어제는 평가~
decimal format:
printf, print.format 대신에 사용가능
package decimalFormat01;
import java.text.DecimalFormat; //ctrl+shift+O 하면 import 됨
import java.text.ParseException;
public class DecimalFormat1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double number = 12344567.89;
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat(".0"); //소수점 출력하고 싶으면 .추가
System.out.println(df.format(number));
df.format(123.789); //format은 원하는 숫자를 넣든가 변수를 넣든가 상관x
// new DecimalFormat(".0").format(123.789);로 쓸 수도 있음
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("0").format(4758.948));
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("0").format(number));
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#").format(number));
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("0.00").format(number));
//0은 그 자리에 수가 없으면 무조건 0으로라도 출력
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.###").format(number));
//#은 그 자리에 수가 있으면 출력,없으면 출력 안함
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("000000000.0").format(number));
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#########.#").format(number));
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
//음수 부호 문자의 자리를 지정가능(실제 값이 음수가 되는 것이 아님)
number = -1234567.89;
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.#-").format(number));
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("-#.#").format(number));
//양수이면+를,음수이면-를 출력하는 방법(실제 음양의 값이 됨)
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("+#.#;-#.#").format(number));
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#,###.#").format(number)); //세 자리마다 ,
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#,####.#").format(number)); //네 자리마다 ,
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("+#,###.#;-#,###.#").format(number));
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("#.#%").format(number));//소수점 사라짐
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("\u00A4#.#").format(number));//통화기호
System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("\\#,###.#").format(number));
//글꼴이 한글일 때만 통화표시
System.out.println("==============================");
//parse() 메서드는 DecimalFormat의 조상인 NumberFormat에 정의되어 있는 메서드
//Number는 Wrapper클래스의 조상 (int,double,char => Integer,Double,Character)
//intValue(), doubleValue() 처럼 문자열을 형변환 시켜줌
String stNum = "1.234,567.89";
DecimalFormat df2 = new DecimalFormat("#,###.##");
try {
Number num = df2.parse(stNum);
System.out.println(num); //String에서 Number객체로 바꾼 거라 num값은 수가 아님. 연산불가
double douNum = num.doubleValue(); //이렇게 해야 실수형으로 변환
System.out.println(douNum*2); //실수라 연산 가능
//위를 한 줄로 표현
System.out.println((new DecimalFormat("#,###.##").parse("1,234,567.89").doubleValue())*3);
}catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
=>
12344567.9
4759
-----------------------------------
12344568
12344568
12344567.89
12344567.89
-----------------------------------
012344567.9
12344567.9
-----------------------------------
-1234567.9-
--1234567.9
-1234567.9
-----------------------------------
-1,234,567.9
-123,4567.9
-1,234,567.9
-----------------------------------
-123456789%
-₩1234567.9
-\1,234,567.9
==============================
1.234
2.468
3703703.67입출력(IO):
Input과 Output의 약자, 컴퓨터 내부 또는 외부 장치와 프로그램간의 데이터를 주고받는 것.
- 스트림(Stream):
입출력 장치에서 데이터를 읽고 쓰기 위해서 자바에서 제공하는 클래스.
모든 스트림은 단방향이며 각각의 장치마다 연결할 수 있는 스트림이 존재.
