AOP
- Aspect Oriented Programming
- 공통 관심 사항(cross-cutting concern) vs 핵심 관심 사항(core concern) 분리
TimeTraceAop.java
시간 측정 AOP 등록
package hello.hellospring.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class TimeTraceAop {
@Around("execution(* hello.hellospring..*(..))")
public Object execute(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("START: " + joinPoint.toString());
try{
return joinPoint.proceed();
}finally {
long finish = System.currentTimeMillis();
long timeMs = finish - start;
System.out.println("END: " + joinPoint.toString() + " " + timeMs + "ms");
}
}
}
👍🏻 해결
- 회원가입, 회원 조회등 핵심 관심사항과 시간을 측정하는 공통 관심 사항을 분리한다.
- 시간을 측정하는 로직을 별도의 공통 로직으로 만들었다.
- 핵심 관심 사항을 깔끔하게 유지할 수 있다.
- 변경이 필요하면 해당 로직만 변경하면 된다.
- 원하는 적용 대상을 선택할 수 있다.
스프링의 AOP 동작 방식
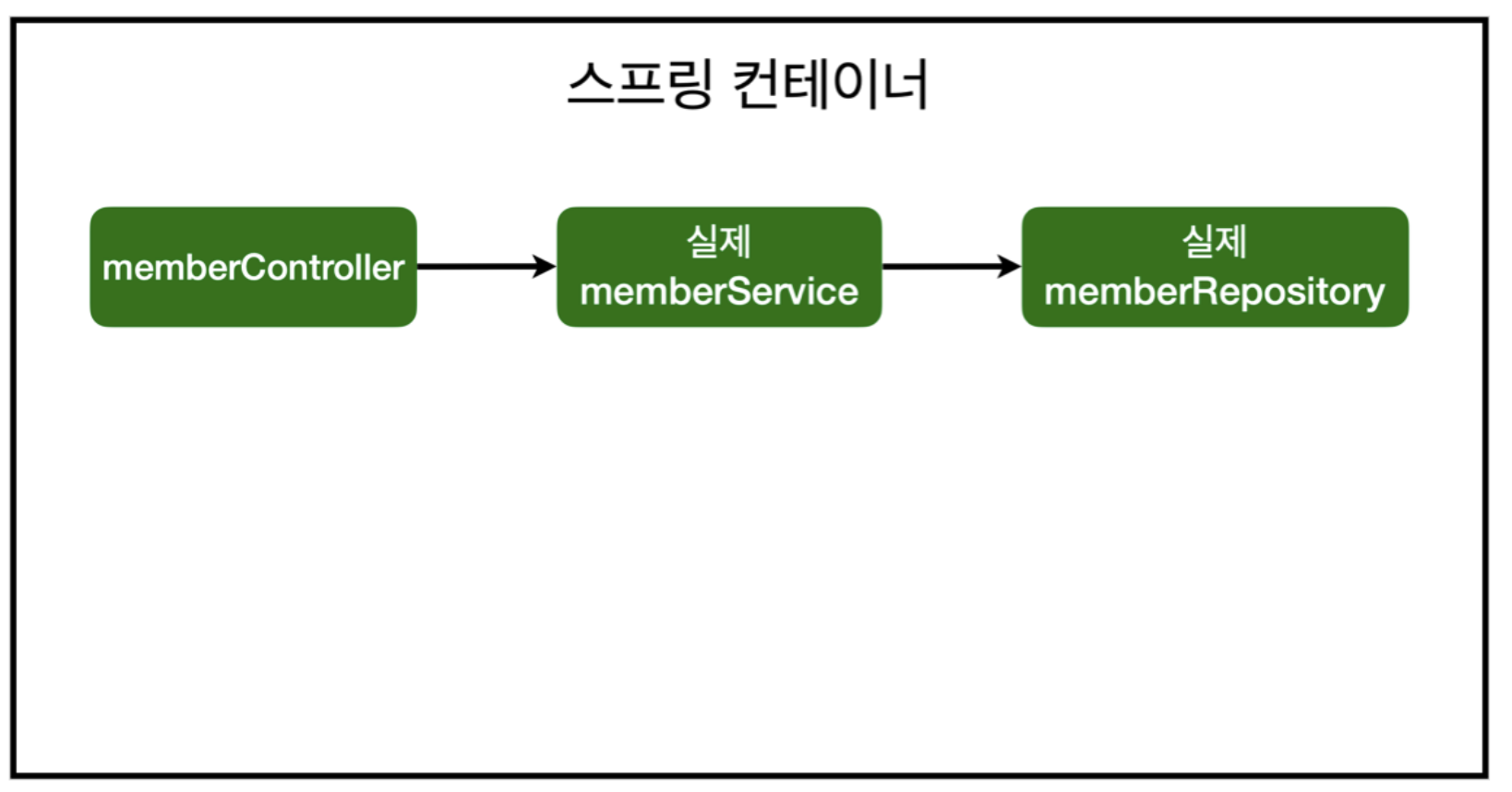
AOP 적용 전 의존관계
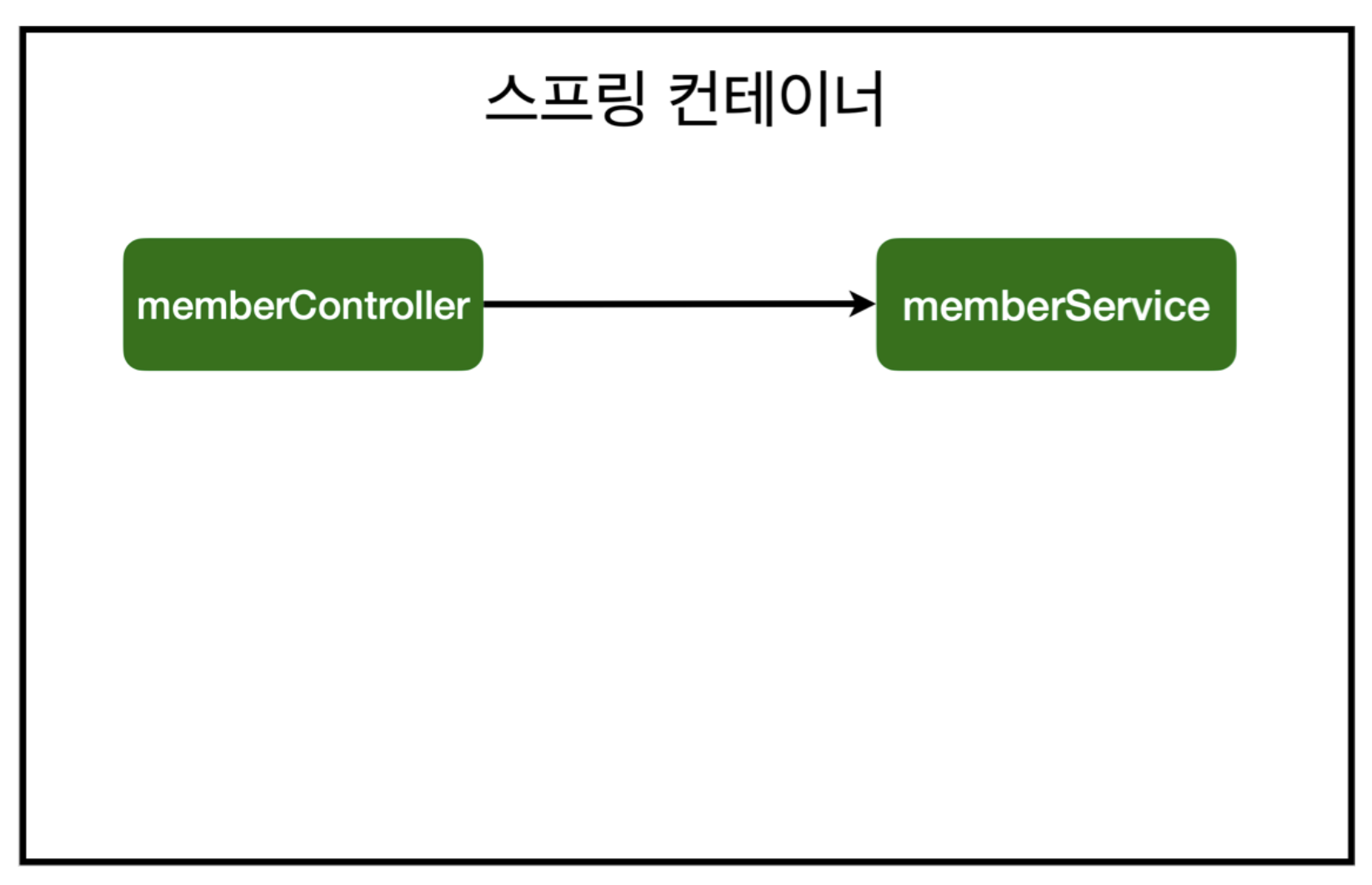
- AOP 적용 전 스프링은 다음과 같은 의존관계로 기능을 구현한다.
