What is JSON?
JSON은 Douglas Crockford가 대중화한 JavaScript 객체 구문을 따르는 텍스트 기반 데이터 형식이다.
자바스크립트 객체 리터럴 구문과 매우 유사하지만, 자바스크립트로부터 독립적으로 사용할 수 있으며, 많은 프로그래밍 환경에서 JSON을 읽고 생성하는 기능이 포함되어 있다.
JSON은 문자열로 이루어져 있는데, 이는 네트워크를 통해 데이터를 전송할 때 유리하다.
데이터에 액세스하려면 JSON을 native JavaScript object로 변환해야 하는데 이는 별로 어렵지 않다.
자바스크립트는 JSON과 native JavaScript object를 서로 변환시킬 수 있는 전역 JSON 객체를 지원한다.
native JavaScript object에서 JSON으로 변환하는 것을 serialization이라 하고 그 반대는 deserialization이라 한다.
JSON 문자열은 기본적으로 확장자가 .json 인 텍스트 파일과 MIME type의 application/json 인 자체파일에 저장할 수 있다.
JSON structure
위에서 설명한 것 처럼 JSON은 자바스크립트의 객체 구문과 비슷하지만 완전히 똑같지는 않다.
자바스크립트의 기본 타입인 string, numbers, array, booleans, object literals만을 JSON에 포함할 수 있다.
그리고 빈 값으로는 null을 사용하며 undefined 은 사용하지 않는다.
{
"squadName": "Super hero squad",
"homeTown": "Metro City",
"formed": 2016,
"secretBase": "Super tower",
"active": true,
"members": [
{
"name": "Molecule Man",
"age": 29,
"secretIdentity": "Dan Jukes",
"powers": ["Radiation resistance", "Turning tiny", "Radiation blast"]
},
{
"name": "Madame Uppercut",
"age": 39,
"secretIdentity": "Jane Wilson",
"powers": [
"Million tonne punch",
"Damage resistance",
"Superhuman reflexes"
]
},
{
"name": "Eternal Flame",
"age": 1000000,
"secretIdentity": "Unknown",
"powers": [
"Immortality",
"Heat Immunity",
"Inferno",
"Teleportation",
"Interdimensional travel"
]
}
]
}만약 위의 JSON을 superHeroes 라는 변수에 담으면 자바스크립트 객체와 같이 dot/bracket notation을 이용해 내부 데이터에 액세스 할 수 있다.
superHeroes.homeTown
superHeroes['active']
superHeroes['members'][1]['powers'][2]Other notes
-
JSON은 순전히 데이터 형식의 문자열이므로 프로퍼티만 포함하고 메서드는 포함하지 않는다.
-
JSON에서는 문자열이나 프로퍼티 이름을 큰따옴표로 감싸야 한다.
작은따옴표는 JSON 전체 문자열을 감싸는 것 외에는 사용할 수 없다. -
쉼표나 콜론을 잘못 입력하면 JSON 파일 전체가 잘못되어서 제대로 동작하지 않을 수 있다.
따라서 JSON의 데이터 유효성을 확인하는 데 주의해야 한다.
물론 프로그래밍적으로 생성된 JSON은 오류가 발생할 확률이 지극히 낮다.
그렇지만 JSONLint➡️와 같은 애플리케이션을 사용하여 JSON을 검증할 수 있다. -
자바스크립트의 객체와는 달리 JSON의 프로퍼티는 큰따옴표로 묶여 있어야만 한다.
Active learning: Working through a JSON example
Getting started
JSON을 스크립트에 로드하여 다음과 같은 화면을 만들어 보자.
기본으로 주어지는 html은 아래와 같다.
<header>
</header>
<section>
</section>
<script>
</script>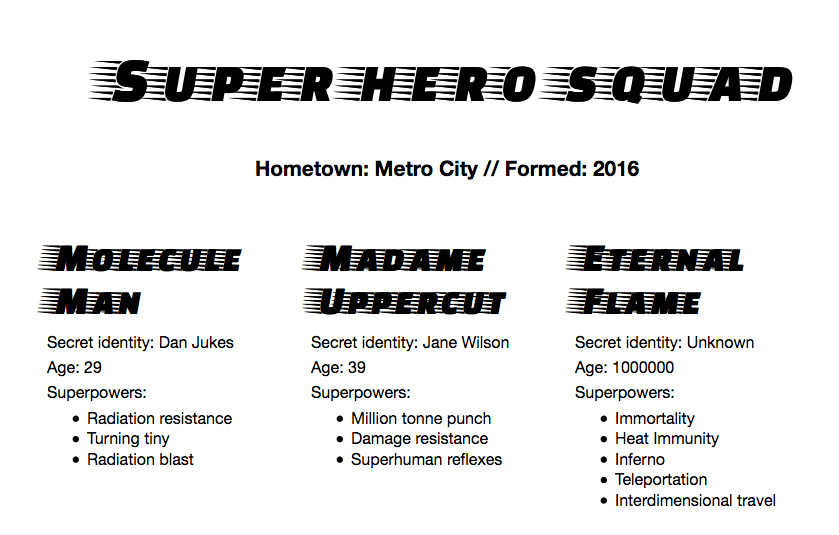
Top-level function
Top-level 함수(최상위 함수)는 다음과 같다.
