IMMERSEVE - #2. Jest, Recursion
0

왜 항상 블로깅 시간은 11시부터죠..😂😂😂
오늘은 파트너분 덕에 씬나게 버스를🚎🚎🚎!!!
그냥 하루가 지나가면 다 까먹으니 복습!
1. Jest [ test - example ]
간단한 Jest 예제로 시작합니다!!! 🤟🏻
먼저 Math.js파일을 보면, 사칙연산을 구현하고 module로 만들고 있습니다!
// Math.js
const add = (num1, num2) => num1 + num2;
const substract = (num1, num2) => num1 - num2;
const multiply = (num1, num2) => num1 * num2;
const divide = (num1, num2) => num2 === 0 ? "cannot divide something with 0" : (num1 / num2);
module.exports = {
add,
substract,
multiply,
divide
};다음은 __test__폴더에 math.test.js파일을 작성합니다.
주어진 질문에 맞게 간단한 테스트 케이스를 구현하였어요.
// math.test.js
const { add, substract, multiply, divide } = require("../math");
describe("#1. test-example 테스트", () => {
// 1. Create test case to check add function works what it is supposed to be.
it('add func works by "1 + 2 = 3"', () => {
expect(add(1, 2)).toEqual(3);
})
// 2. Create test case to check substract function works what it is supposed to be.
it('substract func works by "3 - 1 = 2"', () => {
expect(substract(3, 1)).toEqual(2);
})
// 3. Create test case to check multiply function works what it is supposed to be.
it('multiply func works by "5 * 5 = 25"', () => {
expect(multiply(5, 5)).toEqual(25);
})
// 4. Create test case to check divide function works what it is supposed to be.
it('divide func works by "10 / 2 = 5"', () => {
expect(divide(10, 2)).toEqual(5);
})
// 5. Create test case to check divide function returns "cannot divide something with 0"
// when it tries to divdie a number with zero.
it('divide func cannot divied 5 with 0"', () => {
expect(divide(5, 0)).toEqual("cannot divide something with 0");
})
// 6. Group tests using `describe()`
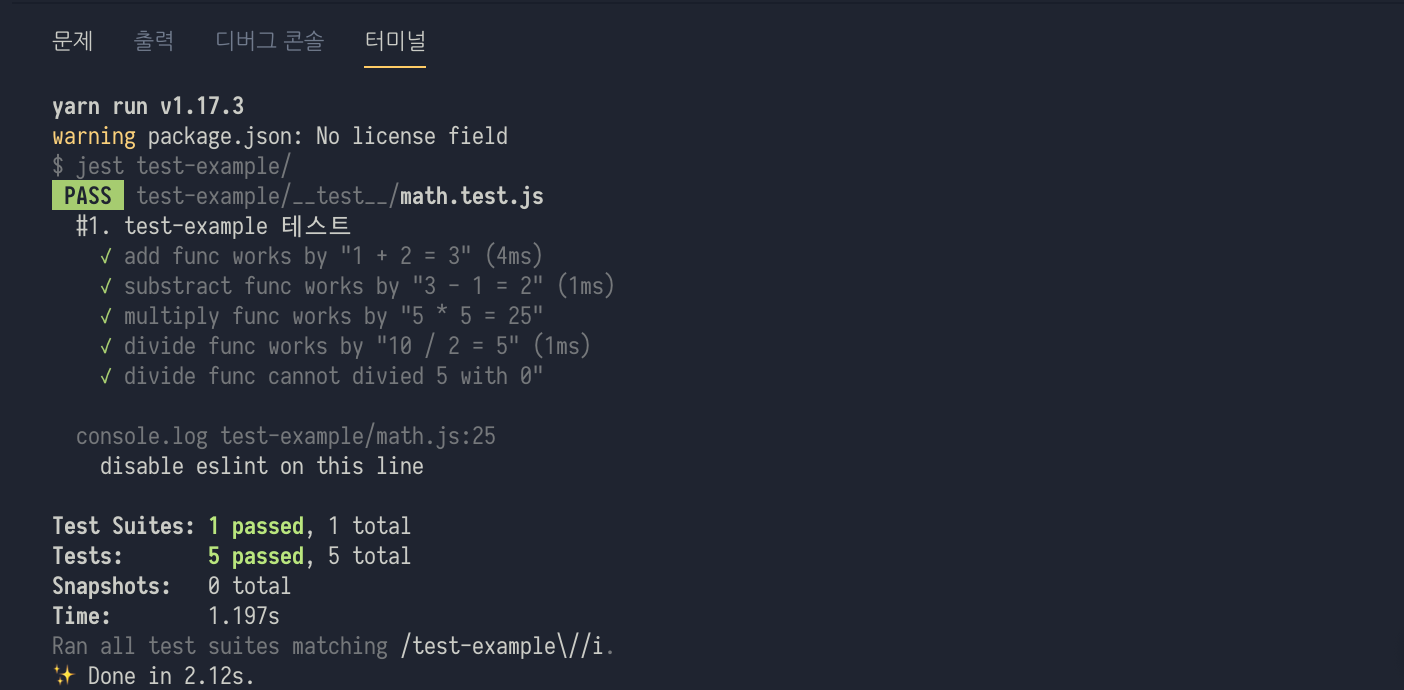
});yarn test:example로 확인해봅시다!🤩
2. Recursion [ stringifyJSON ]
힘겨운 싸움의 시작...🙏🏻
JSON.stringify와 동일한 구현을 위한 데이터 파일을 연결하고, 구현합니다.