하나의 스트림으로 입출력을 동시에 할 수 없어서 동시에 하려면 2개의 스트림 필요
1.바이트 단위 처리: 1Byte, Stream키워드
2.문자 단위 처리: 2Byte, Reader/Writer키워드
package file01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class File1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try { //경로를 지정하지 않고 파일 만들면 내 workspace에 생성됨
File f1 = new File("test.txt");
f1.createNewFile(); //이 메소드(throw포함되어있음)까지 호출해야만 파일이 만들어짐
//존재하고 있는 폴더에 파일 생성: 경로 지정하면 됨
//File f2 = new File("d:\\test.txt"); 역슬래시 쓸거면 두 개씀
File f2 = new File("d:/test.txt");
f2.createNewFile();
//폴더와 파일 새로 생성
File tempfolder = new File("D:/temp");
tempfolder.mkdir();
File f3 = new File("D:/temp/kyr.txt");
f3.createNewFile();
System.out.println(f1.exists()); //파일이 존재하는지 여부 확인
System.out.println(new File("ttt.txt").exists());
//createNewFile(); 안했으니 없는 파일
System.out.println(f1.isFile()); //파일인지 아닌지 확인
System.out.println(tempfolder.isFile()); //디렉토리이기 때문에 아님
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//parent 폴더 만들기
File folder = new File("parent");
folder.mkdir();
File file = new File("parent/person.txt");
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("파일명: " + file.getName());
System.out.println("절대경로: " + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("파일용량: " + file.length());
System.out.println("상위폴더: " + file.getParent());
} catch (IOException e) { //없는 폴더에 생성하라고 할 수 있어서 있는 거
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
=>
true
false
true
false
--------------------------
파일명: person.txt
절대경로: D:\KYR\01_javaWork\day15\parent\person.txt
파일용량: 0
상위폴더: parent- 바이트 스트림 활용
package byteStream02;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteStreamAPI {
/*
* 바이트 기반 스트림:
* - 바이트 스트림: 1Byte단위로 전송하는 통로
* - 기반 스트림: 외부매체와 직접적으로 연결되는 통로
*
* xxxInputStream: xxx매체로부터 데이터를 직접 입력받는 통로
* xxxOutputStream: xxx매체로부터 데이터를 직접 출력하는 통로
*/
//프로그램으로부터 외부매체로 내보내기(파일)
public void fileSave() {
//프로그램으로부터 내보내 저장하는 것이기 때문에 Output
//FileOutputStream: 파일의 형태로 직접적으로 연결하여 1Byte단위 출력하는 스트림
/*
* 순서
* 1. 스트림 생성(통로 생성)
* 2. 스트림으로 데이터를 보내기(출력)
* 3. 다 사용한 후 반드시!! 스트림 반납
*/
//1. 스트림 생성
FileOutputStream fout = null;
try {
fout = new FileOutputStream("a_byte.txt");
//파일이 없으면 만들고 있으면 덮어쓰기함
//fout = new FileOutputStream("a_byte.txt", true);
//파일 내용에 이어서 덧붙임
//2. 데이터 출력
fout.write(97); //'a'유니코드 값
fout.write('b');
byte[] arr = {99,100,101}; //'c,d,e'에 대한 유니코드 값
fout.write(arr);
fout.write(arr, 1, 2); //배열의 길이 1부터 2개만 출력
fout.write('랑'); //2Byte는 깨져서 나옴
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) { //2번에 대한 오류 가능성
e.printStackTrace();
} finally { //finally는 써도 되고 안 써도됨
try {
//3. 스트림 반납
fout.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//프로그램에서 파일 입력 (데이터 가져오기)
public void fileRead() {
//FileInputStream: 파일로부터 1Byte단위로 입력받는 스트림
FileInputStream fin = null;
try {
fin = new FileInputStream("a_byte.txt");
//fin.read() 2씩 호출되기 때문에 하나 건너씩 출력
/*
while(fin.read() != -1) {
System.out.println(fin.read());
}
*/
//해결방법 1. 무한반복을 돌면서 매번 검사
/*
while(true) {
int value = fin.read();
if(value == -1)
break;
System.out.println(value);
}
*/
//해결방법 2. 권장사항
int value=0; //변수에 넣지 않으면 while문에서 다음 것을 검사하기 때문에 퐁당퐁당 값이 됨
while((value = fin.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char)value);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package byteStream02;
public class ByteStreamTest {
/*
* 스트림의 특징
* - 단방향: 입력과 출력이 따로 존재
* - 선입선출(FIFO)
* - 딜레이 생길 수 있음
*
* 스트림의 구분
* > 통로의 사이즈(1byte/2byte)
* - 바이트 스트림: 1Byte 단위로만 보내고 받을 수 있음
* - 문자 스트림: 2Byte 단위로만 보내고 받을 수 있음
* > 외부매체와 직접 연결 유무
* - 기반 스트림: 외부매체와 직접 연결 통로(필수)
* - 보조 스트림: 보조 역할만. 반드시 기반 스트림으로 연결이 돼있어야 사용가능
* 단독으로 사용 불가
*
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteStreamAPI bs = new ByteStreamAPI();
//bs.fileSave();
bs.fileRead();
}
}- 문자 스트림 활용
package char03;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CharAPI {
/*
* 문자기반 스트림
* -문자 스트림: 2Byte단위로 전송하는 통로
* -기반 스트림: 외부매체와 직접 연결하는 통로
*
* xxxReader: 입력용 스트림
* xxxWriter: 출력용 스트림
