python의 데이터 시각화 라이브러리는 굉장히 여러개이다.
그 중에서 가장 많이 쓰는 대표적인 몇개를 소개할까 한다.
- seaborn
- matplotlib
matplotlib
package를 우선 import해준다.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
그래프를 본격적으로 그리기 전에, 자리를 미리 깔아놔야한다.
# 자리깔기
fig = plt.figure() #그래프를 그리기 위한 figure객체 생성
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) # 1행 1열 중 1번째 자리또는 그래프 크기를 정해줄수도 있다.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5,2))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)그래프를 여러개 만들려면 add_subplot을 이용해 추가하면 된다.
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,1) # 2행 2열 중 첫번째
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,2) # 2행 2열 중 두번째
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,4) # 2행 2열 중 4번째그래프 그리기
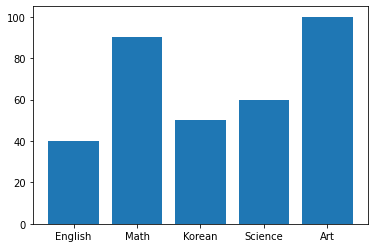
1. bar
bar()를 이용해서 막대 그래프를 그려준다.
[코드]
subject = ['English', 'Math', 'Korean', 'Science', 'Art']
points = [40, 90, 50, 60, 100]
# 축 그리기
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
# 막대 그래프 그리기
ax1.bar(subject,points)[결과]
그래프에 요소 추가하기
label과 title을 추가할 수도 있다.
plt.xlabel('Subject')
plt.ylabel('Points')
plt.title("Result") label title을 추가해서 막대그래프를 다시 그려보자.
#그래프 데이터
subject = ['English', 'Math', 'Korean', 'Science', 'Art']
points = [40, 90, 50, 60, 100]
# 축 그리기
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
# 라벨, 타이틀 달기
plt.xlabel('Subject')
plt.ylabel('Points')
plt.title("Result")
# 그래프 그리기
ax1.bar(subject, points)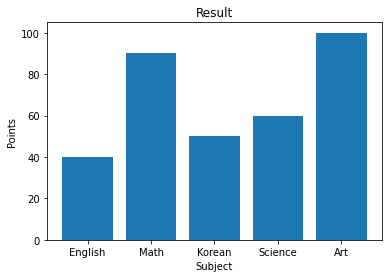
2. line
line을 대표적으로 사용하는 분야는 아마 주식에서 주가 데이터를 나타낼때가 아닐까 싶다.
matplotlib로 주석(annotation)을 달수도 있고, 좌표축(xlim, ylim)을 설정해 줄 수도 있다.
추가로 그래프 배경을 grid 모양으로 바꿀 수도 있다.
그래프를 간단하게 그리기
plt.plot()을 사용하면 위에서 figure()와 add_subplot()과정을 생략하고 바로 그래프를 그릴 수 있다.
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100) #0~10까지 균등한 간격으로 100개 숫자만들기.
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x),'o')
plt.plot(x, np.cos(x),'*-', color='black')
plt.show()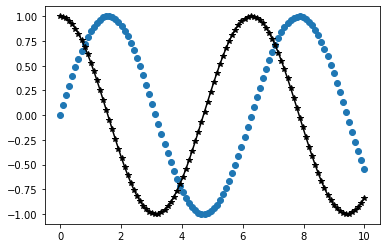
subplot을 이용해서 여러개를 그릴 수도 있다.
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
plt.subplot(2,1,1)
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x),'orange','o')
plt.subplot(2,1,2)
plt.plot(x, np.cos(x), 'orange')
plt.show()
linestyle, marker옵션
x, y데이터는 물론 선 색깔, 마커옵션 등을 바꿀 수도 있다.
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
plt.plot(x, x + 0, linestyle='solid')
plt.plot(x, x + 1, linestyle='dashed')
plt.plot(x, x + 2, linestyle='dashdot')
plt.plot(x, x + 3, linestyle='dotted')
plt.plot(x, x + 0, '-g') # solid green
plt.plot(x, x + 1, '--c') # dashed cyan
plt.plot(x, x + 2, '-.k') # dashdot black
plt.plot(x, x + 3, ':r'); # dotted red
plt.plot(x, x + 4, linestyle='-') # solid
plt.plot(x, x + 5, linestyle='--') # dashed
plt.plot(x, x + 6, linestyle='-.') # dashdot
plt.plot(x, x + 7, linestyle=':'); # dotted
pandas plot()를 이용해서 그래프 그리기
pandas도 시각화를 할 수 있게 지원해주고 있다.
plot() 메소드를 사용하면 가능하다.
