📌 출처
📝 문제 설명
과제를 받은 루는 다음과 같은 순서대로 과제를 하려고 계획을 세웠습니다.
- 과제는 시작하기로 한 시각이 되면 시작합니다.
- 새로운 과제를 시작할 시각이 되었을 때, 기존에 진행 중이던 과제가 있다면 진행 중이던 과제를 멈추고 새로운 과제를 시작합니다.
- 진행중이던 과제를 끝냈을 때, 잠시 멈춘 과제가 있다면, 멈춰둔 과제를 이어서 진행합니다.
- 만약, 과제를 끝낸 시각에 새로 시작해야 되는 과제와 잠시 멈춰둔 과제가 모두 있다면, 새로 시작해야 하는 과제부터 진행합니다.
- 멈춰둔 과제가 여러 개일 경우, 가장 최근에 멈춘 과제부터 시작합니다.
과제 계획을 담은 이차원 문자열 배열 plans가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 과제를 끝낸 순서대로 이름을 배열에 담아 return 하는 solution 함수를 완성해주세요.
⚠ 제한 사항
- 3 ≤ plans의 길이 ≤ 1,000
- plans의 원소는 [name, start, playtime]의 구조로 이루어져 있습니다.
- name : 과제의 이름을 의미합니다.
- 2 ≤ name의 길이 ≤ 10
- name은 알파벳 소문자로만 이루어져 있습니다.
- name이 중복되는 원소는 없습니다.
- start : 과제의 시작 시각을 나타냅니다.
- "hh:mm"의 형태로 "00:00" ~ "23:59" 사이의 시간값만 들어가 있습니다.
- 모든 과제의 시작 시각은 달라서 겹칠 일이 없습니다.
- 과제는 "00:00" ... "23:59" 순으로 시작하면 됩니다. 즉, 시와 분의 값이 작을수록 더 빨리 시작한 과제입니다.
- playtime : 과제를 마치는데 걸리는 시간을 의미하며, 단위는 분입니다.
- 1 ≤ playtime ≤ 100
- playtime은 0으로 시작하지 않습니다.
- 배열은 시간순으로 정렬되어 있지 않을 수 있습니다.
- name : 과제의 이름을 의미합니다.
- plans의 원소는 [name, start, playtime]의 구조로 이루어져 있습니다.
- 진행중이던 과제가 끝나는 시각과 새로운 과제를 시작해야하는 시각이 같은 경우 진행중이던 과제는 끝난 것으로 판단합니다.
⌨ 입출력 예
| targets | result |
|---|---|
| [["korean", "11:40", "30"], ["english", "12:10", "20"], ["math", "12:30", "40"]] | ["korean", "english", "math"] |
| [["science", "12:40", "50"], ["music", "12:20", "40"], ["history", "14:00", "30"], ["science", "history", "computer", "music"] | |
| [["aaa", "12:00", "20"], ["bbb", "12:10", "30"], ["ccc", "12:40", "10"]] | ["bbb", "ccc", "aaa"] |
🖨 입출력 예 설명
입출력 예 #1
"korean", "english", "math"순으로 과제를 시작합니다. "korean" 과제를 "11:40"에 시작하여 30분 후인 "12:10"에 마치고, 즉시 "english" 과제를 시작합니다. 20분 후인 "12:30"에 "english" 과제를 마치고, 즉시 "math" 과제를 시작합니다. 40분 후인 "01:10"에 "math" 과제를 마칩니다. 따라서 "korean", "english", "math" 순으로 과제를 끝내므로 차례대로 배열에 담아 반환합니다.
입출력 예 #2
"music", "computer", "science", "history" 순으로 과제를 시작합니다.
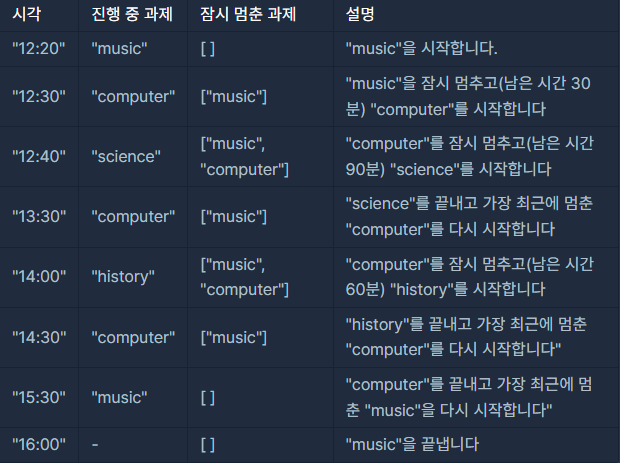
따라서 ["science", "history", "computer", "music"] 순서로 과제를 마칩니다.