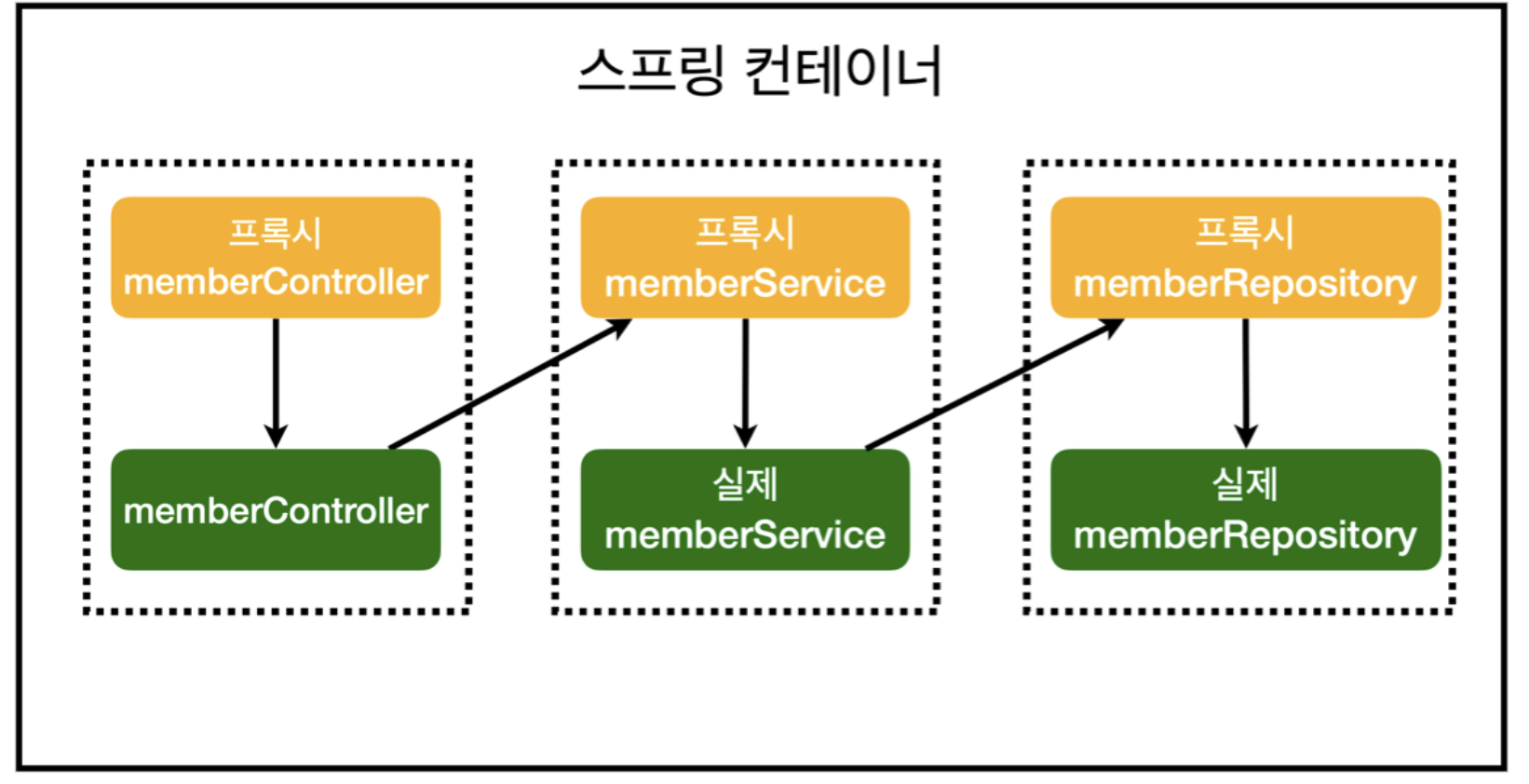
AOP 적용 후 의존관계
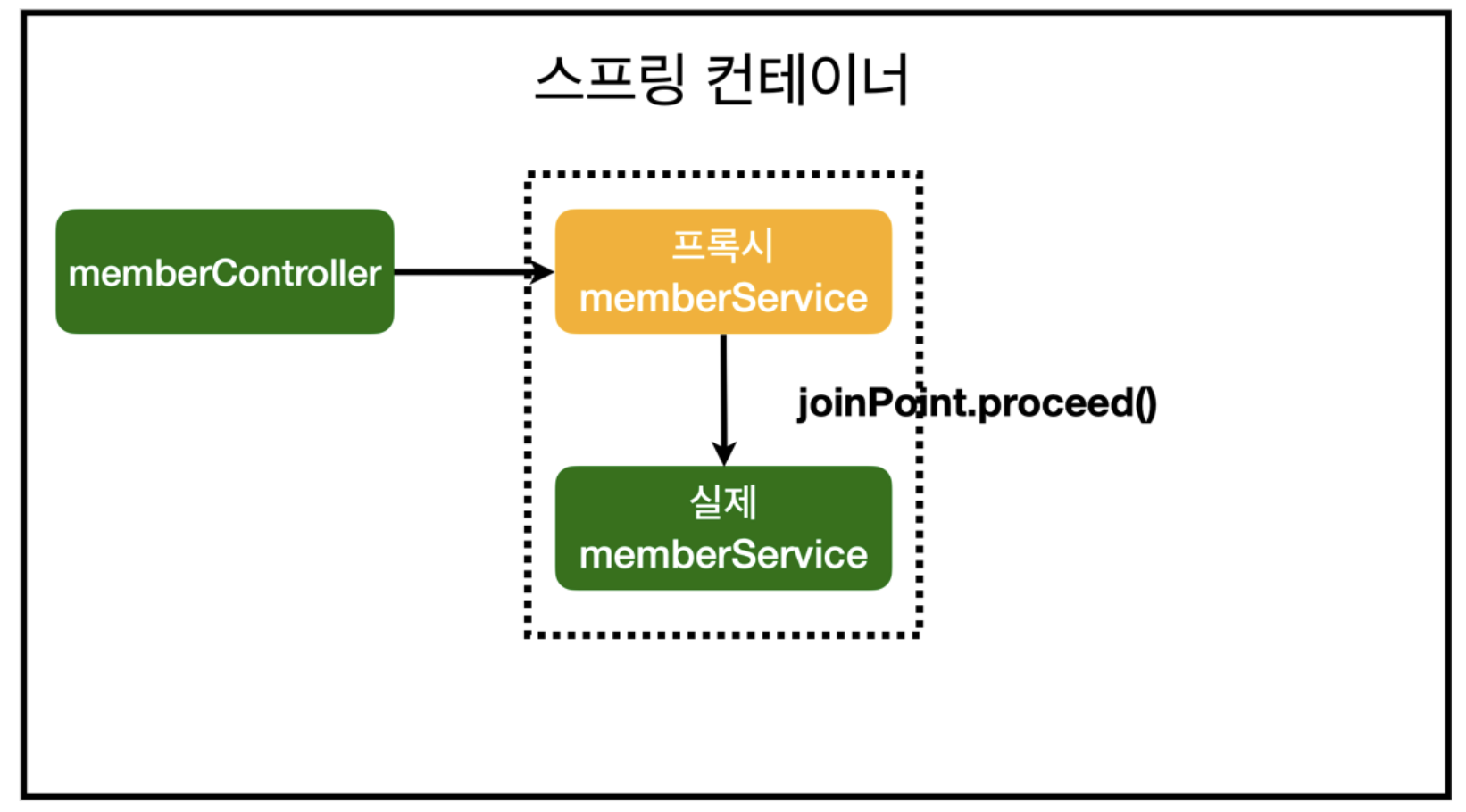
- spring AOP는 프록시 패턴이라는 디자인 패턴을 사용해서 AOP 효과를 낸다.
- 어떤 클래스가 Spring AOP의 대상이라면 그 기존 클래스의 Bean이 만들어질 때 Spring AOP가 프록시(기능이 추가된 클래스)를 자동으로 만들고 원본 클래스 대신 프록시를 빈으로 등록한다.
그리고 원본 클래스가 사용되는 지점에서 프록시를 대신 사용한다.