[예제 코드]
# Series타입의 임의의 데이터 생성
data = pd.Series(np.random.rand(5), index=list('abcde'))
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1)
data.plot(kind='bar', ax=axes[0], color='blue', alpha=1)
data.plot(kind='barh', ax=axes[1], color='red', alpha=0.3)kind에 쓰고 싶은 그래프 이름을 넣어주면 된다.
[예제코드]
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(6,4), columns=pd.Index(['A','B','C','D']))
df.plot(kind='line') # line plotplot의 parameter들
더 자세하게 알고 싶다면 여기를 클릭하면 된다.
- label: 그래프의 범례이름.
- ax: 그래프를 그릴 matplotlib의 서브플롯 객체.
- style: matplotlib에 전달할 'ko--'같은 스타일의 문자열
- alpha: 투명도 (0 ~1)
- kind: 그래프의 종류: line, bar, barh, kde
- logy: Y축에 대한 로그스케일
- use_index: 객체의 색인을 눈금 이름으로 사용할지의 여부
- rot: 눈금 이름을 로테이션(0 ~ 360)
- xticks, yticks: x축, y축으로 사용할 값
- xlim, ylim: x축, y축 한계
- grid: 축의 그리드 표시할 지 여부
data가 DataFrame객체일 경우
- subplots: 각 DataFrame의 칼럼을 독립된 서브플롯에 그린다.
- sharex: subplots=True면 같은 X축을 공유하고 눈금과 한계를 연결한다.
- sharey: subplots=True면 같은 Y축을 공유한다.
- figsize: 그래프의 크기, 튜플로 지정
- title: 그래프의 제목을 문자열로 지정
- sort_columns: 칼럼을 알파벳 순서로 그린다.
정리
그래프를 시각화 하는 방법을 정리하면 다음과 같다.
1. fig=plt.figure() : figure객체를 할당하여 판을 깔아준다.
2. ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) : 축을 그린다.
3. ax.bar(x, y) : 축안에 어떤 그래프를 그릴지 메소드를 선택한 후, 데이터를 x y 각각에 넣어준다.
4. grid, xlabel, ylabel, title ... parameter들은 원하는 대로 추가해준다.
plt.savefig: 그래프를 저장해주는 메소드이다.
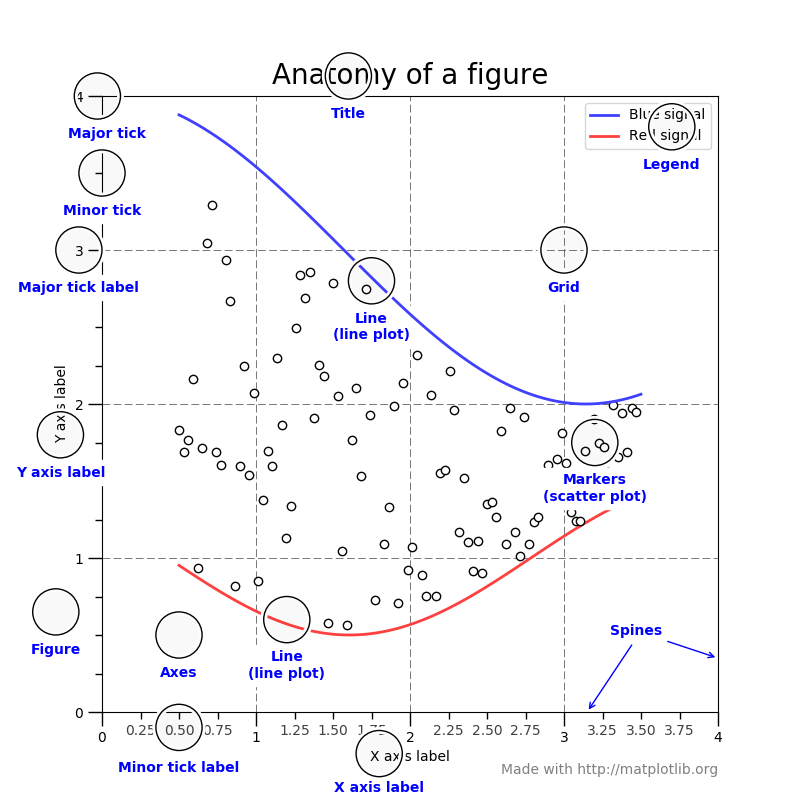
밑에는 그래프의 각 명칭을 나타낸 그림이다.