근삿값
근삿값이란?
특정 값(참값)에 가장 가까운 값을 근삿값이라고 한다.
import random
nums = random.sample(range(0, 50), 20)
print(f'nums: {nums}')
inputNum = int(input('input number: '))
print(f'inputNum: {inputNum}')
nearNum = 0
minNum = 50
for n in nums:
absNum = abs(n - inputNum)
print(f'absNum: {absNum}')
if absNum < minNum:
minNum = absNum
nearNum = n
print(f'nearNum: {nearNum}')입력값이 11일 경우,
결괏값:
nums: [8, 33, 4, 20, 24, 6, 5, 3, 7, 35, 38, 47, 48, 12, 29, 11, 25, 43, 28, 17]
input number: 11
inputNum: 11
absNum: 3
absNum: 22
absNum: 7
absNum: 9
absNum: 13
absNum: 5
absNum: 6
absNum: 8
absNum: 4
absNum: 24
absNum: 27
absNum: 36
absNum: 37
absNum: 1
absNum: 18
absNum: 0
absNum: 14
absNum: 32
absNum: 17
absNum: 6
nearNum: 11근삿값(실습)
실습
근삿값 알고리즘을 이용해서 시험 점수를 입력하면 학점이 출력되는 프로그램을 만들어보자. 평균 점수에 따른 학점 기준 점수는 다음과 같다.
모듈파일: near
# 모듈파일!
def getNearNum(an):
basecores = [95, 85, 75, 65, 55]
nearNum = 0
minNum = 100
for n in basecores:
absNum = abs(n - an)
if absNum < minNum:
minNum = absNum
nearNum = n
if nearNum == 95:
return 'A'
elif nearNum == 85:
return 'B'
elif nearNum == 75:
return 'C'
elif nearNum == 65:
return 'D'
elif nearNum <= 55:
return 'F'실행파일: nearEx
# 실행파일!
import near
scores = []
kor = int(input('input kor score: '))
scores.append(kor)
eng = int(input('input eng score: '))
scores.append(eng)
mat = int(input('input mat score: '))
scores.append(mat)
sci = int(input('input sci score: '))
scores.append(sci)
his = int(input('input his score: '))
scores.append(his)
totalScore = sum(scores)
print(f'totalScore: {totalScore}')
avgScore = totalScore / len(scores)
print(f'avgScore: {avgScore}')
grade = near.getNearNum(avgScore)
print(f'grade: {grade}')결괏값:
input kor score: 70
input eng score: 85
input mat score: 90
input sci score: 77
input his score: 89
totalScore: 411
avgScore: 82.2
grade: B평균
평균
여러 수나 양의 중간값을 갖는 수를 평균이라고 한다.
import random
nums = random.sample(range(0, 100), 10)
print(f'nums: {nums}')
total = 0
for n in nums:
total += n
average = total / len(nums)
print(f'average: {average}')결괏값:
nums: [10, 41, 8, 93, 23, 98, 71, 81, 61, 63]
average: 54.950이상 90이하 수들의 평균
# 50이상 90이하 수들의 평균
import random
nums = random.sample(range(0, 100), 10)
print(f'nums: {nums}')
total = 0
targetNums = []
for n in nums:
if n >= 50 and n <= 90:
total += n
targetNums.append(n)
average = total / len(targetNums)
print(f'targetNums: {targetNums}')
print(f'average: {round(average, 2)}')정수들의 평균
# 정수들의 평균
import random
nums = [4, 5.12, 0, 5, 7.34, 9.1, 9, 3, 3.159, 1, 11, 12.789]
print(f'nums: {nums}')
targetNums = []
total = 0
for n in nums:
if n - int(n) == 0:
total += n
targetNums.append(n)
average = total / len(targetNums)
print(f'targetNums: {targetNums}')
print(f'average: {round(average, 2)}')결괏값:
nums: [4, 5.12, 0, 5, 7.34, 9.1, 9, 3, 3.159, 1, 11, 12.789]
targetNums: [4, 0, 5, 9, 3, 1, 11]
average: 4.71실수들의 평균
# 실수들의 평균
import random
nums = [4, 5.12, 0, 5, 7.34, 9.1, 9, 3, 3.159, 1, 11, 12.789]
print(f'nums: {nums}')
targetNums = []
total = 0
for n in nums:
if n - int(n) != 0:
total += n
targetNums.append(n)
average = total / len(targetNums)
print(f'targetNums: {targetNums}')
print(f'average: {round(average, 2)}')결괏값:
nums: [4, 5.12, 0, 5, 7.34, 9.1, 9, 3, 3.159, 1, 11, 12.789]
targetNums: [5.12, 7.34, 9.1, 3.159, 12.789]
average: 7.5평균(실습)
평균
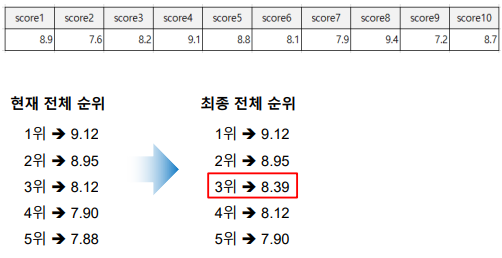
다음은 어떤 체조선수의 점수이다. 평균을 구하고 순위를 정하는 알고리즘을 만들어보자.
