📌 출처
📝 문제
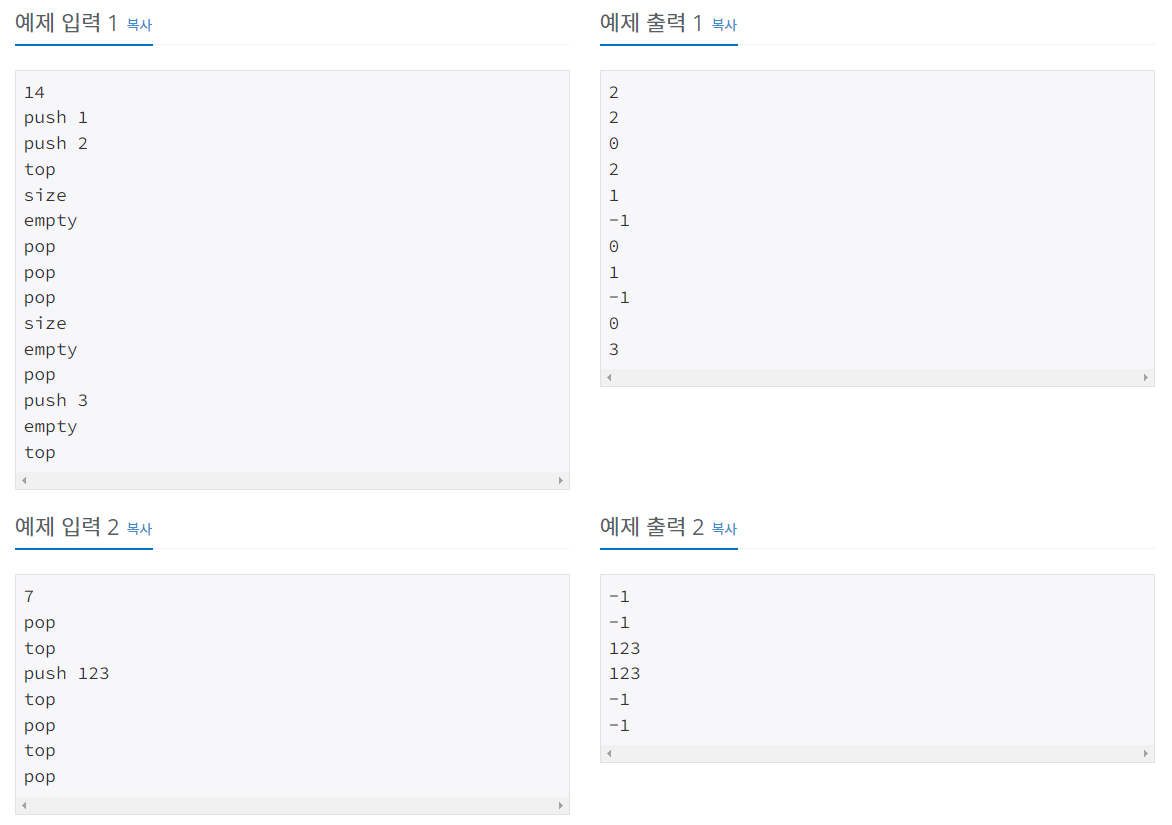
정수를 저장하는 스택을 구현한 다음, 입력으로 주어지는 명령을 처리하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
명령은 총 다섯 가지이다.
- push X: 정수 X를 스택에 넣는 연산이다.
- pop: 스택에서 가장 위에 있는 정수를 빼고, 그 수를 출력한다. 만약 스택에 들어있는 정수가 없는 경우에는 -1을 출력한다.
- size: 스택에 들어있는 정수의 개수를 출력한다.
- empty: 스택이 비어있으면 1, 아니면 0을 출력한다.
- top: 스택의 가장 위에 있는 정수를 출력한다. 만약 스택에 들어있는 정수가 없는 경우에는 -1을 출력한다.
⌨ 입력
첫째 줄에 주어지는 명령의 수 N (1 ≤ N ≤ 10,000)이 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에는 명령이 하나씩 주어진다. 주어지는 정수는 1보다 크거나 같고, 100,000보다 작거나 같다. 문제에 나와있지 않은 명령이 주어지는 경우는 없다.
🖨 출력
출력해야하는 명령이 주어질 때마다, 한 줄에 하나씩 출력한다.
💻 내 코드
1. 리스트를 사용하여 구현
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.Buffer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
private static List<Integer> stack = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String commandLine = br.readLine();
command(commandLine);
}
}
public static void command(String commandLine) {
if (commandLine.startsWith("push")) {
stack.add(Integer.parseInt(commandLine.substring(5)));
}
if (commandLine.equals("pop")) {
if(stack.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(-1);
} else {
int num = stack.get(stack.size() - 1);
System.out.println(num);
stack.remove(stack.size() - 1);
}
}
if (commandLine.equals("size")) {
System.out.println(stack.size());
}
if (commandLine.equals("empty")) {
if(stack.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(1);
} else {
System.out.println(0);
}
}
if (commandLine.equals("top")) {
if(stack.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(-1);
} else {
System.out.println(stack.get(stack.size() - 1));
}
}
}
}2. 스택 라이브러리를 사용하여 구현
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.Buffer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
private static Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String command = br.readLine();
checkCommand(command);
}
}
public static void checkCommand(String command) {
if (command.startsWith("push")) {
String[] tmp = command.split(" ");
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(tmp[1]));
}
if (command.equals("pop")) {
if(stack.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(-1);
} else {
int num = stack.pop();
System.out.println(num);
}
}
if (command.equals("size")) {
System.out.println(stack.size());
}
if (command.equals("empty")) {
if(stack.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(1);
} else {
System.out.println(0);
}
}
if (command.equals("top")) {
if(stack.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(-1);
} else {
System.out.println(stack.peek());
}
}
}
}
✏ 설명
처음에는 리스트를 사용하여 구현하였다. 데이터를 넣었다 뺏다 하기 쉽기 때문이었다.
그닥 어렵지 않게 구현하였는데 혹시 몰라서 찾아보니까 스택 라이브러리가 있었다...
당연한 얘기지만 훨씬 쉬웠다ㅎ