*/
//프로그램에서 파일로 출력
public void fileSave() {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
//1. 객체 생성
fw = new FileWriter("b_char.txt");
//2. 데이터 출력
fw.write("안녕하세요");
fw.write('A');
fw.write("\n");//엔터치라는 말
fw.write("안녕히가세요");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//3. 스트림 반납
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 프로그램으로 파일 입력
public void fileRead() {
//FileReader: 파일로부터 데이터를 2Byte단위로 읽어 오는 스트림
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("b_char.txt");
int value =0; //변수에 넣지 않으면 while문에서 다음 것을 검사하기 때문에 퐁당퐁당 값이 됨
while((value = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char)value);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package char03;
public class CharTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CharAPI cr = new CharAPI();
cr.fileSave();
cr.fileRead();
}
}- 보조 스트림(Buffer):
보조 스트림은 보통 BufferedRead를 많이 사용함
package buffer04;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BufferAPI {
//프로그램 -> 파일(출력)
public void fileSave() {
//FileWriter
//BufferedWriter: 버퍼라는 공간을 제공해주는 보조스트림(속도 향상)
//1. 기반 스트림 먼저 생성
//FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("c_buffer.txt");
//2. 보조 스트림
//BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
//위에것을 한 줄로
/* BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("c_buffer.txt"));
//3. 보조 스트림을 이용한 출력
bw.write("안녕?\n");
bw.write("반가워요");
bw.newLine(); //줄바꿈 메서드
bw.write("잘가요");
//버퍼라는 공간에 계속 쌓아놨다가 한꺼번에 출력 => 속도 향상
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//4. 보조 스트림 반납
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
*/
//try ~ with ~ resource 구문으로 자원반납을 자동으로 해줌
//JDK 1.7버전 이상부터 사용가능
/*
* try(반납할 스트림 객체 생성){
*
* } catch(예외클래스 e) {
*
* }
*/
try(BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("c_buffer.txt"))) {
//반납할 거 많으면 변수에 ;넣고 또 넣어주면 됨
bw.write("안녕?\n");
bw.write("반가워요");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("잘가요");
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//프로그램 <- 파일(입력)
public void fileRead() {
//FileReader
//BufferedReader
try(BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("c_buffer.txt"))){
String value = null; //int형은 값이 없으면 -1 String이면 null
while((value=br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package buffer04;
public class BufferTest {
/*
* 보조 스트림: 기반스트림만으로는 부족한 성능을 보다 향상 시켜주는 스트림
* 기반스트림에서 제공하지 않는 추가적인 메소드 제공
* 속도 향상 등등
* >>외부매체와 직접 연결 안 됨
* 단독사용 불가(반드시 기반 스트림과 함께)
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferAPI bf = new BufferAPI();
bf.fileSave();//한 번 저장하면 주석 처리해도 됨
bf.fileRead();
}
}- 객체 입출력 보조 스트림:
(역)직렬화: 객체를 보내려면 통로가 좁기 때문에 통로에 들어갈 수 있게 문자 크기로 일렬로 나열해주는 것
package object05;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Phone implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int price;
public Phone() { }
public Phone(String name, int price) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Phone [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
package object05;
import java.io.EOFException;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class ObjectDao {
// 프로그램 -> 파일(출력)
public void fileSave() {
Phone ph1 = new Phone("아이폰", 1800000);
Phone ph2 = new Phone("갤럭시", 1700000);
Phone ph3 = new Phone("갤럭시노트", 2100000);
//FileOutputStream: 1Byte 기반 스트림
//ObjectOutputStream: 객체 단위로 출력할 수 있도록 도움을 주는 보조 스트림
// (ObjectWriter없음)
try(ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d_phone.txt"))){
oos.writeObject(ph1); //직렬화 하지 않으면 예외발생 Phone 클래스에 implements Serializable를 해야 됨
oos.writeObject(ph2);
oos.writeObject(ph3);
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//프로그램 <- 파일(입력)
public void fileRead() {
try(ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("d_phone.txt"))) {
while(true)
System.out.println(ois.readObject());
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(EOFException e) {//object는 값이 없을 때 -1,null도 아닌 예외가 발생해서 IO예외를 상속받는 EOF를 명시.
