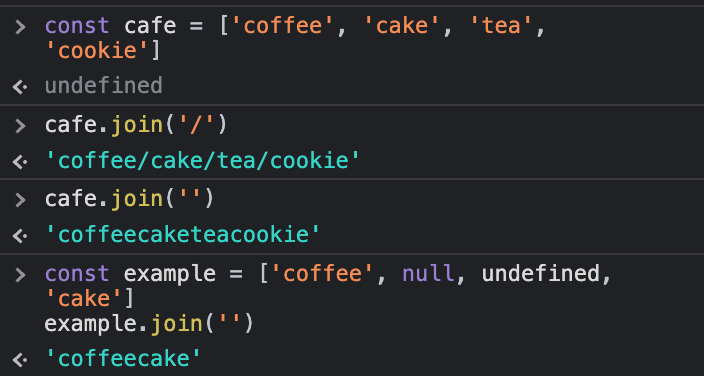
- 매개변수를 생략하면 쉼표로 구분되며, 빈 문자열을 넣을 시 띄어쓰기 없이 연결된다. 요소가
null또는undefined일 경우 빈 문자열로 반환된다.
fill();
모두 똑같은 요소로 채우고 싶을때
해당 메소드는 원본을 변경하는 메소드로, 복사본이 아닌 this 객체로 변경해 반환한다는 특징이 있다.const cafe = ['coffee', 'cake', 'tea', 'cookie']
cafe.fill('bread')
//expected output: ['bread', 'bread', 'bread', 'bread']
- 첫 번째 매개변수만 입력할 경우, 배열 내 모든 요소가 해당 매개변수의 값으로 변경된다.
- 두 번째 매개변수에는 배열 내에 첫 번째 매개변수에 입력한 값을 채우기 시작할 지점의 인덱스를 입력한다. 생략이 가능하며 입력하지 않을 시 기본값은
0이다.
const cafe = ['coffee', 'cake', 'tea', 'cookie']
//expected output: ['coffee', 'cake', 'tea', 'bread']
- 음수를 입력할 경우, 배열 내 마지막 원소의 인덱스가 -1이 되며 마지막부터 세기 시작한다.
위의 const cafe 예시에서 cafe.fill('bread', -1)을 입력할 경우, 맨 뒤에서 마지막 한 개의 요소만 변경하기 때문에['coffee', 'cake', 'tea', 'bread']가 출력되며 맨 마지막 요소만 'bread' 로 변경된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
flat();
배열을 원하는 깊이로 평탄화하고 싶을때let arr = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, [9, [10, 11]]]]
arr.flat();
//expected output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, [9, [10, 11]]]
arr.flat(1);
//expected output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, [9, [10, 11]]]
arr.flat(2);
//expected output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, [10, 11]]
arr.flat(3);
//expected output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
arr.flat(Infinity);
//expected output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
includes();
특정 요소가 포함되었는지 확인할 때const cafe = ['coffee', 'cake', 'tea', 'cookie']
cafe.includes('bread');
//expected output: false
cafe.includes('cake');
//expected output: true
cafe.includes('cake', -3);
//expected output: true
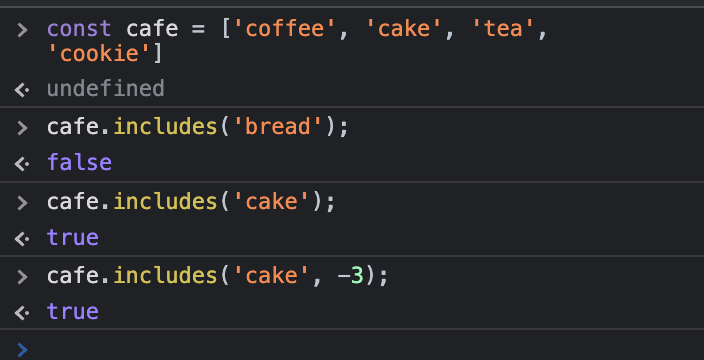
- 탐색하려는 요소가 문자열일 경우에는 대소문자를 구분한다.
find();
하나의 요소라도 조건을 만족하는지 확인할 때
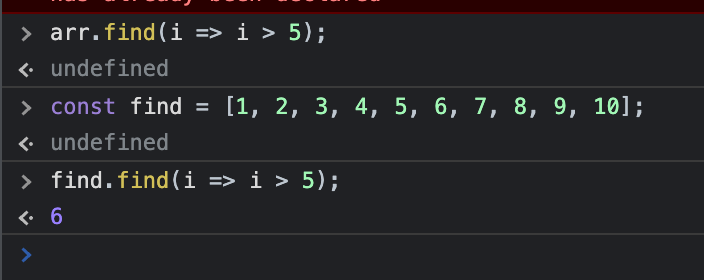
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10];
arr.find(i => i > 5);
//expected output: 6
-
filter();와 다른점은 단 하나의 요소만을 찾는다는 점이 다르다.