Top-level function는 맨 처음 호출되는 함수이다.
async function populate() {
const requestURL = 'https://mdn.github.io/learning-area/javascript/oojs/json/superheroes.json';
const request = new Request(requestURL);
const response = await fetch(request);
const superHeroes = await response.json();
populateHeader(superHeroes);
populateHeroes(superHeroes);
}JSON을 얻기 위해 Fetch 라는 API를 사용했다.
이 API를 사용하면 자바스크립트를 통해 서버에서 리소스를 검색하도록 네트워크 요청을 할 수 있다.
즉, 전체 페이지를 다시 로드하지 않고도 콘텐츠의 작은 섹션을 업데이트 할 수 있다.
이 함수에서 처음 네 줄은 서버에서 JSON을 가져오기 위해 Fetch API를 사용한 부분이다.
-
GitHub URL을 저장할
requestURL변수를 선언한다. -
URL을 사용하여 새
Request객체를 초기화한다. -
fetch()함수를 사용하여 네트워크 요청을 하고,Response객체를 반환받는다. -
Response객체의json()메서드를 사용하여 JSON 객체를 반환받는다.fetch()API는 비동기 함수이다.
모든 작업이 완료되면 superHeroes 는 JSON기반의 자바스크립트 객체가 될 것이다.
그 후, 두 함수의 argument로 전달한다.
Populating the header
function populateHeader(obj) {
const header = document.querySelector('header');
const myH1 = document.createElement('h1');
myH1.textContent = obj.squadName;
header.appendChild(myH1);
const myPara = document.createElement('p');
myPara.textContent = `Hometown: ${obj.homeTown} // Formed: ${obj.formed}`;
header.appendChild(myPara);
}Creating the hero information cards
function populateHeroes(obj) {
const section = document.querySelector('section');
const heroes = obj.members;
for (const hero of heroes) {
const myArticle = document.createElement('article');
const myH2 = document.createElement('h2');
const myPara1 = document.createElement('p');
const myPara2 = document.createElement('p');
const myPara3 = document.createElement('p');
const myList = document.createElement('ul');
myH2.textContent = hero.name;
myPara1.textContent = `Secret identity: ${hero.secretIdentity}`;
myPara2.textContent = `Age: ${hero.age}`;
myPara3.textContent = 'Superpowers:';
const superPowers = hero.powers;
for (const power of superPowers) {
const listItem = document.createElement('li');
listItem.textContent = power;
myList.appendChild(listItem);
}
myArticle.appendChild(myH2);
myArticle.appendChild(myPara1);
myArticle.appendChild(myPara2);
myArticle.appendChild(myPara3);
myArticle.appendChild(myList);
section.appendChild(myArticle);
}
}Calling the top-level function
마지막으로 top-level function(최상위 함수)인 populate() 를 호출하면 된다.
populate();Converting between objects and text
위에서 본 예제에서는 자바스크립트 객체에 액세스하는것이 간단했다.
왜냐하면 네트워크의 response를 response.json() 을 이용해 다이렉트로 자바스크립트 객체로 변환시켰기 때문이다.
하지만, response 객체 없이 raw JSON 문자열을 받아서 JSON 객체를 만들어야 하는 상황이 생길 수 있다.
또한 자바스크립트 객체를 네트워크로 전송할 때 JSON 문자열로 변환한 후에 전송해야 한다.
이렇듯 raw JSON 문자열과 JSON 객체간의 변환이 빈번하게 일어난다.
다행히도 브라우저에는 빌트인 JSON 객체가 있어서 쉽게 서로간에 변환이 가능하다.
parse():
JSON string ➡️ 자바스크립트 객체stringify():
자바스크립트 객체 ➡️ JSON string
다음 예제에서는 response.json() 이 아닌 response.text() 를 호출하여 JSON string으로 만든 후에 JSON string을 빌트인 JSON 객체를 사용하여 자바스크립트 객체로 변경한다.
async function populate() {
const requestURL = 'https://mdn.github.io/learning-area/javascript/oojs/json/superheroes.json';
const request = new Request(requestURL);
const response = await fetch(request);
const superHeroesText = await response.text();
const superHeroes = JSON.parse(superHeroesText);
populateHeader(superHeroes);
populateHeroes(superHeroes);
}[참고] : MDN