디버깅용 콘솔을 제작하여 출력을 확인하면서 비교하면 비교적(?) 쉬워요!
포인트만 주석으로 설명합니다 :)
// stringifyJSON.js
const { stringifiableObjects, unstringifiableValues } = require('./data.js')
const LOG = console.log;
const stringifyJSON = obj => {
if (typeof obj === 'string') return `"${obj}"`; // str -> "str"
if (typeof obj === 'number' || typeof obj === 'boolean' || obj === null) return `${obj}`;
if (Array.isArray(obj)) { // Array Check
let newArr = [];
obj.map(val => newArr.push(stringifyJSON(val)))
return `[${newArr.join(',')}]`
}
if(Object.keys(obj).length === 0) { // {}, except check
return '{}';
} else { // Object Check
let newArr = [];
for(const key in obj) { // undefined & function => skip
if(typeof(obj[key]) === "undefined" || typeof(obj[key]) === "function") {
continue;
}
newArr.push(`${stringifyJSON(key)}:${stringifyJSON(obj[key])}`);
}
return `{${newArr.join(',')}}`;
}
}
// 디버깅을 위한 콘솔
stringifiableObjects.forEach(item => {
LOG(`INPUT : ${item}`);
LOG(`JSON.stringify : ${JSON.stringify(item)}`);
LOG(`stringifyJSON : ${stringifyJSON(item)}`);
LOG('')
});
unstringifiableValues.forEach(item => {
LOG(`INPUT : ${item}`);
LOG(`JSON.stringify : ${JSON.stringify(item)}`);
LOG(`stringifyJSON : ${stringifyJSON(item)}`);
LOG('')
});3. Recursion - [ parseJSON ]
2번과 마찬가지로 각 테스트케이스에 맞게 작성하면 됩니다~!
최대한 리팩토링하여 코드를 깔끔하게 만들었는데요!
핵심 부분만 주석으로 달아놓았는데, 이해에 도움이 되었으면 좋겠습니다!
const { parseableStrings, unparseableStrings } = require('./data.js');
const LOG = console.log;
const parseJSON = json => {
// 1. json의 공백을 제거
json = json.trim();
// 2. 문자열 검사
if (json[0] === `"`) {
let arr = [];
for (let i = 1; i < json.length - 1; i++) {
json[i] === "\\" && i++;
arr = [...arr, json[i]];
}
return arr.join('');
}
// 3. 예외인 boolean, null, [], {}는 그대로 파싱
if (json === "true") return true;
if (json === "false") return false;
if (json === "null") return null;
if (json === "[]") return [];
if (json === "{}") return {};
// 4. 배열 검사
if (json[0] === "[") {
let newArr = []; // empty Arr
let arrLevel = 0; // level of Array
let objLevel = 0; // level of Object
let first = 1; // start Index
let inString = false; // true: String, false: not String
for (let i = 1, len = json.length; i < len; i++) {
if (json[i] === `"` && json[i-1] !== '\\') { // String Check, but except \"
inString = !inString;
}
if (arrLevel === 0 && json[i] === "]" && !inString) {
return [...newArr, parseJSON(json.slice(first, i))]
};
if (arrLevel === 0 && objLevel === 0 && json[i] === "," ) {
newArr.push(parseJSON(json.slice(first, i)));
first = i + 1;
}
if (json[i] === "{") objLevel++;
if (json[i] === "}") objLevel--;
if (json[i] === "[") arrLevel++;
if (json[i] === "]") arrLevel--;
}
throw new SyntaxError();
}
// 5. 객체 검사
if (json[0] === "{") {
let newObj = {}; // empty Object
let objLevel = 0; // level of Object
let arrLevel = 0; // level of array
let first = 1; // first Index of Key
let last; // last Index of Key
let inString = false; // true: String, false: not String
for (let i = 1, len = json.length; i < len; i++) {
if (json[i] === `"` && json[i-1] !== '\\') { // String Check, but except \"
inString = !inString;
}
if (json[i] === ":" && objLevel === 0 && !inString ) { // find lastIndex of Key in Object
last = i;
}
if (json[i] === "," && objLevel === 0 && arrLevel === 0 && !inString) { // make Object {key:value}
newObj[parseJSON(json.slice(first, last))] = parseJSON(json.slice(last + 1, i))
first = i + 1;
}
if (json[i] === "}" && objLevel === 0 ) { // make Object {key:value} & return Object
newObj[parseJSON(json.slice(first, last))] = parseJSON(json.slice(last + 1, i))
return newObj;
}
if (json[i] === "{") objLevel++;
if (json[i] === "}") objLevel--;
if (json[i] === "[") arrLevel++;
if (json[i] === "]") arrLevel--;
}
throw new SyntaxError();
}
return +json; // last case return number type
};
parseableStrings.forEach(item => {
LOG(`INPUT : ${item}`);
LOG(`JSON.parse : `, JSON.parse(item));
LOG(`parseJSON : `, parseJSON(item));
LOG('')
});
// unparseableStrings.forEach(item => {
// LOG(`INPUT : ${item}`);
// LOG(`JSON.parse : ${JSON.stringify(item)}`);
// LOG(`parseJSON : ${parseJSON(item)}`);
// LOG('')
// })