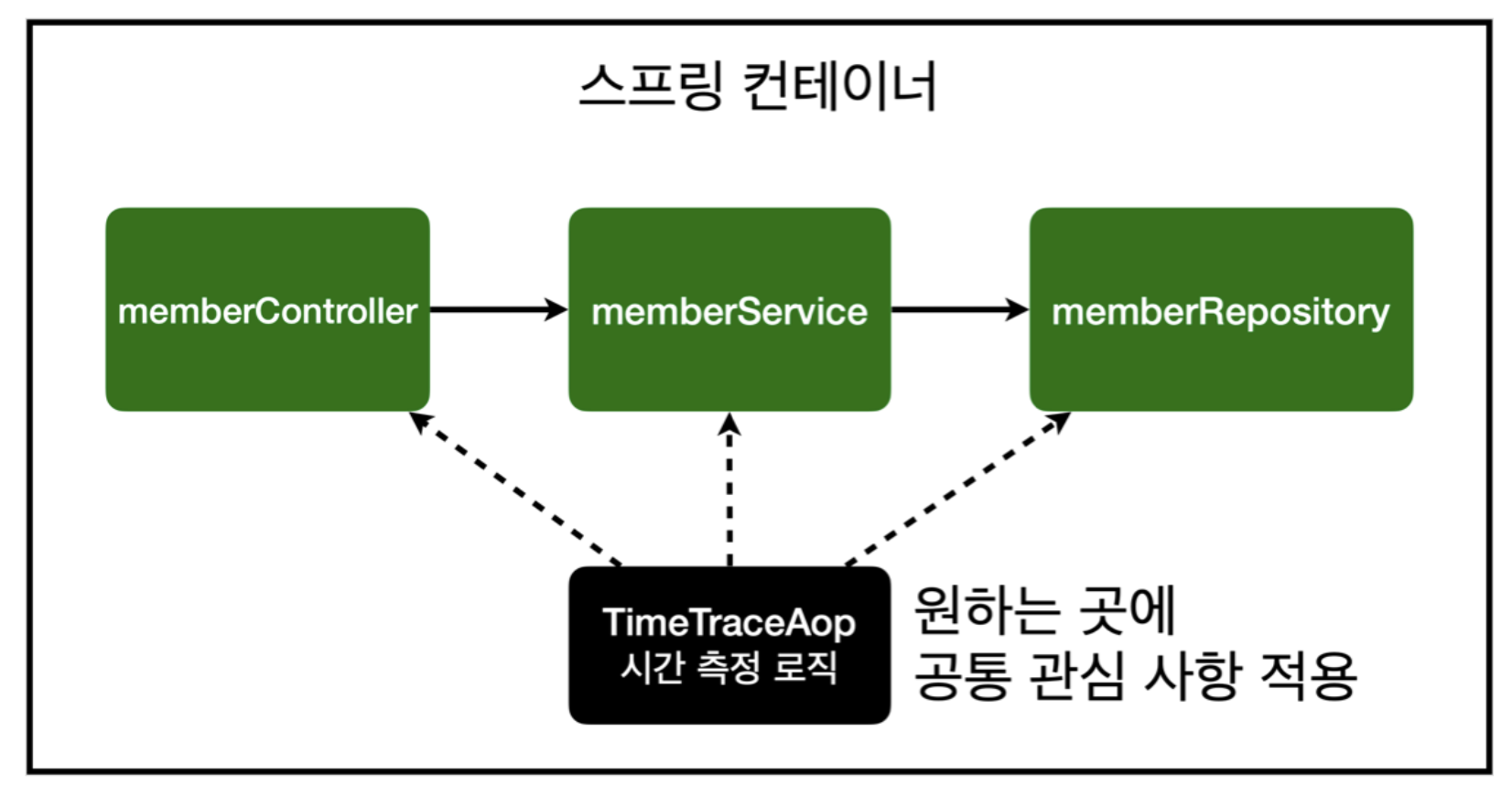
AOP 적용 전 전체 그림
AOP 적용 후 전체 그림
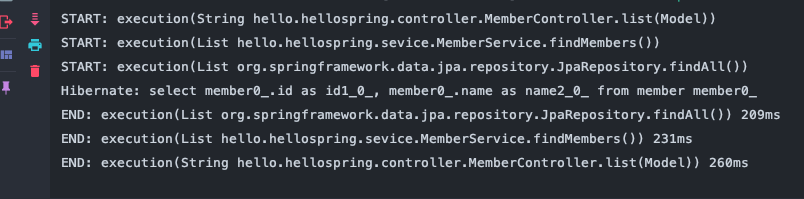
실행결과