-
find() 메서드는 주어진 판별 함수를 만족하는 첫 번째 요소의 값을 반환한다.
filter();
모든 요소가 조건을 만족하는지 확인할 때const arr = [{
'name' : 'title1',
'contents' : 'contents1',
'dataNum' : 1
}, {
'name' : 'title2',
'contents' : 'contents2',
'dataNum' : 2
}, {
'name' : 'title3',
'contents' : 'contents3',
'dataNum' : 3
}, {
'name' : 'title4',
'contents' : 'contents4',
'dataNum' : 4
}, {
'name' : 'title5',
'contents' : 'contents5',
'dataNum' : 5
}];
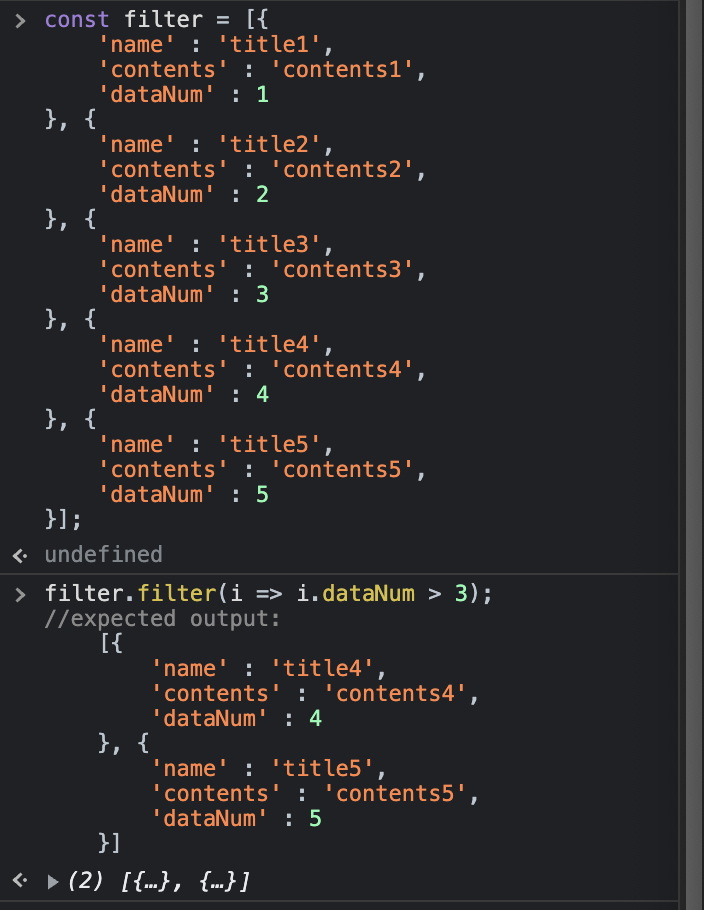
arr.filter(i => i.dataNum > 3);
//expected output:
[{
'name' : 'title4',
'contents' : 'contents4',
'dataNum' : 4
}, {
'name' : 'title5',
'contents' : 'contents5',
'dataNum' : 5
}]
- 배열에서 특정 조건에 부합하는 값을 찾고 그 값들로 이루어진 새로운 배열을 만들어 출력한다.