입출력 예 #3
설명 생략
💻 내 코드
1. 리스트를 사용하여 구현
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public static String[] solution(String[][] plans) {
List<Project> answerList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Project> projects = new ArrayList<>();
for(String[] plan : plans) {
String name = plan[0];
String[] startStr = plan[1].split(":");
int[] start = new int[]{Integer.parseInt(startStr[0]), Integer.parseInt(startStr[1])};
int playtime = Integer.parseInt(plan[2]);
Project project = new Project(name, start, playtime);
projects.add(project);
}
Collections.sort(projects, new Comparator<Project>() {
@Override
public int compare(Project p1, Project p2) {
if(p1.start[0] == p2.start[0]) {
return p1.start[1] - p2.start[1];
}
return p1.start[0] - p2.start[0];
}
});
int cnt = 1;
PriorityQueue<Project> result = new PriorityQueue<>();
projects.get(0).cnt = cnt++;
result.add(projects.get(0));
for(int i = 1; i < projects.size(); i++) {
Project project = result.peek();
Project project2 = projects.get(i);
int time = calculate(project.start, project2.start);
while(true) {
if (time == project.playtime) {
answerList.add(result.poll());
break;
} else if(time > project.playtime) {
answerList.add(result.poll());
time -= project.playtime;
if(result.isEmpty()) break;
project = result.peek();
} else {
project.playtime -= time;
break;
}
}
project2.cnt = cnt++;
result.add(project2);
}
while(!result.isEmpty()) {
answerList.add(result.poll());
}
String[] answer = new String[answerList.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < answerList.size(); i++) {
answer[i] = answerList.get(i).name;
}
return answer;
}
public static int calculate(int[] time1, int[] time2) {
if(time1[0] == time2[0]) {
return time2[1] - time1[1];
}
if(time1[0] < time2[0]) {
int time = (time2[0] - time1[0]) * 60;
if(time1[1] <= time2[0]) {
time += time2[1] - time1[1];
return time;
} else {
time -= time1[1] - time2[1];
return time;
}
}
return 0;
}
static class Project implements Comparable<Project> {
String name;
int[] start;
int playtime;
int cnt;
public Project (String name, int[] start, int playtime) {
this.name = name;
this.start = start;
this.playtime = playtime;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Project o) {
return o.cnt - this.cnt;
}
}
}✏ 설명
- 과제를 시작하는 시간을 기준으로 오름차순으로 정렬
- 과제 시작
- 각 과제가 시작할 시간이 되었을 때 이전 과제가 끝났는지 확인
- 끝났으면 밀려있는 과제도 끝났는지 확인 (반복)
- 안 끝났으면 현재 과제부터 시작(우선순위 큐에 넣음)
- 각 과제가 시작할 시간이 되었을 때 이전 과제가 끝났는지 확인
이런 방식으로 먼저 들어온 과목이 뒤로 가게 우선순위 큐를 사용했는데 생각해보니까 그냥 "스택" 사용하면 됐다;;
암튼 이 문제를 해결했는데 기록을 남기는 이유는 정렬할 때 사용하는 코드들 정리하려고!
우선순위 큐를 사용할 때는 Comparable을 implements 후 compareTo 메소드를 오버라이드 하면 된다.
static class Project implements Comparable<Project> {
String name;
int[] start;
int playtime;
int cnt;
public Project (String name, int[] start, int playtime) {
this.name = name;
this.start = start;
his.playtime = playtime;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Project o) {
return o.cnt - this.cnt;
}
}앞에 왔으면 좋겠는게 앞으로 오면 된다.
ex) 오름차순 : this.cnt - o.cnt, 내림차순 : o.cnt - this.cnt;
리스트나 배열 정렬 시에 커스텀을 하고 싶으면
Collections.sort(projects, new Comparator<Project>() {
@Override
public int compare(Project p1, Project p2) {
if(p1.start[0] == p2.start[0]) {
return p1.start[1] - p2.start[1];
}
return p1.start[0] - p2.start[0];
}
});이런 식으로 직접 재정의해주면 된다.