System.out.println("파일을 모두 읽었습니다.");
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package object05;
public class ObjectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectDao dao = new ObjectDao();
dao.fileSave();
dao.fileRead();
}
}API 클래스에 implements Serializable 해주면 직렬화 됨.
*Serializable에 ctrl누른채로 클릭하면 클래스 구성 볼 수 있음
새로운 클래스 생성시 주석 뜨는 거 없애는 방법:
Window - Preperences - Code Templates - Method body - edit - 주석문 지우기 - Ok - Apply
Catch block body - 주석문 지우기 - ok
Constructor body - 주석문 지우기 - ok
네트워크:
여러대의 컴퓨터를 통신회선으로 연결한 것.
사내나 어느 공간 안에서만 쓸 수 있는 통신망을 인트라넷이라고 함.
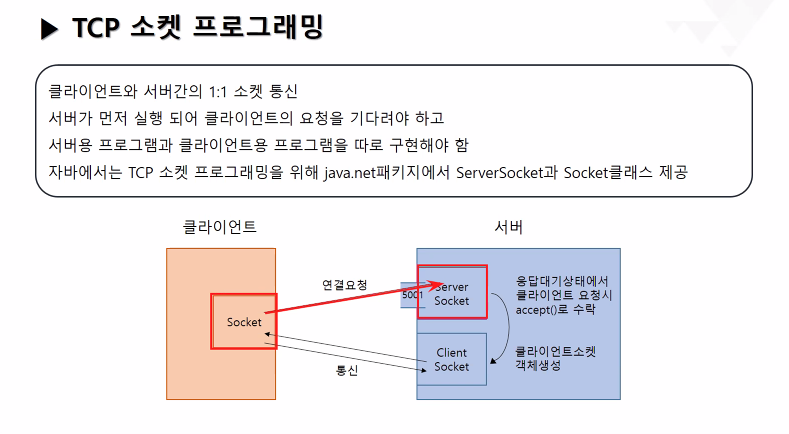
서버는 소켓 2개 필요
클라이언트는 소켓 1개 필요


package network;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class Network01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//서버에 요청을 위해서 서버의 ip와 port번호가 있어야 됨
//InetAddress : 네트워크 정보(ip주소 관련)를 확인할 수 있는 클래스
try {
InetAddress localhost = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); //static으로 되어있어서 new로 객체 생성 안 함
System.out.println(localhost); //내 pc명 + 내 ip주소
System.out.println("내 pc명: " + localhost.getHostName());
System.out.println("내 ip주소: " + localhost.getHostAddress());
System.out.println("---------------------------");
//도메인을 통해 그 서버에 관련된 정보 얻기
InetAddress googleHost = InetAddress.getByName("google.com");
System.out.println("google 서버명: " + googleHost.getHostName());
System.out.println("google ip주소: " + googleHost.getHostAddress());
// 도메인을 통해 그 서버에 관련된 정보를 배열로 얻기
InetAddress[] naverHost = InetAddress.getAllByName("naver.com");//getallbyname이어야 배열 모두 가져올 수 있음.
System.out.println("네이버 호스트 개수: " + naverHost.length);
for(InetAddress n : naverHost) {
System.out.println("naver 서버명: " + n.getHostName());
System.out.println("naver ip주소: " +n.getHostAddress());
}
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
=>
DESKTOP-HSRD9DI/192.168.20.43
내 pc명: DESKTOP-HSRD9DI
내 ip주소: 192.168.20.43
---------------------------
google 서버명: google.com
google ip주소: 142.250.66.46
네이버 호스트 개수: 4
naver 서버명: naver.com
naver ip주소: 223.130.200.104
naver 서버명: naver.com
naver ip주소: 223.130.200.107
naver 서버명: naver.com
naver ip주소: 223.130.195.200
naver 서버명: naver.com
naver ip주소: 223.130.195.95