findIndex();
조건을 만족하는 첫 번째 인덱스를 찾을 때const cafe = [{
'item' : 'coffee',
'amount' : 5
},{
'item' : 'cake',
'amount' : 4
},{
'item' : 'tea',
'amount' : 7
},{
'item' : 'cookie',
'amount' : 3
}];
const index = cafe.findIndex(obj => obj.item.length <= 3)
index
//expected output: 2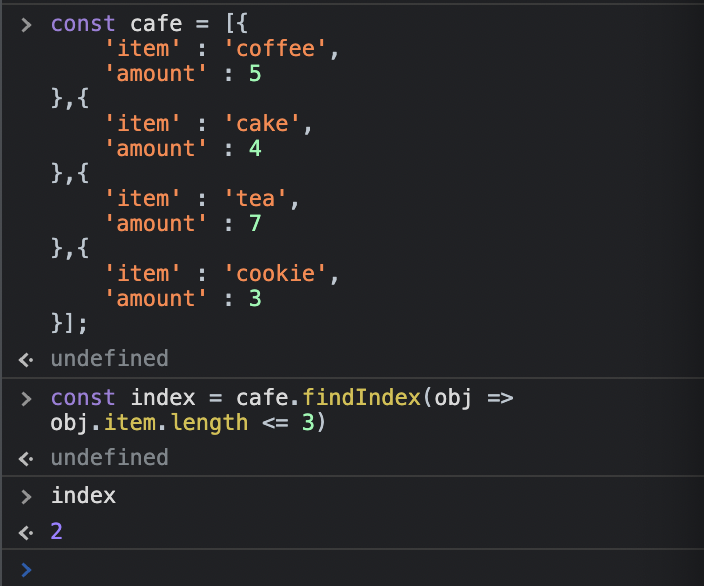
-
주어진 조건에 부합하는 배열의 맨 첫 번째 요소의 인덱스를 반환한다.
-
배열 내에서 조건에 부합하는 요소가 존재하지 않으면 -1을 반환한다.
-
findIndex() 메서드는 주어진 판별 함수를 만족하는 배열의 첫 번째 요소에 대한 인덱스를 반환
map();
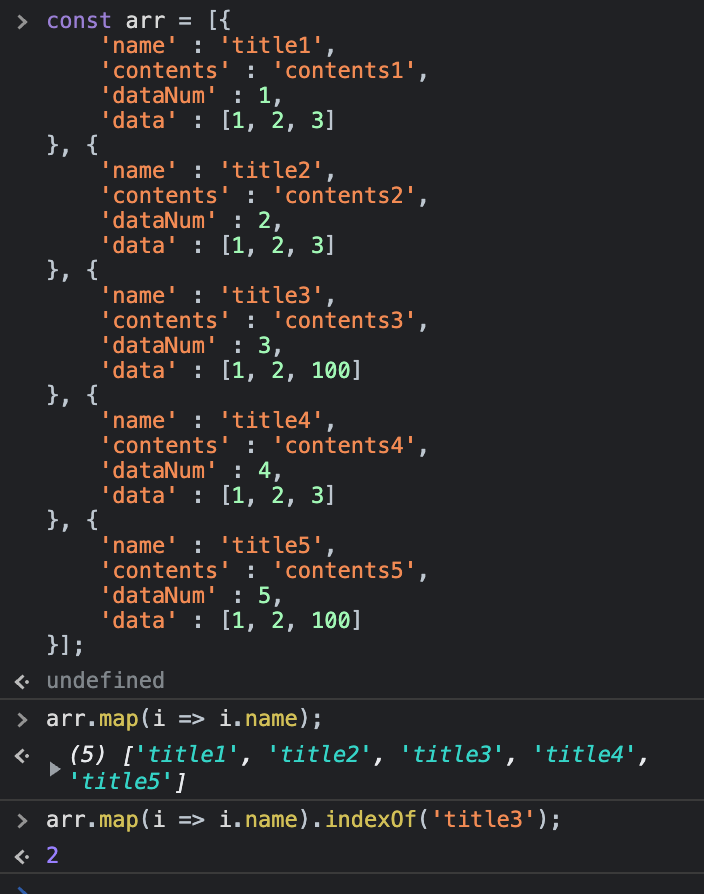
각각 요소에 함수를 호출할 때const arr = [{
'name' : 'title1',
'contents' : 'contents1',
'dataNum' : 1,
'data' : [1, 2, 3]
}, {
'name' : 'title2',
'contents' : 'contents2',
'dataNum' : 2,
'data' : [1, 2, 3]
}, {
'name' : 'title3',
'contents' : 'contents3',
'dataNum' : 3,
'data' : [1, 2, 100]
}, {
'name' : 'title4',
'contents' : 'contents4',
'dataNum' : 4,
'data' : [1, 2, 3]
}, {
'name' : 'title5',
'contents' : 'contents5',
'dataNum' : 5,
'data' : [1, 2, 100]
}];
-
배열 내에 있는 요소에 오름차순으로 접근해서 주어진 함수를 호출한 결과를 모아 새로운 배열을 반환한다.
