Reflection이란?
자바에서의 Reflection(이하, 리플렉션)은 우리가 작성한 Class가 힙 메모리에 올라간 실제 객체, 즉 instance를 통해 해당 객체의 정보를 가져오는 기술이다.
리플렉션은 거울에 반사하다라는 의미의 단어인데, 쉽게 생각해서 객체가 메모리에 올라가 있고, 그 객체 앞에 거울을 두어 반사된 객체를 이용하는 셈이다.
어떻게 쓸까?
private static class MyClass {
private final String name;
private final int age;
private MyClass(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
private void print() {
System.out.println(name + " : " + age);
}
}
@Test
void usingPrivateConstructorAndMethods() throws Exception {
// given
Class<MyClass> clazz = MyClass.class; // Class 객체 생성
Constructor<MyClass> constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class); // 생성자 정보를 가져온다
constructor.setAccessible(true); // 접근 할 수 있게 한다. 설정하지 않고 사용하면 `IllegalAccessException` 발생한다
Method declaredMethod = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("print"); // 메서드 정보 가져온다
declaredMethod.setAccessible(true); // 마찬가지
// when
MyClass instance = constructor.newInstance("도기", 10); // 인스턴스 객체를 생성한다
// then
declaredMethod.invoke(instance); // 가져온 메서드 정보에 인스턴스 객체를 파라미터로 전달하여 호출한다. --> 즉, instance 객체의 print()가 호출된다.
// additional
// MyClass의 필드는 모두 private final이지만 아래처럼 리플렉션을 쓰면 런타임에 값을 변경할 수 있다.
// 이를 활용하면 전략패턴도 동적으로 갈아끼울 수도 있겠다 !
Field declaredName = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");
declaredName.setAccessible(true);
Field declaredAge = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
declaredAge.setAccessible(true);
declaredName.set(instance, "도기2");
declaredAge.set(instance, 100);
declaredMethod.invoke(instance);
}getName(), getCanonicalName() getSimpleName(), getTypeName() 차이
리플렉션의 이름을 가져오는 메서드는 다양하다.
-
getName(): 해당 리플렉션을 ClassLoader에서 동적으로 가져올 때의 이름
-
getCanonicalName(): import문에서 작성되는 이름 (java.util.List)
-
getSimpleName(): 클래스를 식별할 수 있는 이름. 하지만 유일하다고 보장할 순 없다. 다른 패키지에 같은 이름의 클래스가 존재할 수 있으니까!
-
getTypeName(): Type 이름
좀 더 자세한 내용은 여기를 참고하자.
getMethods(), getDeclaredMethods()
getMethods()는 Object 객체에서 상속받은 메서드들도 모두 가져온다.
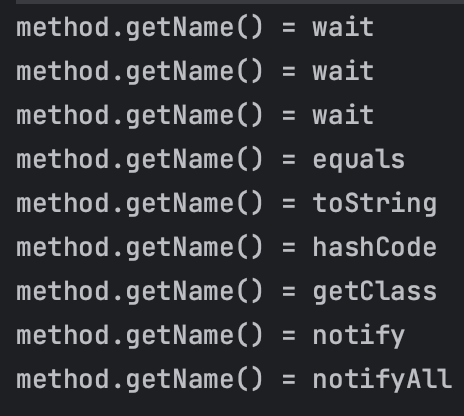
getDeclaredMethods()는 해당 클래스에서 선언한 메서드들만 가져온다.
상속받고 있는 객체를 getMethods 했을 때 상속받는 메서드들도 모두 가져올까 의문이 들어 방법을 찾아봤지만, getSuperClass()를 해서 직접 가져오는 수 밖에 없다.
private static class MyClass {
private final String name;
private final int age;
private MyClass(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
private void print() {
System.out.println(name + " : " + age);
}
}
private static class MySecondClass extends MyClass {
private MySecondClass(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
private void print2() {
System.out.println("This is MySecondClass's print Method");
}
}
@Test
void getMethodsTest2() {
Class<MySecondClass> secondClazz = MySecondClass.class;
Method[] methods = secondClazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("mySecondClass's method.getName() = " + method.getName());
}
}위 코드가 테스트 해본 코드인데, 만약 영 가져오고 싶다면 부모 객체의 메서드 접근자를 public으로 수정하면 getMethods()로 가져올 수 있다.