모둘(클래스) 파일
# 모둘(클래스) 파일!
class Top5Players:
def __init__(self, cs, ns):
self.currentScores = cs
self.newScores = ns
def setAlignScore(self):
nearIdx = 0
nearScore = 0
minNum = 10.0
for i, s in enumerate(self.currentScores):
absNum = abs(self.newScores - s)
if absNum < minNum:
minNum = absNum
nearIdx = i
nearScore = s
if self.newScores >= self.currentScores[nearIdx]:
for i in range(len(self.currentScores)-1, nearIdx, -1):
self.currentScores[i] = self.currentScores[i-1]
self.currentScores[nearIdx] = self.newScores
else:
for i in range(len(self.currentScores) - 1, nearIdx+1, -1):
self.currentScores[i] = self.currentScores[i-1]
self.currentScores[nearIdx] = self.newScores
def getFinalTop5Scores(self):
return self.currentScores실행파일
# 실행파일!
import near
scores = [8.9, 7.6, 8.2, 9.1, 8.8, 8.1, 7.9, 9.4, 7.2, 8.7]
top5PlayerScores = [9.12, 8.95, 8.12, 7.90, 7.88]
print(f'top5PlayerScores: {top5PlayerScores}')
total = 0; average = 0
for n in scores:
total += n
average = round(total / len(scores), 2)
print(f'total: {total}')
print(f'average: {average}')
tp = near.Top5Players(top5PlayerScores, average)
tp.setAlignScore()
top5PlayerScores = tp.getFinalTop5Scores()
print(f'top5PlayerScores: {top5PlayerScores}')결괏값:
top5PlayerScores: [9.12, 8.95, 8.12, 7.9, 7.88]
total: 83.9
average: 8.39
top5PlayerScores: [9.12, 8.95, 8.39, 8.39, 7.9]재귀 알고리즘
재귀 알고리즘이란?
나 자신을 다시 호출하는 것을 재귀라고 한다.
반복문 대신 재귀 함수를 이용한 예
def recusion(num):
if num > 0:
print('*' * num)
return recusion(num-1)
else:
return 1
recusion(10)결괏값:
**********
*********
********
*******
******
*****
****
***
**
*재귀 알고리즘를 이용한 팩토리얼 구하기
# 101 = 10 * 9*8*7*6
def factorial(num):
if num > 0:
return num * factorial(num - 1)
else:
return 1
print(f'factorial(10): {factorial(10)}')결괏값:
factorial(10): 3628800
재귀 알고리즘(실습)
실습
재귀 알고리즘을 이용한 최대공약수 계산

for문을 사용해서 최대공약수 구하기 (유클리드 호제법 사용 X)
def greatestCommonDevide(n1, n2):
maxNum = 0
for i in range(1, (n1+1)):
if n1 % i == 0 and n2 % i == 0:
maxNum = i
return maxNum
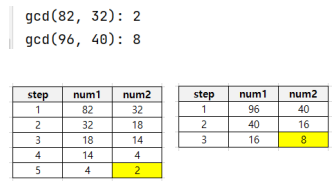
print(f'greatestCommonDevide(82, 32): {greatestCommonDevide(82, 32)}')
print(f'greatestCommonDevide(96, 40): {greatestCommonDevide(96, 40)}')결괏값:
greatestCommonDevide(82, 32): 2
greatestCommonDevide(96, 40): 8유클리드 호제법 사용
def gcd(n1, n2):
if n1 % n2 == 0:
return n2
else:
return gcd(n2, n1 % n2)
print(f'gcd(82, 32): {gcd(82, 32)}')
print(f'gcd(96, 40): {gcd(96, 40)}')결괏값:
gcd(82, 32): 2
gcd(96, 40): 8