-
filter();, find();, forEach(); 등 순회하는 메소드 에서도 사용 가능하다.
const arr 내의 data가 100인 title3와 title5를 출력하려면 어떻게 해야 할까?
arr.map((i) => {
if (i.data.includes(100)) {
return i.name
}
return
}).filter(i => i);
//expected output: ['title3', 'title5']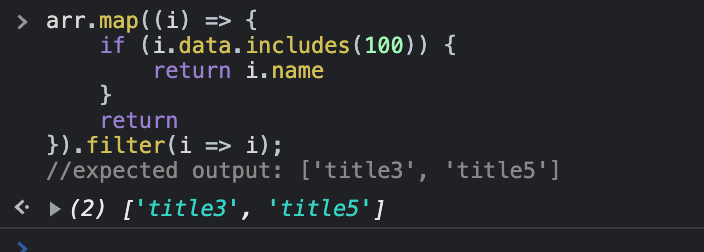
flatMap();
함수를 실행하는 동시에 배열을 평탄화할 때const coffee = ["iced americano and latte", "espresso", " ", "macchiato", " ", "cappuccino"]
const map = coffee.map(i => i.split(' '));
const flapMap = coffee.flatMap(i => i.split(' '));
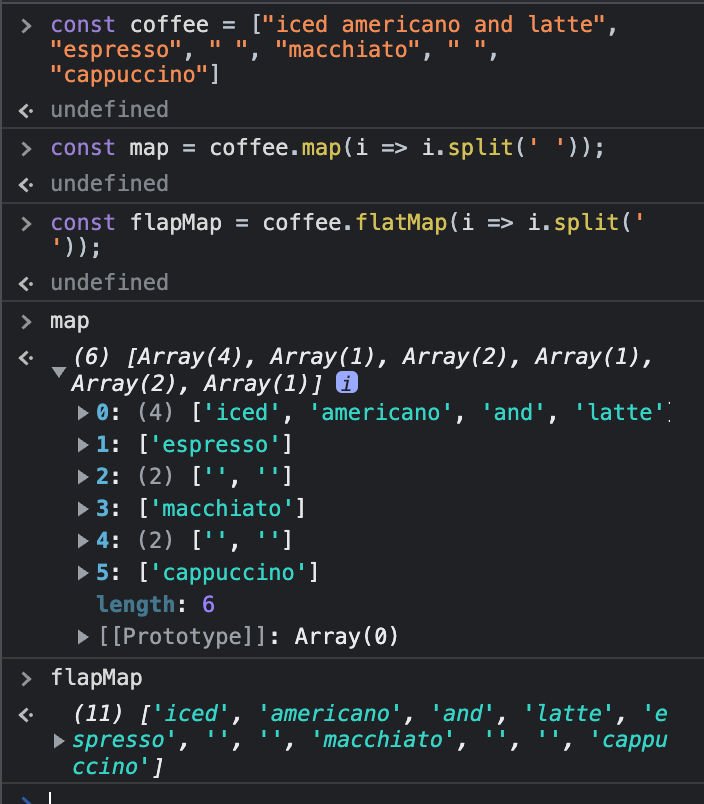
- 배열 내 요소에 순차적으로 주어진 함수를 실행하는 map과 기능과 배열을 편탄화하는 flat의 기능을 합친 것과 같다. (효율적이다)
forEach();
각각의 요소를 실행하고 싶을 때
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10];
arr.forEach(i => console.log(i));
// expected output: 1
// expected output: 2
// expected output: 3
// expected output: 4
// expected output: 5
// expected output: 6
// expected output: 7
// expected output: 8
// expected output: 9
// expected output: 10
- 메소드는 배열의 각 요소에 콜백을 1회 씩 실행하며 희소 배열과 같이 초기화 및 삭제되지 않은 인덱스 속성에 대해서는 실행하지 않는다. 콜백은 요소 값, 요소 인덱스, 순회 중인 배열과 같은 세 인수와 함께 호출된다.
- map은 새로운 배열을 생성하는 반면 forEach는 순회만 하는 차이점이 있다.
- 어려워 어려워 어려워 뭔가 재미도 있다, 익숙해지는게 최우선일 것 같다.
눈에 계속 바르고, 손에 익히자
